Non-equal probability constellation labeling method based on absolute phase shift keying (APSK) constellation diagram
A technology of constellation mapping and constellation diagram, which is applied in the field of approximate constellation mapping, can solve the problems that further shaping gains cannot be provided, and non-equal approximate APSK constellation mapping cannot approach the Shannon limit, so as to achieve excellent performance, reduce the threshold of signal-to-noise ratio, and improve performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
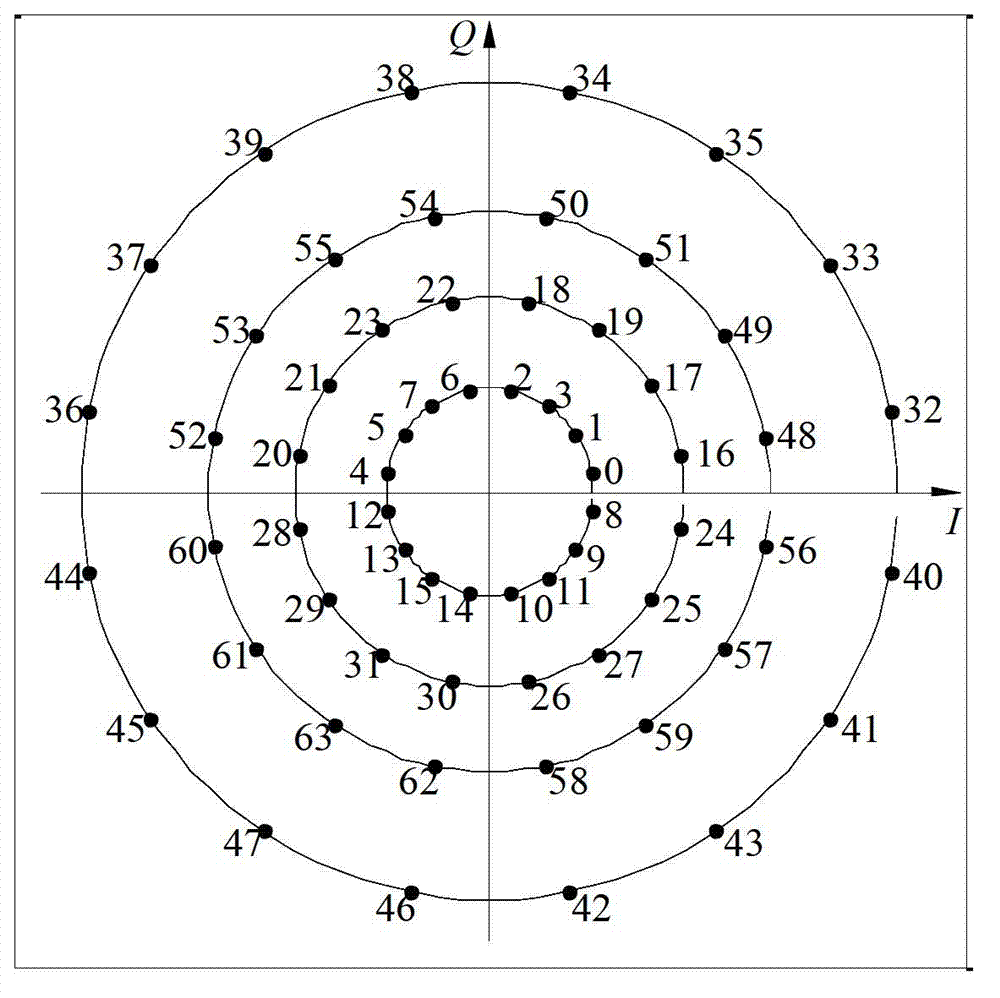
[0047] According to the mapping scheme of a 64-order non-isoprobable APSK constellation obtained by the non-isoprobable constellation mapping method based on the APSK constellation diagram described in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, the generating method includes steps:
[0048] S1. Construct an APSK constellation diagram, the constellation mapping order is M, M=2 m , m is a positive integer; the constellation points of each ring are equal, and the phase offset of each ring is also equal;
[0049] Among them, the parameters are selected as follows, assuming that the constellation mapping order M=64, the number of rings R=4, the number of constellation points on each ring is 16, and the phase offset of all rings is π / 16; the radius value of the lth ring is given by formula Calculated; After the average power is normalized, the radii of the first ring to the fourth ring are 0.3818, 0.7164, 1.0348, 1.5067 respectively.
