Method for evaluating WLAN (Wireless Local Area network) indoor single-source gauss location fingerprint locating performance based on conditional information entropy
A conditional information and fingerprint positioning technology, which is applied in the field of information systems, can solve problems such as high computing and storage overhead, and difficult performance comparison between systems, and achieve the effect of reducing computational complexity and time storage overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
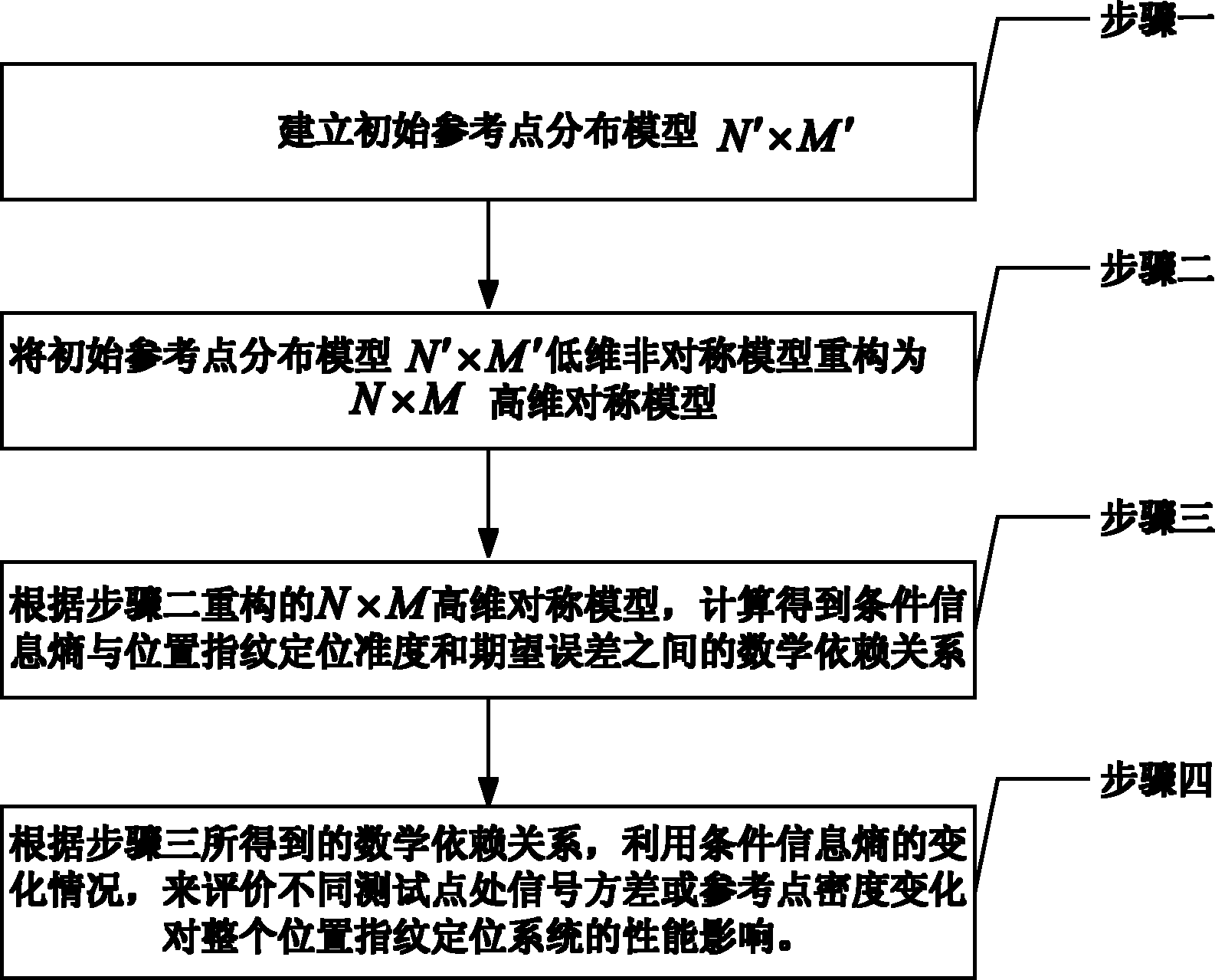
[0019] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 and figure 2 Describe this embodiment, the WLAN indoor single-source Gaussian position fingerprint positioning performance evaluation method based on conditional information entropy described in this embodiment, the method includes the following steps:
[0020] Step 1. Establish the initial reference point distribution model N′×M′:
