Molecular marker of rice resistance gene Xa23 and application of molecular marker
A molecular marker and resistance gene technology, applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as loss of resistance to bacterial blight resistance genes, pathogenic variation of pathogenic bacteria, etc., achieve high reliability, and eliminate the effect of field inoculation identification work.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
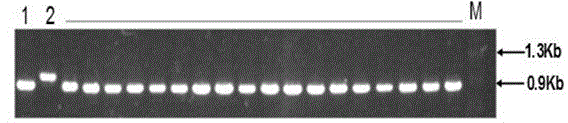
[0019] Example 1 Determination of Lj74 Molecular Marker
[0020] 1 plant material
[0021] The susceptible reincarnated parent King Kong 30 (JG30) is the female parent, carrying the bacterial blight resistance gene Xa23 The near isogenic line CBB23 was used as the male parent. Crossing JG30 with CBB23, F 1 Single harvest. f 1 F 2 A total of 2,562 individual plants were obtained from the isolated populations from generation to generation, and were planted in the net room of the Institute of Crop Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, under conventional water and fertilizer management.
[0022] Rice bacterial blight
[0023] Rice bacterial blight wide-pathogenic strain PXO99 (called P6) was introduced from the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), stored in vacuum at –70°C, rejuvenated on Wakimoto Tetsu’s medium before use, and placed at 28°C Cultivate for 48 hours, prepare the inoculum solution with sterile water, and adjust the concentration t...
Embodiment 2
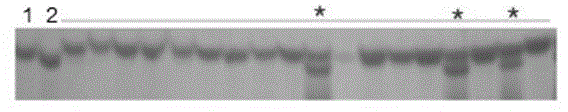
[0042] Example 2 Verification of molecular markers
[0043] In order to further verify whether the molecular marker Lj74 is only for the molecular marker of the Xa23 gene, molecular detection was carried out on varieties containing different genes and some varieties currently being promoted.
[0044] Since primer Lj74 is with Xa23 Gene co-segregation markers, only containing Xa23 The variety of the gene can expand the DNA fragment consistent with the CBB23 band pattern, which does not contain Xa23 The extended DNA band pattern of the variety was inconsistent with the CBB23 band pattern. Therefore, we selected 25 cultivars containing different bacterial blight resistance genes that have been mapped and cloned, including IR24 (no resistance gene), IRBB1 ( Xa1 ), IRBB2 ( Xa2 ), IRBB3 ( Xa3 ), IRBB4 ( Xa4 ), IRBB5 ( xa5 ), IRBB7 ( Xa7 ), IRBB8 ( xa8 ), IRBB10 ( Xa10 ), IRBB11 ( Xa11 ), IRBB13 ( xa13 ), IRBB14 ( Xa14 ), M41 ( xa15 ), Tetep ( Xa16 ),...
Embodiment 3
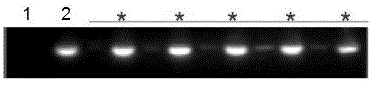
[0046] Example 3 Molecular markers Lj74 sequencing
[0047] In order to further study the molecular marker Lj74 is the sequence difference between the resistant variety and the non-resistant variety, the molecular marker Lj74 determined in the embodiment example, that is, using SEQ ID NO: 1 and 2 as the primer amplified fragment was sequenced. The fragment sequence amplified from the resistant variety CBB23 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3, and the fragment sequence amplified from the resistant variety CBB23 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 4.
[0048] After comparing the files, it is found that the resistant variety has two copies of the nucleotide sequence fragment shown in SEQ ID NO: 6, that is, the nucleotide sequence fragment shown in SEQ ID NO: 5, while the non-resistant variety has only one copy A fragment of the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:6. Based on this finding, those skilled in the art can design primer pairs or probes based on the sequence for detection (not limited t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com