FLASH memorizer long-distance on-line upgrade method based on field programmable gate array (FPGA)
A FLASH memory, remote technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of complex operation, DSP cannot bootstrap operation, increase cost, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
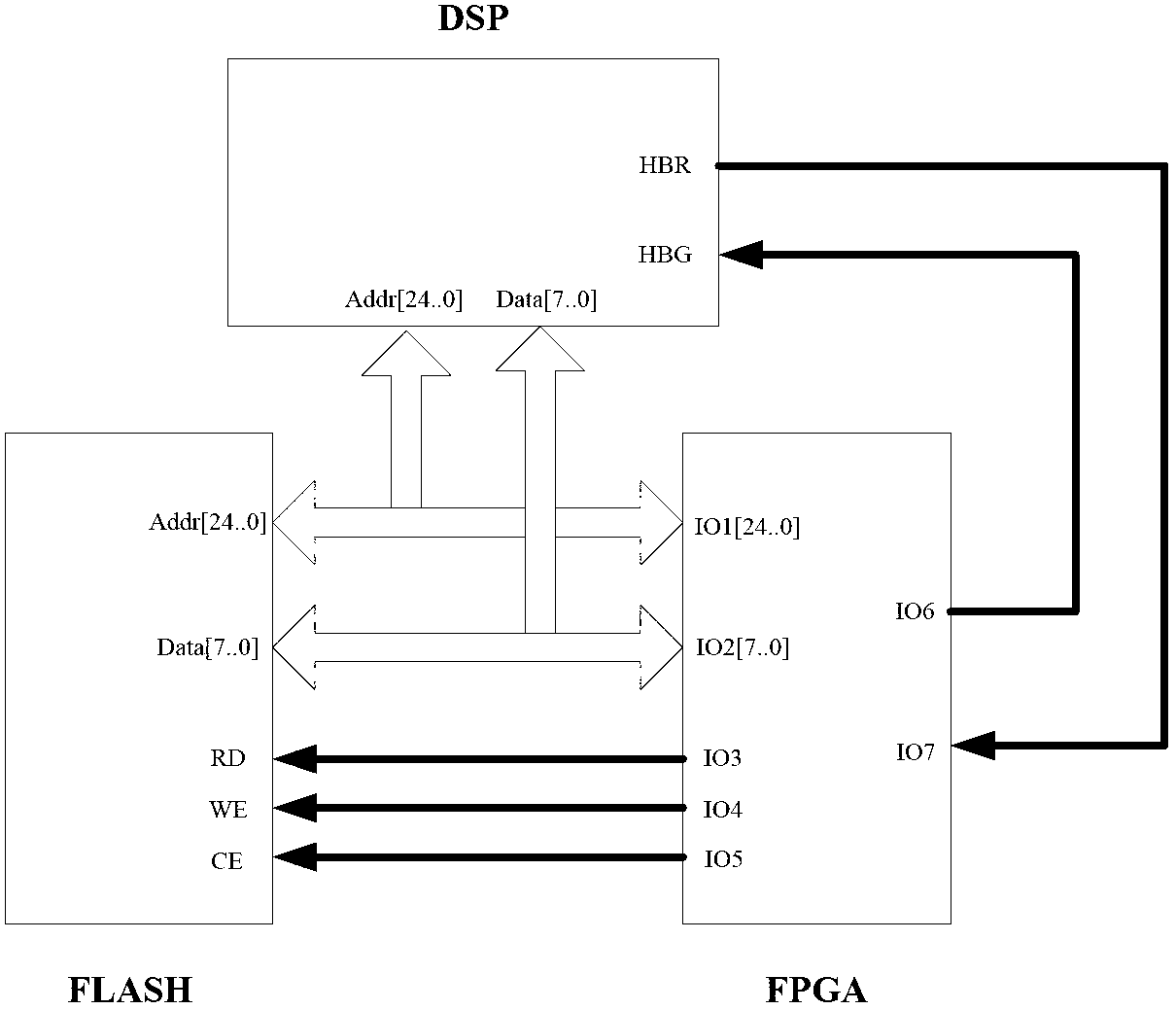
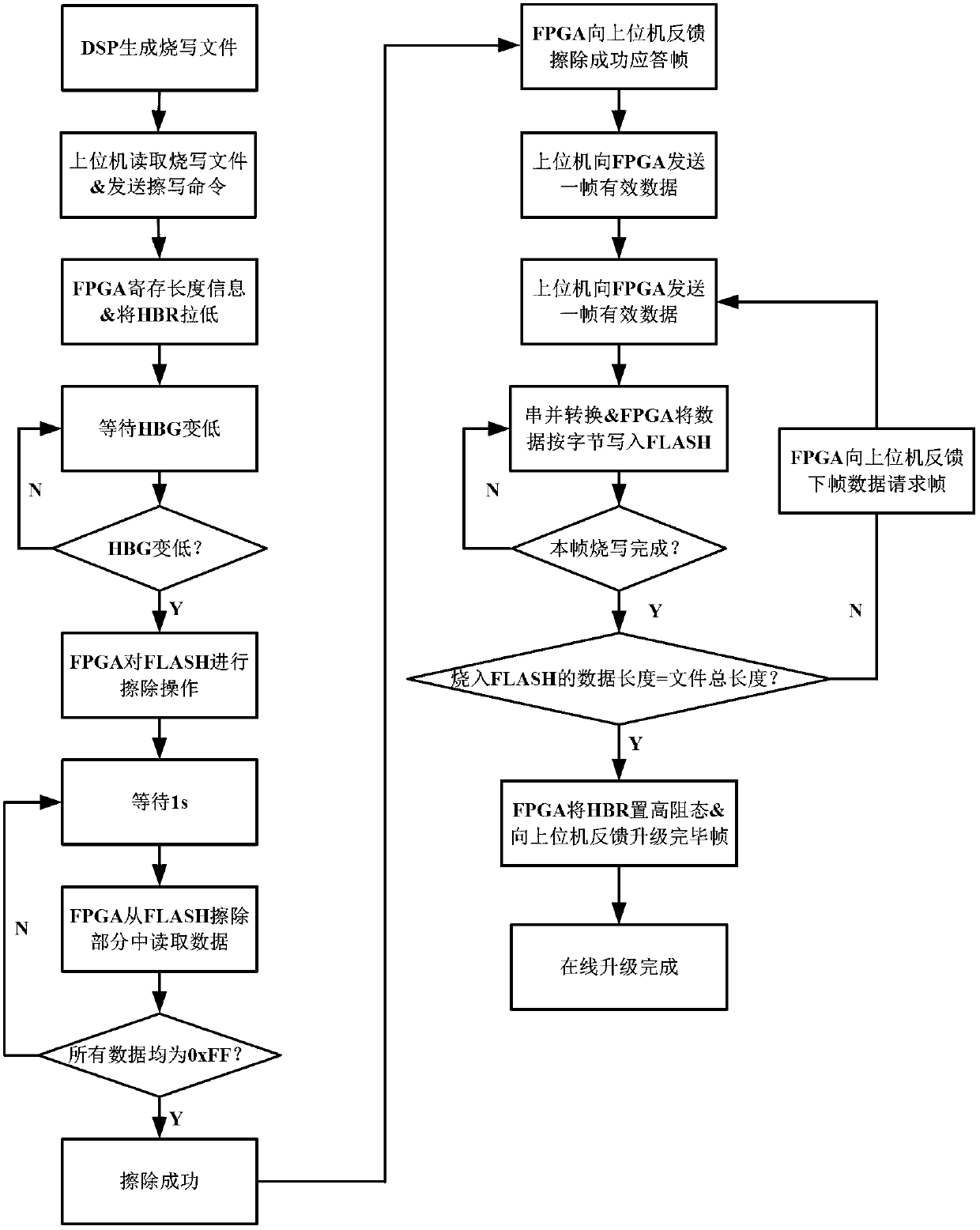
[0015] The invention uses FPGA as the main control chip to receive the command frame issued by the upper computer, feed back the response frame to the upper computer, and perform erasing and programming operations on the FLASH memory. The FPGA receives the command frame sent by the host computer through the serial port protocol, and judges whether the command frame is a FLASH erasing command or a FLASH data frame through the flag bit of the command frame. The FLASH erasing command contains the total length information of the DSP programming file. The FLASH data frame contains the specific content of the DSP programming file.
[0016] The present invention mainly covers four parts: a host computer part, an FPGA part, a DSP part and a FLASH part. The upper computer sends a FLASH erase command to the FPGA, reads the DSP programming file and sends it to the FPGA frame by frame according to the 232 serial port protocol; the FLASH remote online upgrade module solidified in the FPGA ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com