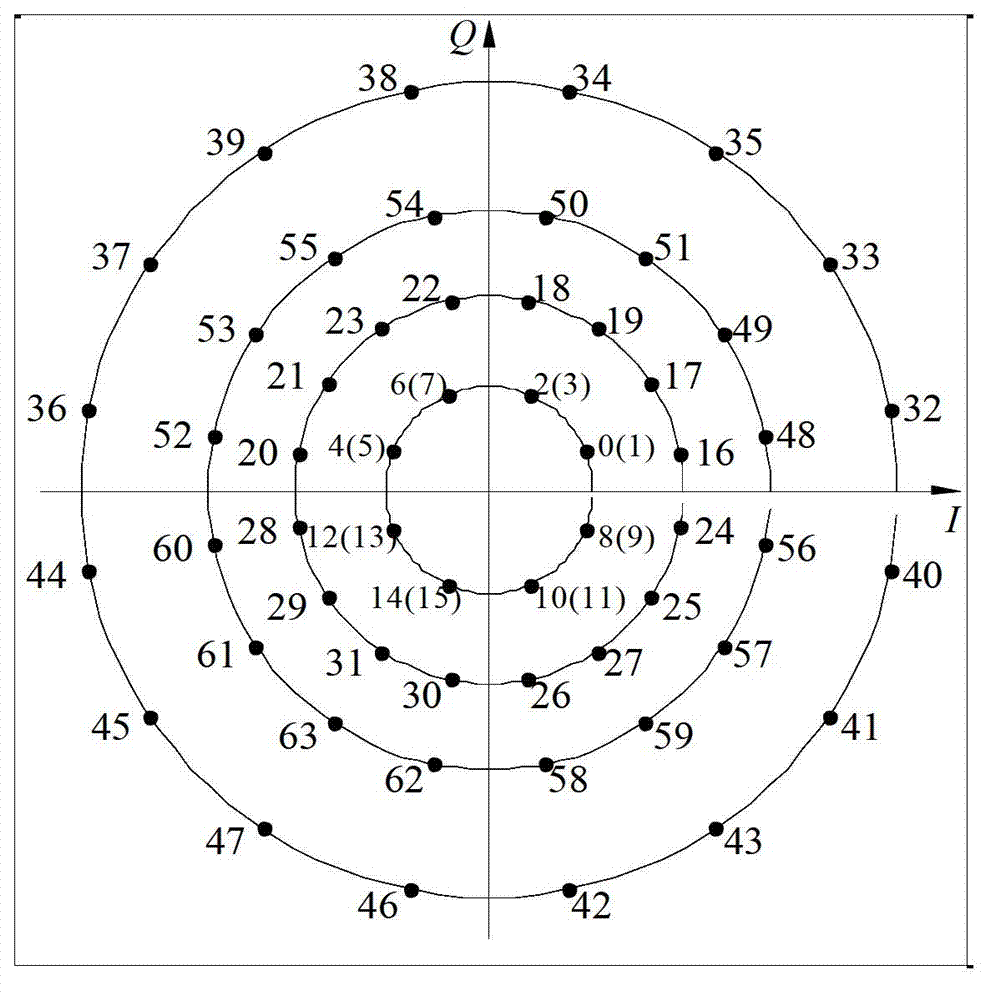
[0050] S2. Designing a constellation mapping met...
Embodiment 2
[0063] According to a scheme of 256-order non-isoprobable APSK constellation mapping obtained by the non-isoprobable constellation mapping method based on the APSK constellation diagram described in Embodiment 2 of the present invention, the generating method includes steps:
[0064] S1. Construct an APSK constellation diagram, the constellation mapping order is M, M=2 m , m is a positive integer; the constellation points of each ring are equal, and the phase offset of each ring is also equal;
[0065] Among them, the parameter selection is as follows, the constellation mapping order M=256, the number of rings R=8, the number of constellation points on each ring is 32, and the phase offset of all rings is π / 32. The radius of the lth ring is given by the formula calculated. After the average power is normalized, the radii of the first ring to the eighth ring are 0.2596, 0.4657, 0.6256, 0.7752, 0.9293, 1.1023, 1.3223, and 1.7018 respectively. Fine-tuning the above radius valu...
Embodiment 3
[0080] A 256-order non-isoprobable constellation mapping scheme obtained according to the non-isoprobable constellation mapping method based on the APSK constellation diagram described in the embodiment of the present invention, the generating method includes the steps:
[0081] S1. Construct an APSK constellation diagram, the constellation mapping order is M, M=2 m , m is a positive integer; the constellation points of each ring are equal, and the phase offset of each ring is also equal;
[0082] Among them, the parameter selection is as follows, the constellation mapping order M=256, the number of rings R=8, the number of constellation points on each ring is 32, and the phase offset of all rings is π / 32. The radius of the lth ring is given by the formula Calculated, after the average power is normalized, the radii of the 1st ring to the 8th ring are 0.2596, 0.4657, 0.6256, 0.7752, 0.9293, 1.1023, 1.3223, 1.7018, fine-tuning the above radius value between 0.9 and 1.1 times ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com