GPSR (Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing) dynamic routing method and system on basis of energy-aware
A technology of energy sensing and routing, applied in the field of routing algorithms of sensor networks, can solve the problems of affecting the service life of wireless sensor networks, large energy consumption of nodes, etc., and achieve the effect of prolonging the existence time and simple execution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0040] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
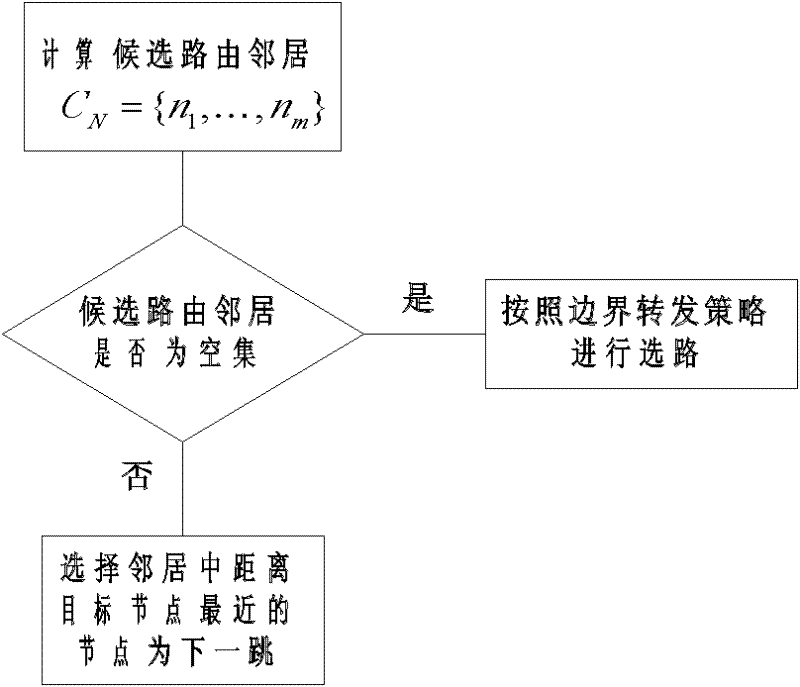
[0041] In order to solve the routing hotspot problem mentioned above, it is necessary to distribute the routing load to other routing nodes in a balanced manner. In order to effectively perform dynamic route selection based on the energy status of nodes, we assume that neighbor nodes periodically exchange energy information, which can be carried in GPSR broadcast packets, such as periodic beacon signals. Each time a node selects a route dynamically according to the energy state of its neighbors. The present invention provides two strategies, random selection strategy and deterministic selection strategy.
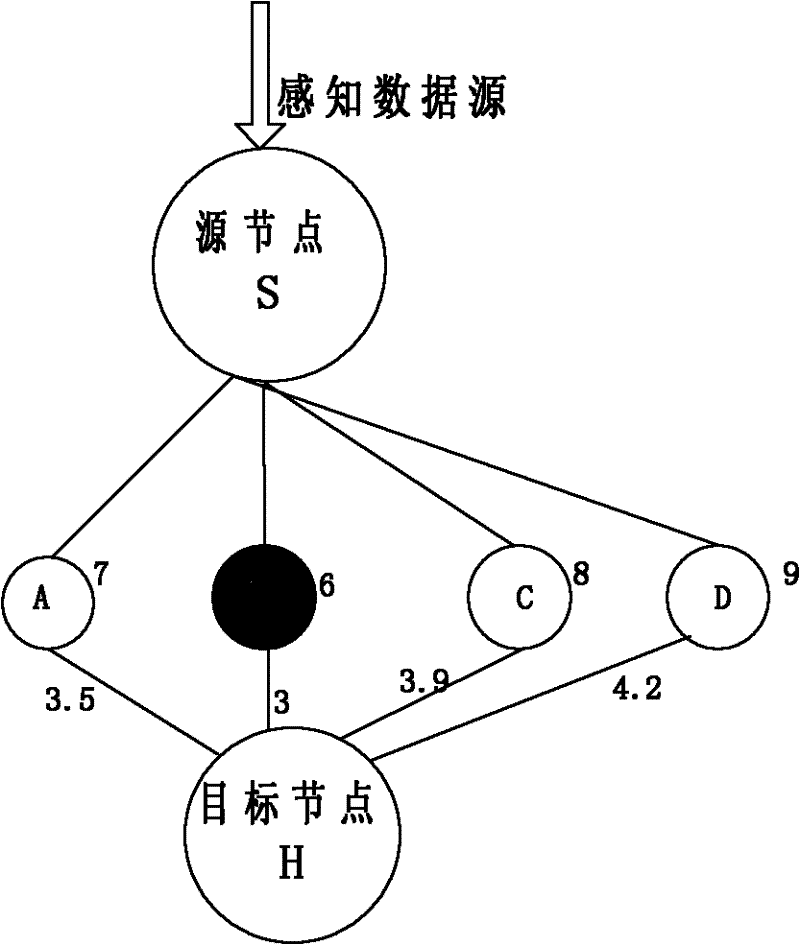
[0042] Such as image 3 shown and combined with figure 2 , image 3 It is a flowchart of the random routing strategy based on energy-aware GPSR protocol. The node first determines the "candidate routing neighbor", which is defined as th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com