A test method for simulating the change of shear strength of dewatered soil in foundation pit
A technology of shear strength and test method, which is used in the application of stable shear force to test the strength of materials and the preparation of test samples, can solve the problems of not considering the influence of the shear strength of foundation pit precipitation and the unreasonable results.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Specific steps are as follows:
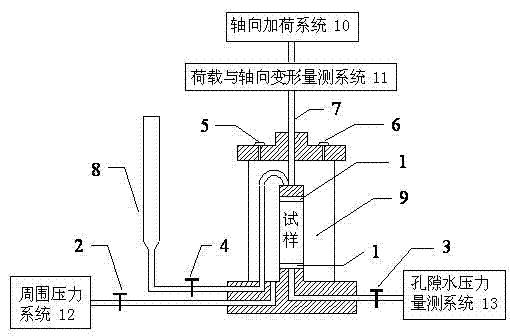
[0031] (1) Take the undisturbed soil sample, and prepare a soil column with a diameter of φ39.1mm and a height of 80mm with equipment such as a wire saw, a soil cutter, and a soil cutter;
[0032] (2) After putting the sample into the vacuum tank, carry out pumping and water saturation;
[0033] (3) Install the specimen in the triaxial pressure chamber. When installing, first put the latex film on the film support tube, use a suction ball to inhale air from the air nozzle, make the latex film close to the tube wall, and cover the outside of the prepared sample; then open the pore water pressure valve, After filling and exhausting the permeable stone at the sample base of the pressure chamber and the piping system connected to it, close the valve, put a piece of filter paper on the permeable stone, put the sample covered with latex film on the base of the pressure chamber, turn over Tie the lower end of the lower latex membrane with the...
Embodiment 2
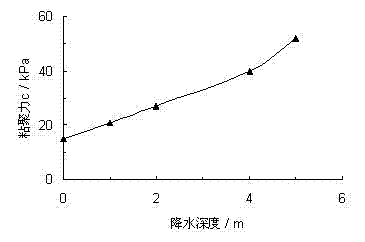
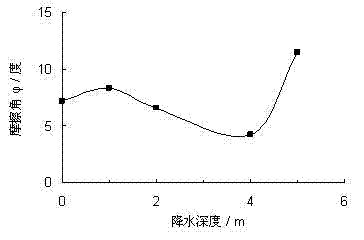
[0039] The sample is the undisturbed soil taken from a deep foundation pit in the urban area of Shanghai. The sample soil is gray muddy clay of layer ④, with a buried depth of 9.5-17.5m and a weight of 16.7kN / m 3 , the average self-weight stress is 100.0kPa. The test simulated four working conditions of no precipitation and 2.0m, 4.0m, and 8.0m of precipitation, and the corresponding consolidation pressures were 100.0kPa, 120.0kPa, 140.0kPa, and 180.0kPa; The precipitation samples were consolidated in two stages; a total of 4 groups of tests were done. Table 1 shows the shear strength index of gray muddy clay soil in layer ④ before and after precipitation measured according to the above test procedures. The cohesion c and internal friction angle φ of layer ④ gray silty clay change with precipitation depth, see Figure 4~5 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0041] The sample is the undisturbed soil taken from a deep foundation pit in the urban area of Shanghai. The sample soil is ⑤-1 layer of gray clay, with a buried depth of 17.5-22.0m and a weight of 17.5kN / m 3 , the average self-weight stress is 150.0kPa. The test simulated four working conditions of no precipitation and 2.0m, 4.0m, and 8.0m of precipitation, and the corresponding consolidation pressures were 150.0kPa, 170.0kPa, 190.0kPa, and 230.0kPa; The precipitation samples were consolidated in two stages; a total of 4 groups of tests were done. Table 1 shows the shear strength indexes of the gray clay layer ⑤-1 before and after precipitation measured according to the above test procedures. ⑤ The cohesion c and internal friction angle φ of gray clay layer 1 vary with precipitation depth, see Figure 6~7 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com