Control devices for internal combustion engines
A control device and internal combustion engine technology, applied in engine control, electrical control, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve problems such as the difficulty in clearly judging the end of combustion, the inability to obtain the amount of heat generated, and delaying the opening period of the exhaust valve.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0057] [Configuration of Embodiment 1]
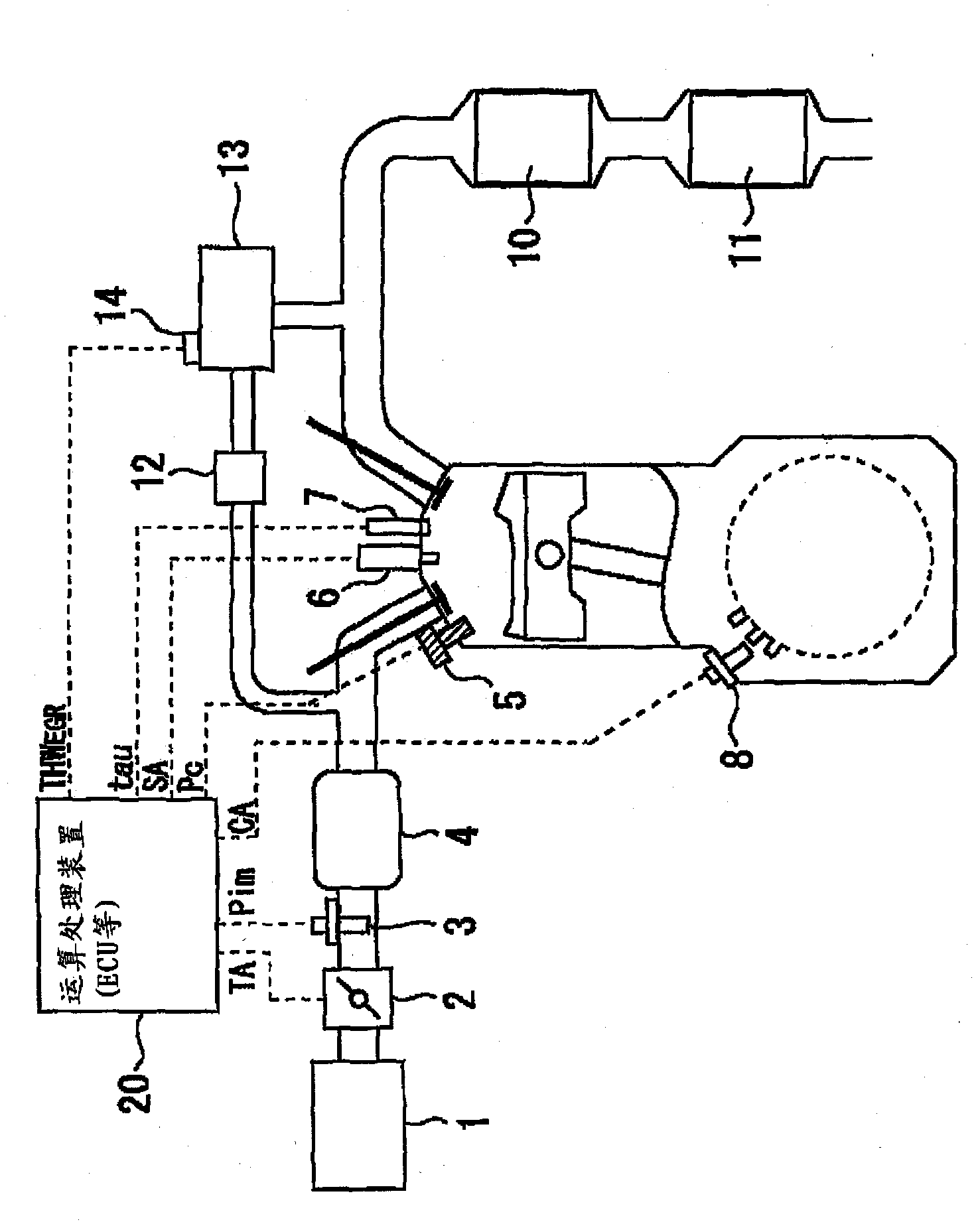
[0058] figure 1 It is a figure which shows the structure of the control apparatus of the internal combustion engine which concerns on Embodiment 1 of this invention. The control device of the present embodiment is suitable for controlling a mobile body such as a vehicle, specifically, an internal combustion engine mounted on an automobile.
