Active and reactive coordination control method for permanent-magnet direct-driven wind turbines in low-voltage ride-through process
A low-voltage ride-through, wind turbine technology, applied in reactive power adjustment/elimination/compensation, reactive power compensation, single-grid parallel feeding arrangement, etc. It can improve the low voltage ride-through capability, reduce the DC voltage fluctuation, and reduce the active power loss.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
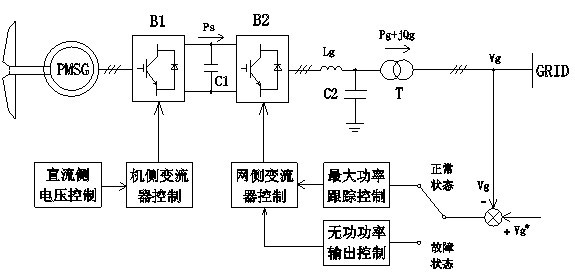
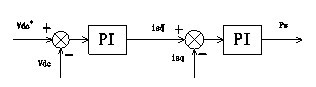
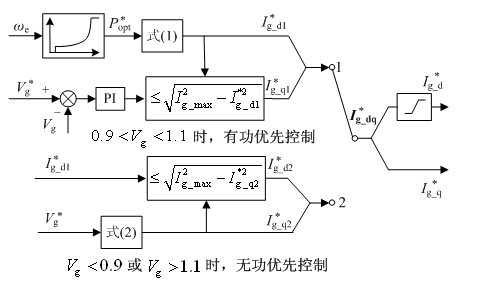
[0032] According to the change degree of the grid voltage amplitude, the invention realizes the coordinated control of the active power and reactive power of the wind turbine before and after the grid voltage mutation by switching the control strategy of the grid side converter. see figure 1 , when the grid voltage is in the normal range, the maximum power tracking control is realized through the grid-side converter, and the machine-side converter controls the DC voltage to be stable. When the grid voltage fails, the grid-side converter is controlled to implement reactive power priority control mode, and the inertial energy storage of the wind turbine is used to share the sudden change of active power at both ends of the DC bus capacitor, reducing the active power loss of the wind turbine unit and stabilizing the DC bus voltage. Enhance the fault ride-through capability of the wind power system, and quickly and accurately provide reactive power support to the grid to support ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com