Method for increasing fermentation yield of epothilone by using competitive microorganism and application thereof
A microbial fermentation and epothilone technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of increasing production, low potential, and low efficiency of strain improvement methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
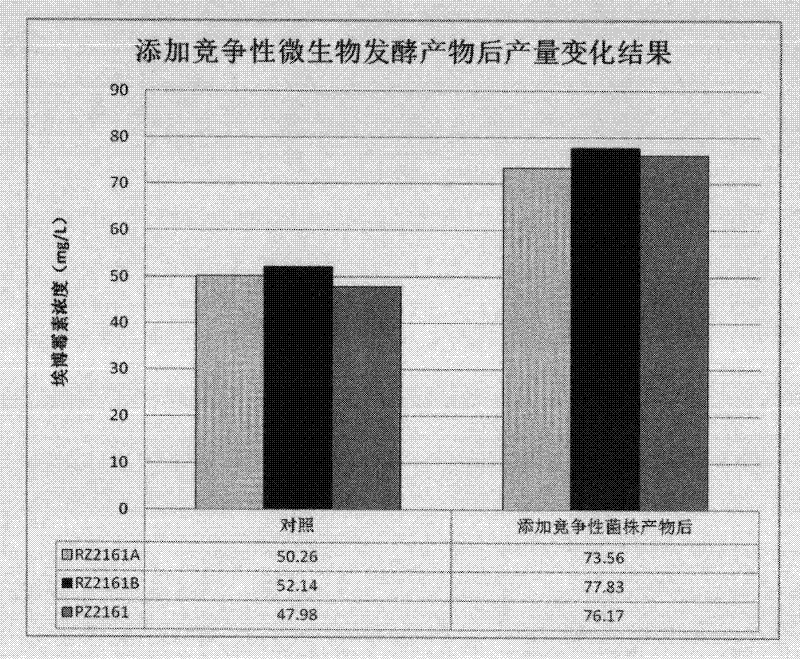
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036]1. The preparation method of Rhizopus aurizopus ATCC56015 fermentation product, the steps are as follows:
[0037] (1) Take the preserved strain and inoculate it into the activation medium, culture conditions: temperature 29°C, culture for 3 days for activation.
[0038] (2) Take the activated Rhizopus strain and inoculate it in the nutrient medium, and culture it for 4 days under the culture conditions of 30° C. and 150 r / min.
[0039] (3) Add ethyl acetate to the fermentation broth at a volume ratio of 1:1, stir and extract at 200 r / min for 3 hours, repeat 2 times, combine the ethyl acetate phases, and vacuum dry.
[0040] (4) Dissolving the dry product obtained in step (3) with acetone at 1 / 200 of the fermentation broth volume, and the supernatant after microfiltration is the metabolite of the competing strain.
[0041] The activation medium in the step 1 is: potato (peeled): 200g, glucose: 20g, agar: 20g, water: 1000mL, and the pH value is natural.
[0042] The nut...
Embodiment 2
[0050] 1. The method for preparing the metabolite of Rhizopus aurizopus ATCC56015, the steps are as follows:
[0051] (1) Inoculate the rhizopus strain into the activation medium, culture conditions: temperature 30°C, culture for 3 days for activation.
[0052] (2) Take the activated Rhizopus strain and inoculate it in the seed medium, and cultivate it for 4 days under the culture conditions of 30° C. and 150 r / min.
[0053] (3) Add ethyl acetate to the fermentation broth at a volume ratio of 1:1, stir and extract at 200 r / min for 3 hours, repeat 2 times, combine the ethyl acetate phases, and vacuum dry.
[0054] (4) Dissolve the dry product obtained in step (3) with 1 / 200 of the fermentation broth volume in methanol, centrifuge at 10,000 r / min for 10 min and the supernatant is the metabolite of the competing strain.
[0055] The activation medium in the step 1 is: potato (peeled): 200g, glucose: 20g, agar: 20g, water: 1000mL, and the pH value is natural.
[0056] The nutrie...
Embodiment 3
[0064] 1. The preparation method of the metabolite of Penicillium decumbens CGMCC 4075, the steps are as follows:
[0065] (1) Inoculate the Penicillium strain into the activation medium, culture conditions: temperature 30°C, culture for 3 days for activation.
[0066] (2) Take the activated Penicillium strain and inoculate it in the nutrient medium, and culture it for 4 days under the culture conditions of 30° C. and 150 r / min.
[0067] (3) Add ethyl acetate to the fermentation broth at a volume ratio of 1:1, stir and extract at 200 r / min for 3 hours, repeat 2 times, combine the ethyl acetate phases, and vacuum dry.
[0068] (4) Dissolve the dry product obtained in step (3) with 1 / 200 of the fermentation broth volume in ethanol, centrifuge at 10,000 r / min for 10 min, and the supernatant is the metabolite of the competing microorganisms.
[0069] The activation medium in the step 1 is: potato (peeled): 200g, glucose: 20g, agar: 20g, water: 1000mL, and the pH value is natural....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com