Parallel mechanism modal space control method suitable for ophthalmic microsurgery
A technology of microsurgery and control methods, applied in the fields of medicine, control and machinery, which can solve the problems of sequence change between modalities, slow convergence speed, and modal transitions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
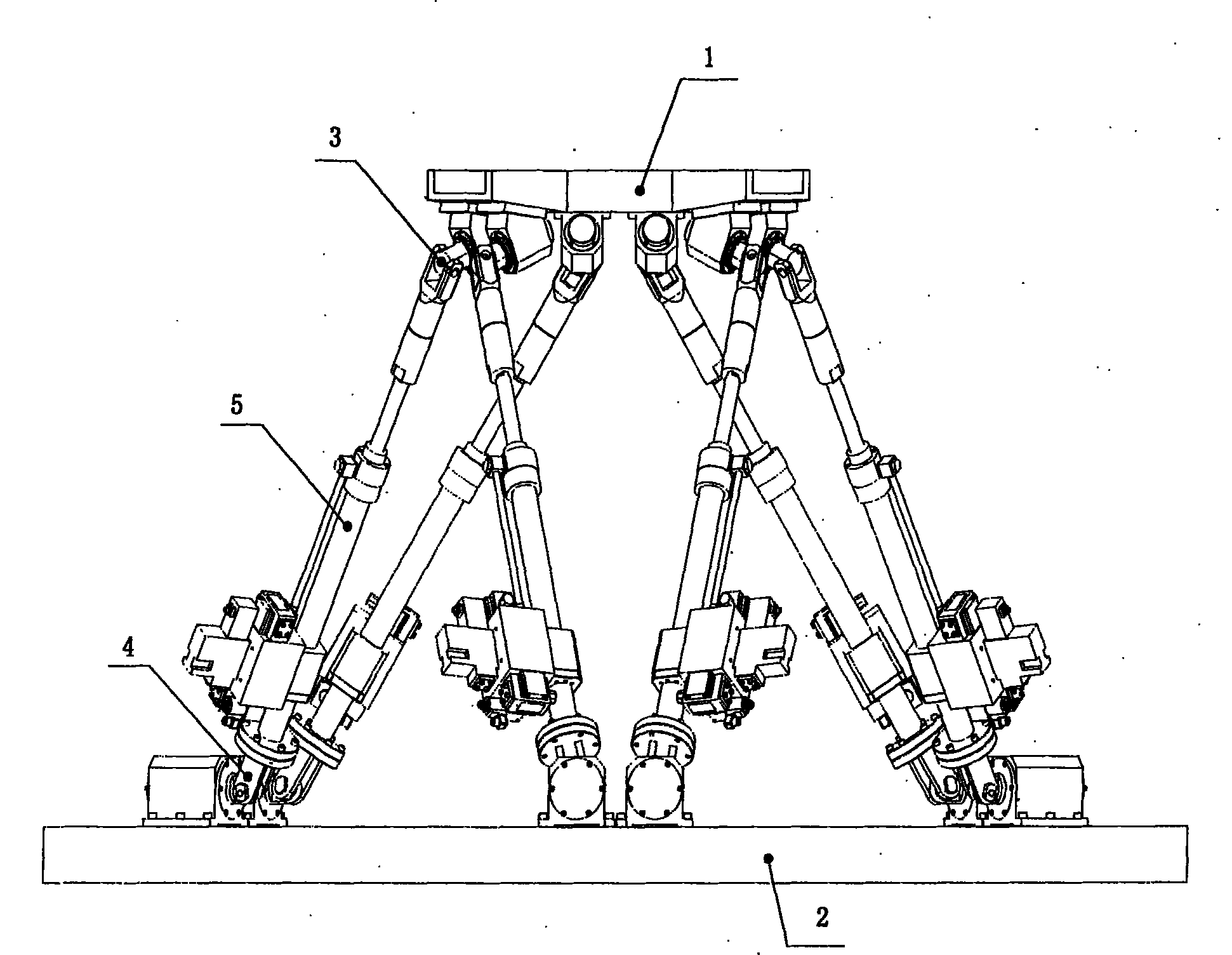
[0062] Six degrees of freedom parallel mechanism such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a moving platform 1, a fixed platform 2, an upper connecting hinge 3, a lower connecting hinge 4 and a linear actuator 5.
[0063] The structure of the modal space controller is as follows figure 2 As shown, its control process is:
[0064] Step 1: System setting signal sx des After the kinematics anti-solution module, the signal array of the set length of the six linear actuators is generated l com , and the actual length signal array l of the six linear actuators are subtracted to generate a deviation matrix e, e=l com -l.
