Method for calculating a system, for example an optical system
A computing system and optical system technology, applied in optics, computing, optical components, etc., can solve problems such as limiting optical systems, achieve the effects of less time-consuming, simplified optimization problem indicators, and less complicated optimization methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
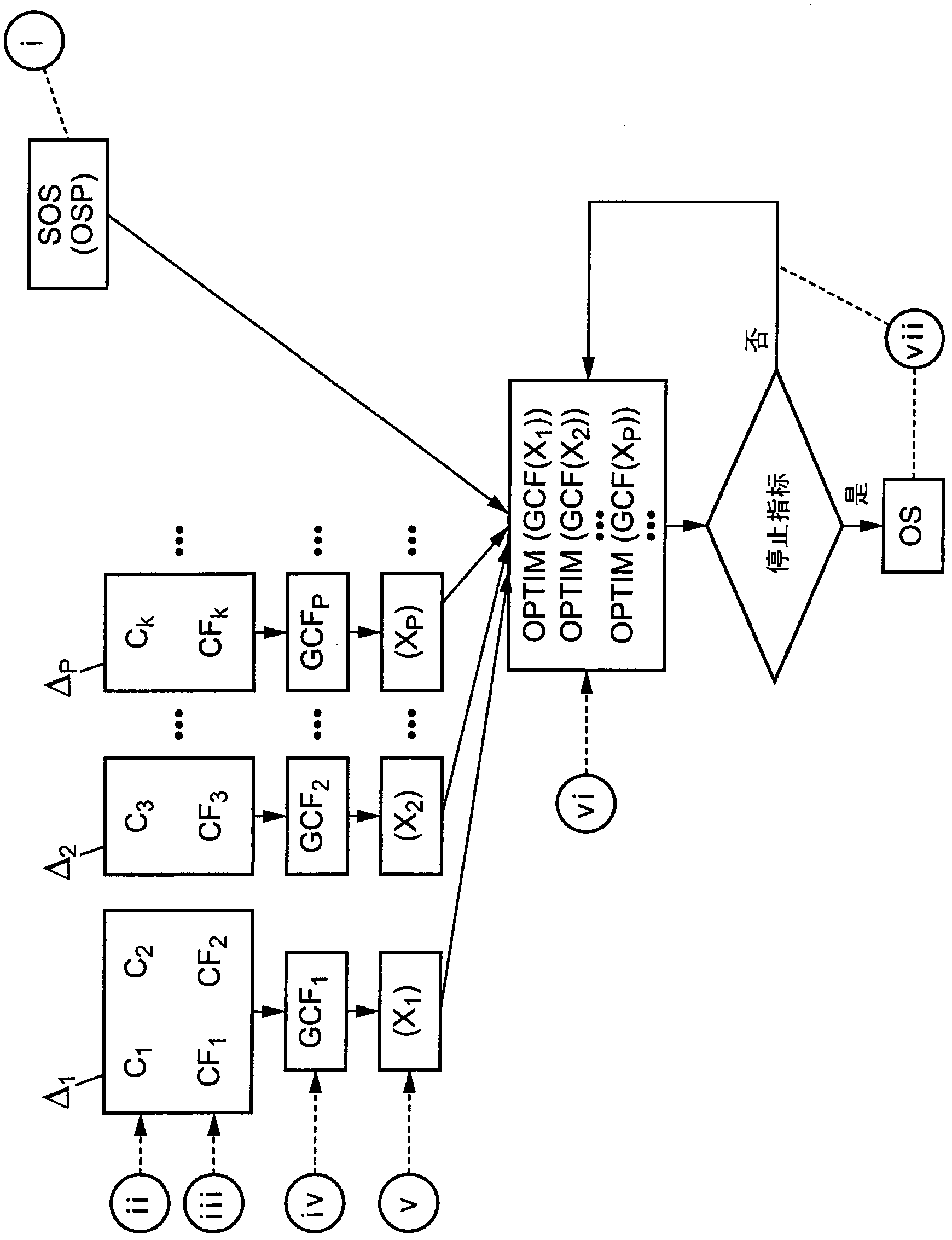
[0105] refer to Figure 1a , the method for calculating an optical system (OS) by optimization according to the present invention will now be described.
[0106] The method comprises providing step i, wherein a set of optical system parameters (OSP) is provided to define a starting optical system (SOS). Set each optical system parameter (OSP) as a starting value.
