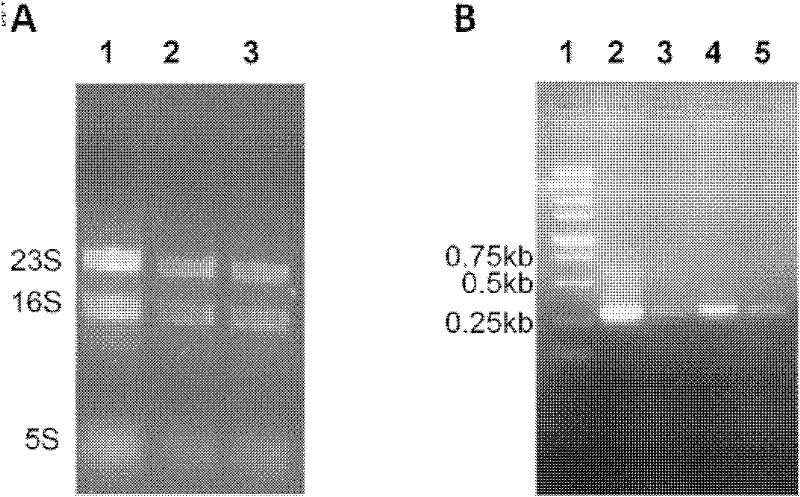
A mutant strain of Streptomyces flavum, its construction method and its use
A technology of Streptomyces flavum and mutant strains, which is applied in the field of microbial genetic resources and genetic engineering, and can solve the problems of complicated process and high cost of separation and purification of SFA
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0129] Example 1: Cloning of a large number of actively transcribed polyketide synthase genes under fermentation conditions.
[0130] Inoculate 500 microliters of S.flaveolus spores into 50 milliliters of sanglifellin-fermented seed culture medium, and cultivate them for 24 hours at 27 degrees and 250 rpm; transfer 3 milliliters of the culture medium to 50 milliliters of the main fermentation medium And cultivated for 4 days under the conditions of 25 degrees and 250 rotations. Centrifuge the fermentation broth at 4 degrees and 5000 rpm, pour off the supernatant, and gently scrape a little bacteria (about 100 microliters) attached to the surface of the sediment with a steel spoon. After quick freezing and grinding in liquid nitrogen, RNA was extracted with Trizol (purchased from Shanghai Yingjun Company) (see Practical Streptomyces Genetics for the operation steps), and finally dissolved in 100 microliters of water. Take out 43 microliters of RNA, add 5 microliters of 10×DNas...
Embodiment example 4
[0142] Example 4: Interruption of PKS and NRPS genes can completely block the biosynthesis of aminosatriene, confirming that the gene cluster is the biosynthetic gene cluster of aminosatriene
[0143] The plasmid containing five sets of PKS genes and one set of NRPS gene fragments was digested with EcoRI and HindIII, and then cloned into the EcoRI-HindIII site of pKC1139. These plasmids were transformed into sangliferin-producing bacteria through the method of indirect conjugative transfer of E. coli-Streptomyces developed by the present inventors (Mol. BioSyst. 2011, 7, 852-861). The resulting zygote was streaked on the ISP-4 medium containing 50 micrograms / ml of apramycin (Apramycin) and cultured at 37 degrees to induce gene disruption, to obtain the gene disruption mutant strain TL3016 (interrupted mycD1 gene ), TL3017 (disrupted mycD2 gene), TL3018 (disrupted mycD3 gene), TL3019 (disrupted mycD4 gene), TL3020 (disrupted mycD5 gene), TL3021 (disrupted mycC gene). genotype ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com