Predictive routing method for bus delay tolerant network
A delay-tolerant network and bus technology, applied in data exchange networks, digital transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of node mobility, improved routing performance, lack of pertinence, and large network resource consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
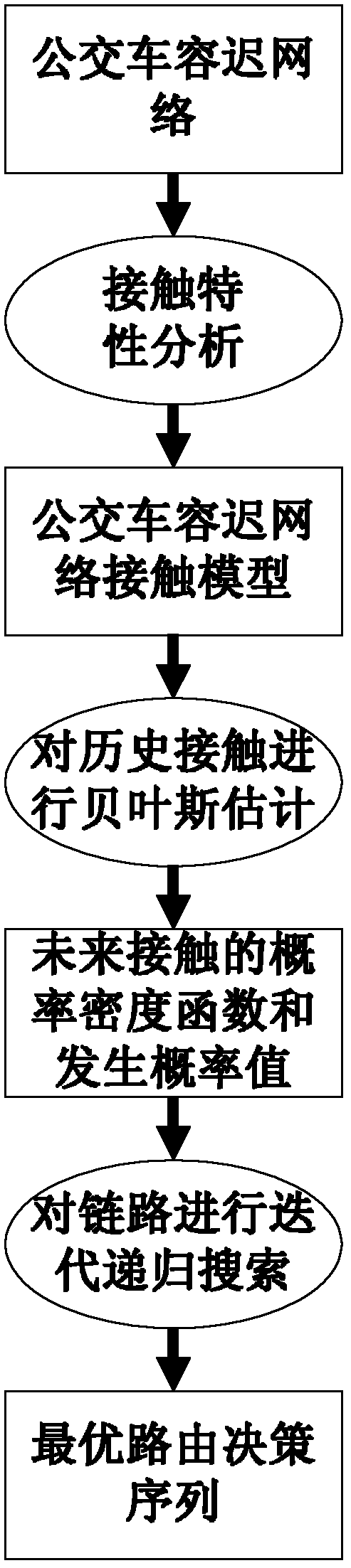
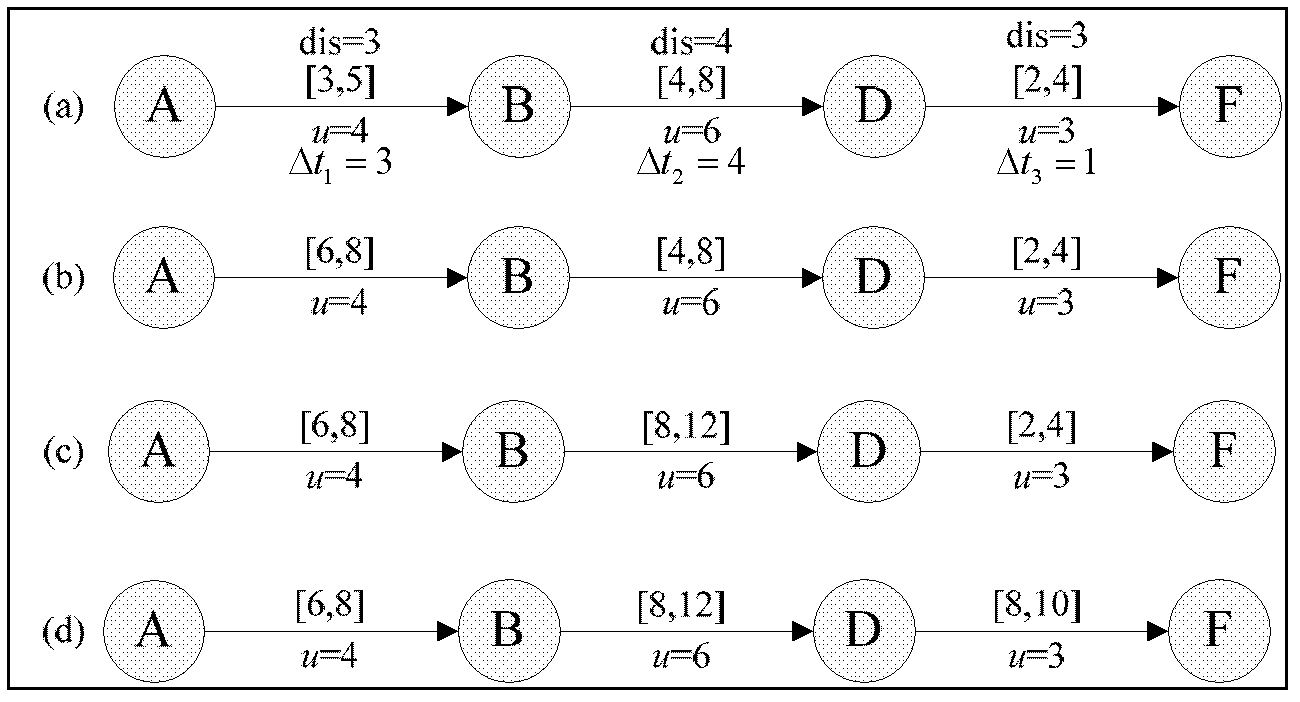
[0035] 1. Describe the uncertainty of bus arrival time
[0036] The bus arrival time is an uncertain time. We define: a time interval IT (Interval Time) is an interval number, which is a closed interval composed of two real numbers, and the two real numbers are the upper and lower limits of the time interval. The upper limit corresponds to the latest time of the uncertain moment; the lower limit corresponds to the earliest time of the uncertain moment.
[0037] The bus arrival time is a continuous random variable, and we use X to denote the event of bus arrival. Let its probability density function be f(x), if the time interval of event X occurring is (0,+∞), we need to intercept the interval of its occurrence to obtain a finite time interval. We define: for event X in the time interval [t - ,t + ] within the probability of occurrence, represented by the letter P, namely: P ( t - ≤ ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com