Wastewater treatment apparatus, wastewater treatment method, and wastewater treatment system
A waste water treatment and waste water technology, applied in metallurgical waste water treatment, neutralized water/sewage treatment, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of low treatment efficiency and achieve the effect of reducing the concentration of heavy metals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
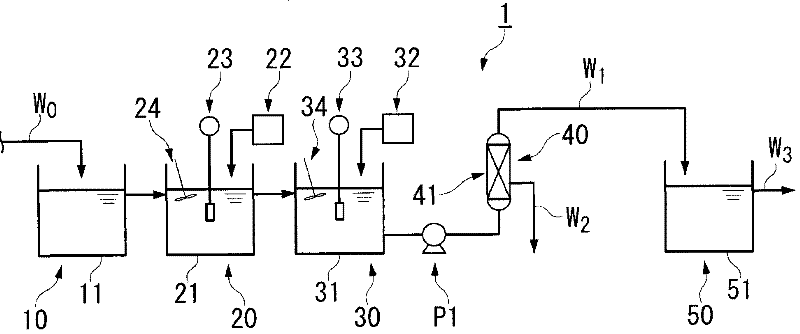
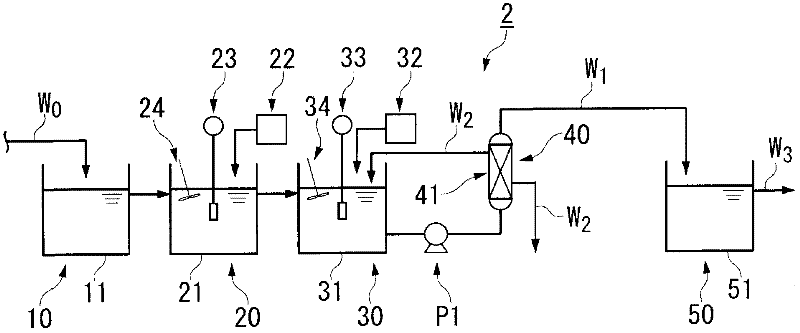
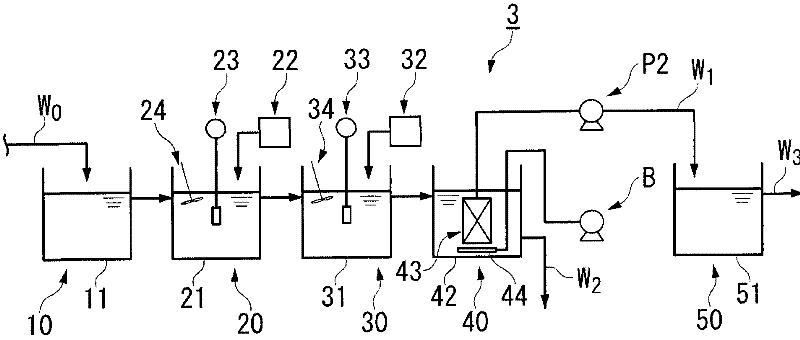
[0129] The wastewater treatment device of the present invention is not limited to figure 1 The processing device 1 is shown. For example, in figure 1 The treatment device 1 provided with the pH adjustment device 50 does not need to include the pH adjustment device 50 if the pH of the filtered water W1 already matches the discharge pH to a river or the like.
[0130] In addition, when a chlorine-based oxidizing agent is added from the oxidizing agent adding device 22 to the oxidation treatment facility 20, odorous components such as chlorine gas or chloramine generated by oxidation of ammonia may be generated. Therefore, it is desirable to properly set up the gas recovery equipment according to the concentration generated.
[0131] Specific examples of gas recovery facilities include exhaust gas scrubbers and activated carbon-type gas purification devices.
[0132] in addition, figure 1 The processing device 1 has a full-scale membrane separation device 40, but as figu...
Embodiment 1
[0222] As the wastewater, nickel-containing wastewater discharged from the electroless nickel plating process was used. The concentration of nickel in the waste water is 6.5mg / L. In addition, this waste water contains ammonia as a complex-forming compound. Ammonia concentration, expressed as ammoniacal nitrogen (NH 3 -N) concentration was 3.8mg / L.
[0223] 0.5 mL of sodium hypochlorite solution (available chlorine concentration: 12% by mass) was added as an oxidizing agent to 500 mL of the nickel-containing wastewater, and stirred for 15 minutes to oxidize ammonia (oxidation treatment step).
[0224]Then, in the oxidized waste water, add sodium hydroxide solution adjusted to 0.1 mol / L as an insolubilizer to adjust the pH to 10, stir for 30 minutes, and generate nickel insoluble matter (insolubilization treatment process).
[0225] Next, the insolubilization-treated wastewater was subjected to membrane separation using a hollow fiber membrane made of polyvinylidene fluoride ...
Embodiment 2
[0229] An oxidation treatment step was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1.
[0230] To the nickel-containing wastewater after the oxidation treatment step, 2.5 mL of an aqueous solution of sodium sulfate 9 hydrate adjusted to 0.1 mol / L was added, and stirred for 30 minutes to generate nickel insoluble matter (insolubilization treatment step).
[0231] Next, a membrane separation step was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1, the concentrations of nickel and ammoniacal nitrogen in the filtered water were measured, and the particle distribution of nickel insoluble matter was measured. These results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com