[0065] Step 2: Transform the deviation matrix e into the modal space to generate the modal deviation matrix e d , e d =U T e. Its modal decoupling matrix U is obtained through the global modal calculation module, which is related to the pose signal sx obtained from the real-time kinematics forward solution. This step is the key to modal control. After the mo...
Embodiment
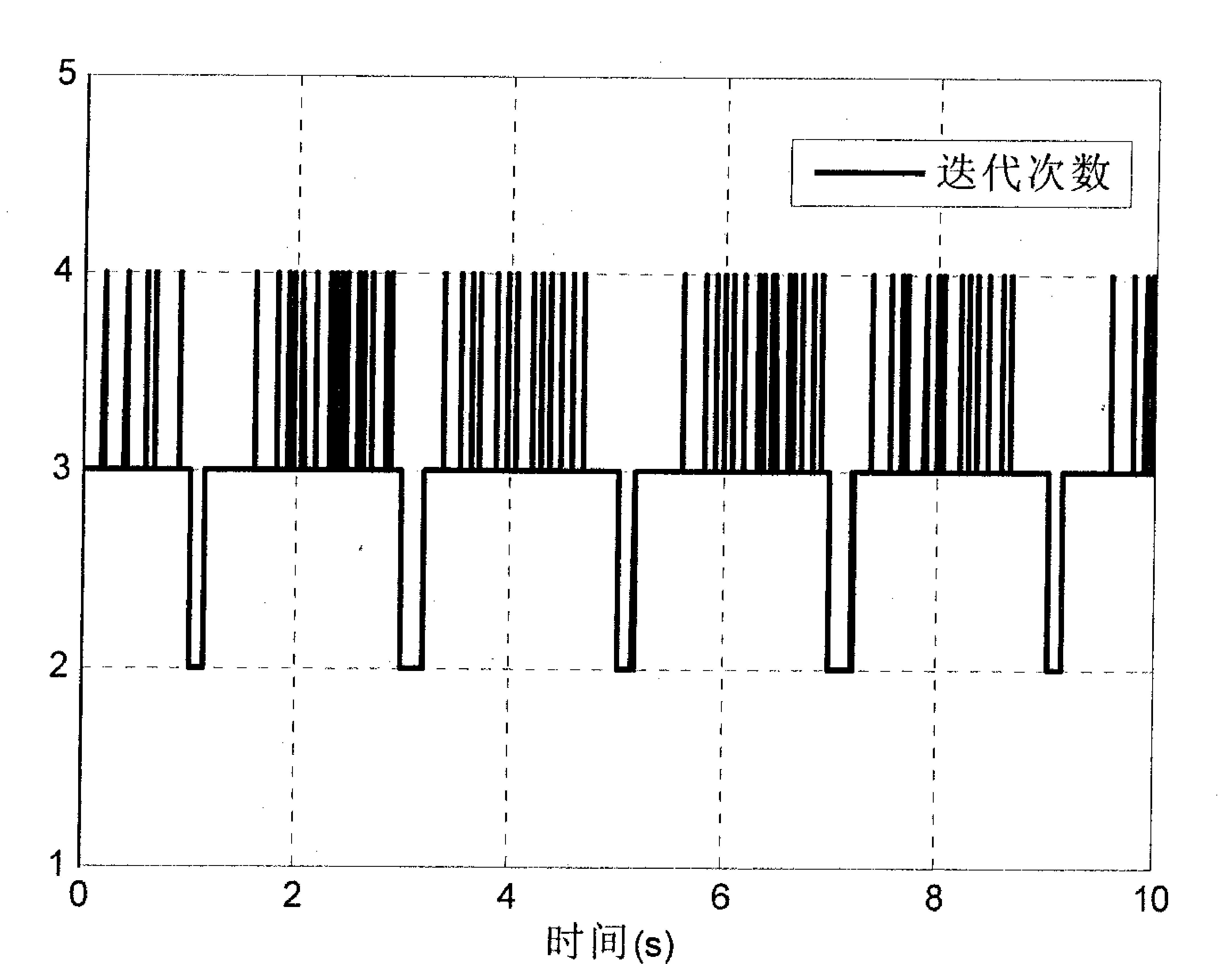
[0112] The present invention will be further described in conjunction with the modal transition and efficiency issues of modal space control when a six-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism is used for compound pose control in the global workspace.
[0113] The platform related parameters are:
[0114] The height of the platform is 2.6519m in the middle position, the stroke of the actuator is 1.2m, the radius of the upper hinge circle is 2.1148m, and the radius of the lower hinge circle is 2.6519m.
[0115] Load inertia parameters are: m=13642.000kg, Ixx=46477.100kgm 2 , Iyy=49396.100kgm 2 ,Izz=53865.000kgm 2 .
[0116] The initial modal decoupling matrix U:
[0117] U = 0.4082 - 0.4868 - 0.3104 0.4082 - ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com