[0059] figure 1 is a diagram showing an internal combustion engine (hereinafter simply referred to as an engine) to which the control device of the present embodiment is applied. figure 1 The engine shown is a spark-ignited 4-stroke reciprocating engine with spark plugs 6 . In addition, there is also an in-cylinder direct injection engine including a direct fuel injection injector 7 that directly injects fuel into the cylinder. In addition, the engine to which the present invention is applied is not limited to the in-cylinder direct injection engine of this embodiment. The invention can also be...
Embodiment approach 2
[0120] The hardware structure and software structure of Embodiment 2 can be executed except for the control device related to Embodiment 2 Figure 7 Except for this point of the shown routine, the structure is basically the same as that of the first embodiment. The following uses to avoid repetition, and appropriately omits or simplifies descriptions.
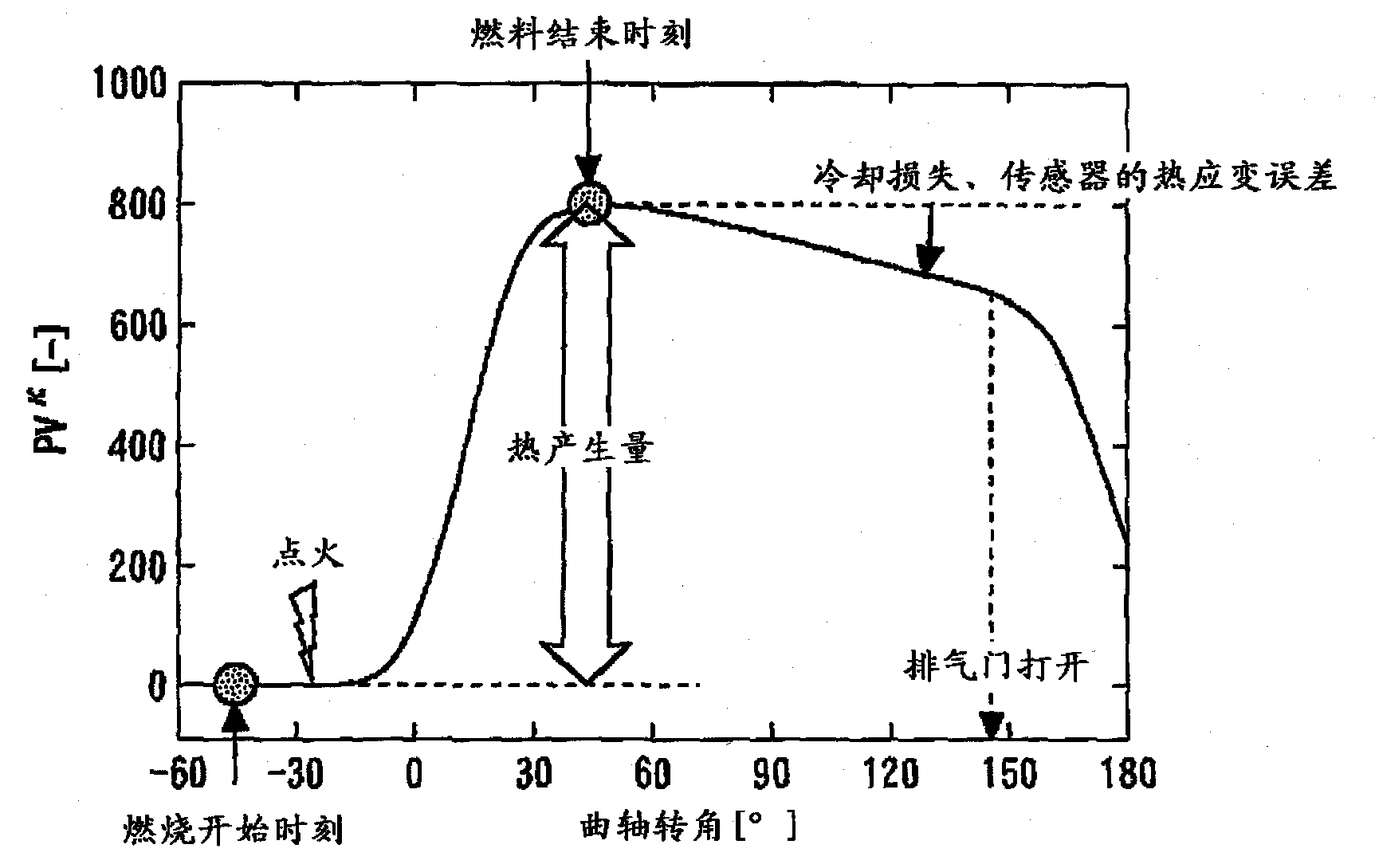
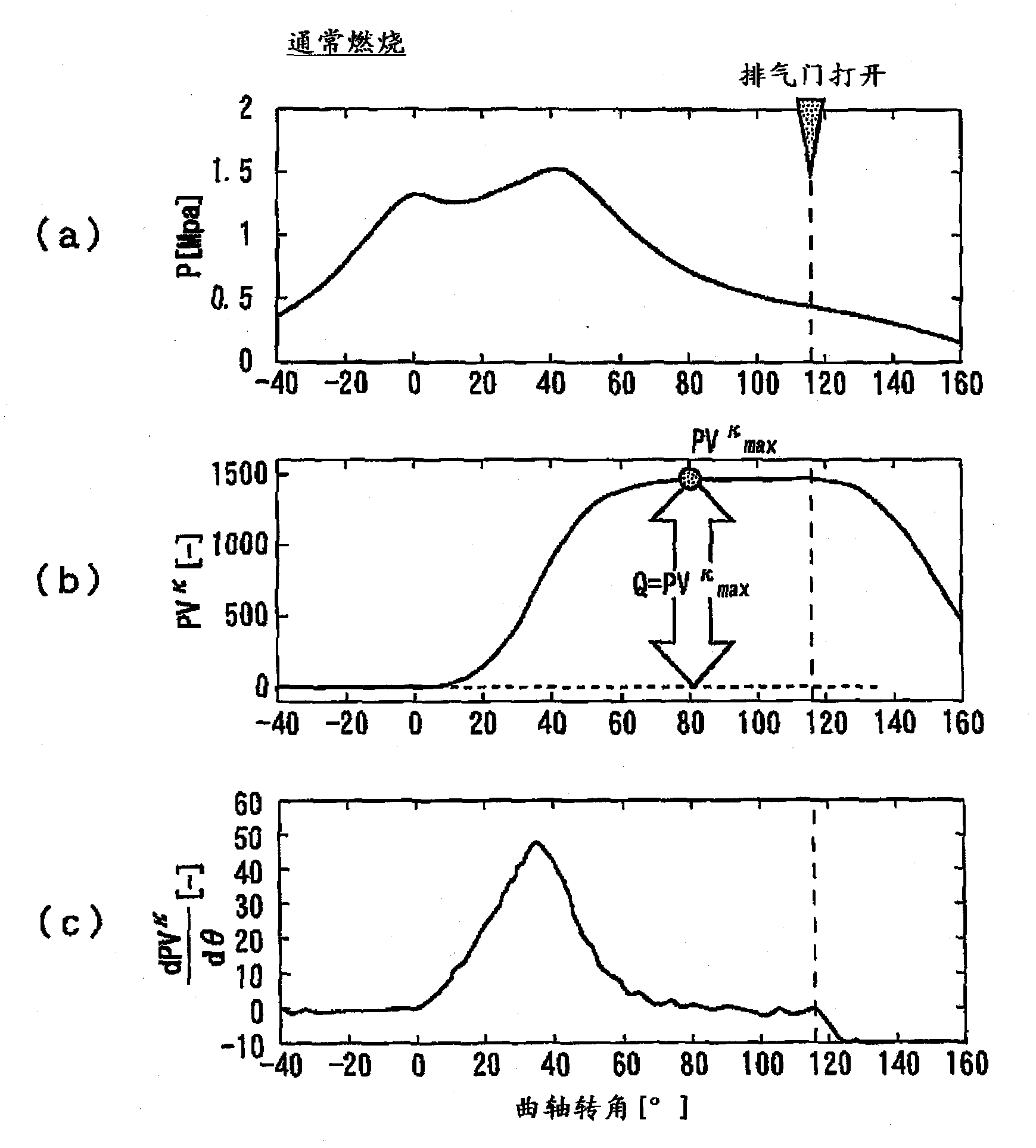
[0121] In large amounts of external EGR and lean burn, retarded combustion can occasionally occur when leaving normal combustion and entering an unstable combustion region. Therefore, in the second embodiment, it is not determined whether or not the catalyst warm-up retardation control is being executed, but θ is always monitored. CA50 , based on ΔPV in the combustion cycle at a retarded angle compared to the specified value k CA50 Estimated calorific value.
[0122] use Figure 7 Specific processing executed in the internal combustion engine control device according to Embodiment 2 will be described. Figure 7 It is a fl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com