[0107] The method further comprises an index definition step ii, wherein a plurality of indexes (C 1 ,...,C m ). Then, in indicator association step iii, at least one value function (CF k ) is associated with each indicator (C k ). Therefore, consider a set of m indicators (C 1 ,...,C m ), associated with m value functions (CF 1 ,...,CF m ).
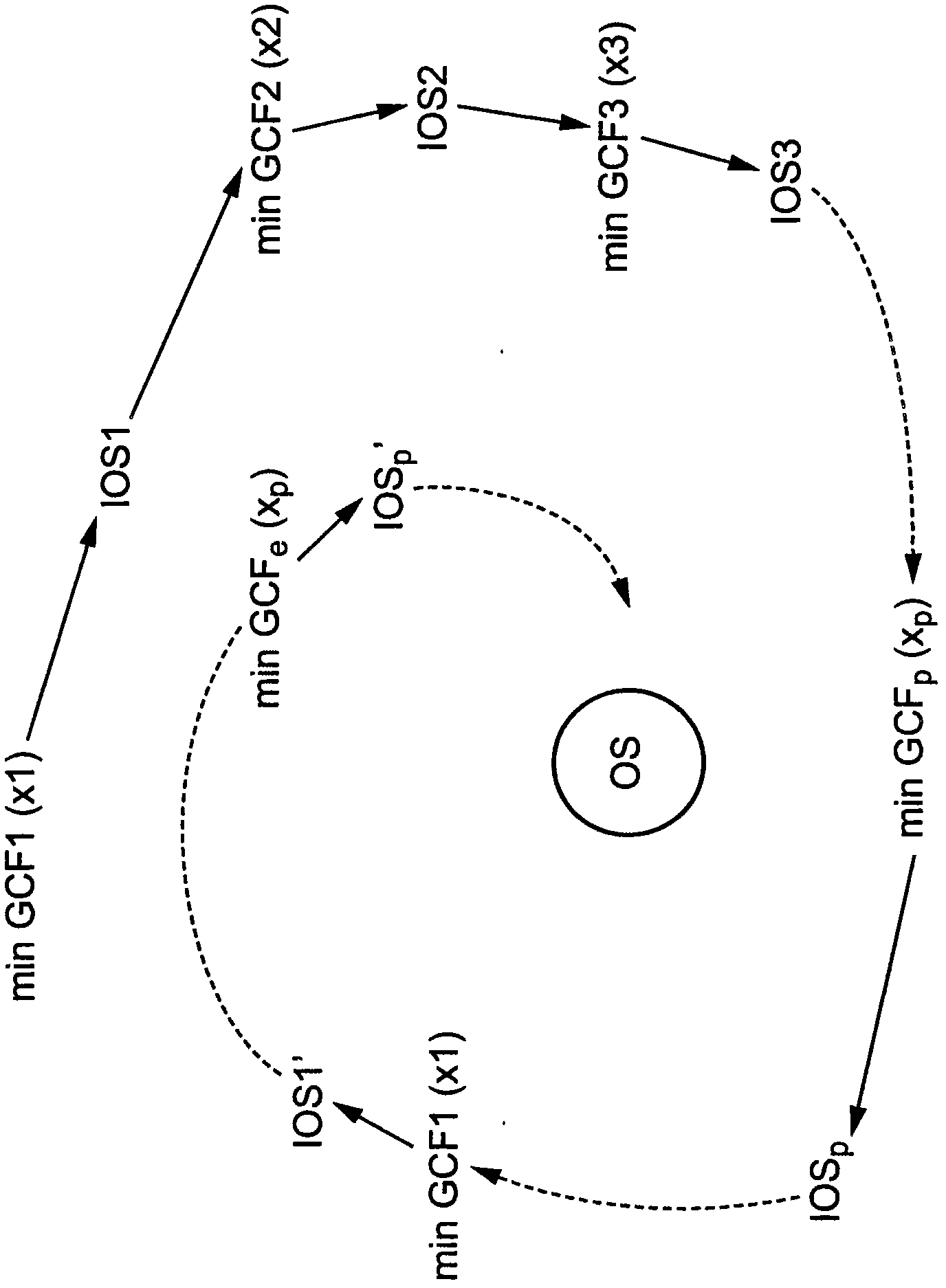
[0108] The method further comprises a global cost function definition step iv, wherein by adding at least one cost function (CF k ) is associated with each global value function (GCF p ) to define multiple global value functions (GCF 1 ,...,GCF ND ). Every globa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com