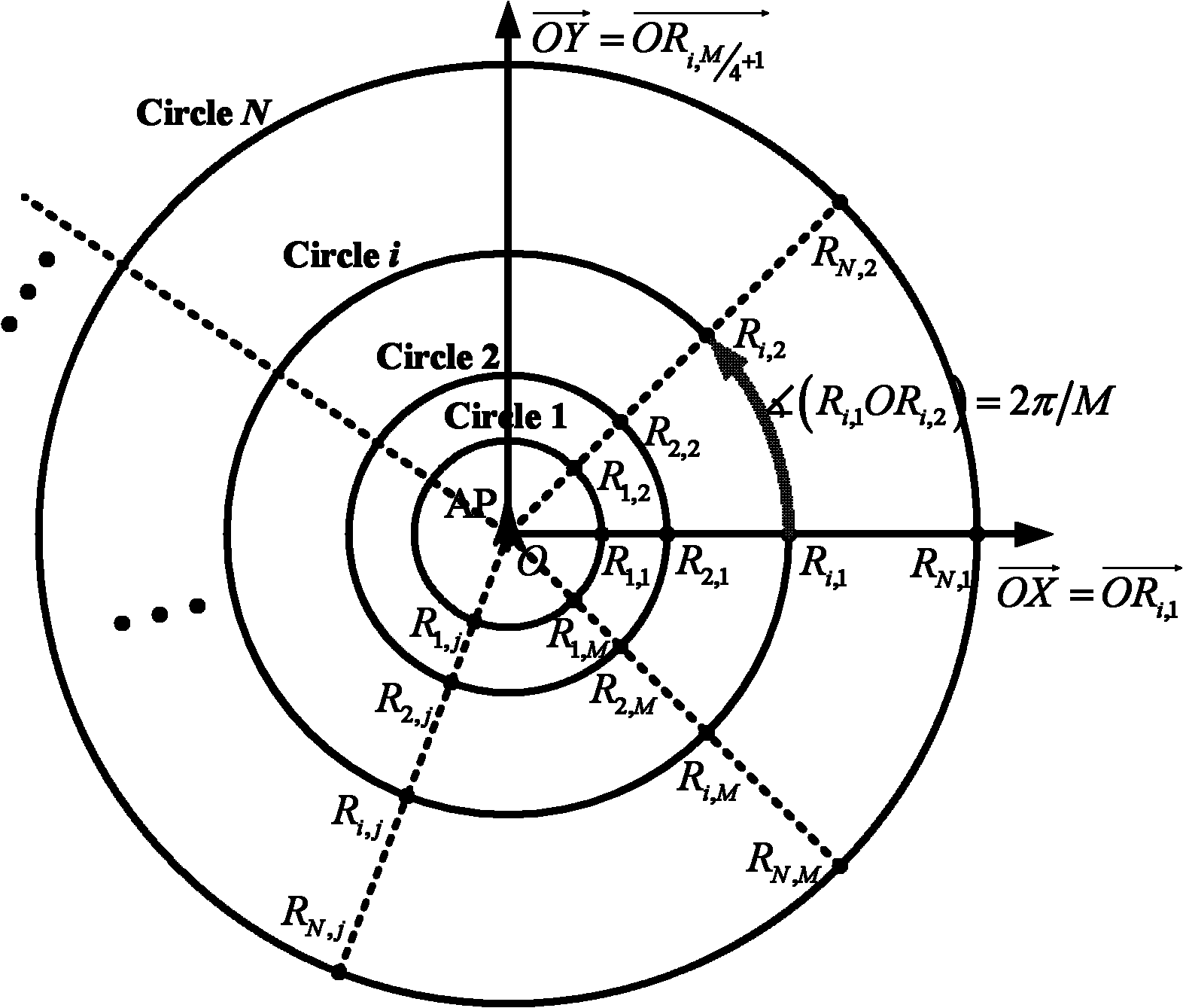
[0021] For any single-source logarithmic Gaussian distribution positioning environment, with the access point AP as the center and the radius d m Multiple reference points are set on the N′ rings of , and the number of reference points on the mth ring is M′ i , that is, the initial reference point distribution model can be expressed as an N′×M′ low-dimensional asymmetric model, where m=1,…,N′;
[0022] Step 2. Reconstruct the initial reference point distribution model N′×M′ low-dimensional asymmetric model into an N×M high-dimensional symmetric model, in which, the mea...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Specific implementation mode 2: This implementation mode further explains the implementation mode 1. In step 2, the specific implementation process of reconstructing the initial reference point distribution model N′×M′ low-dimensional asymmetric model into an N×M high-dimensional symmetric model is as follows:
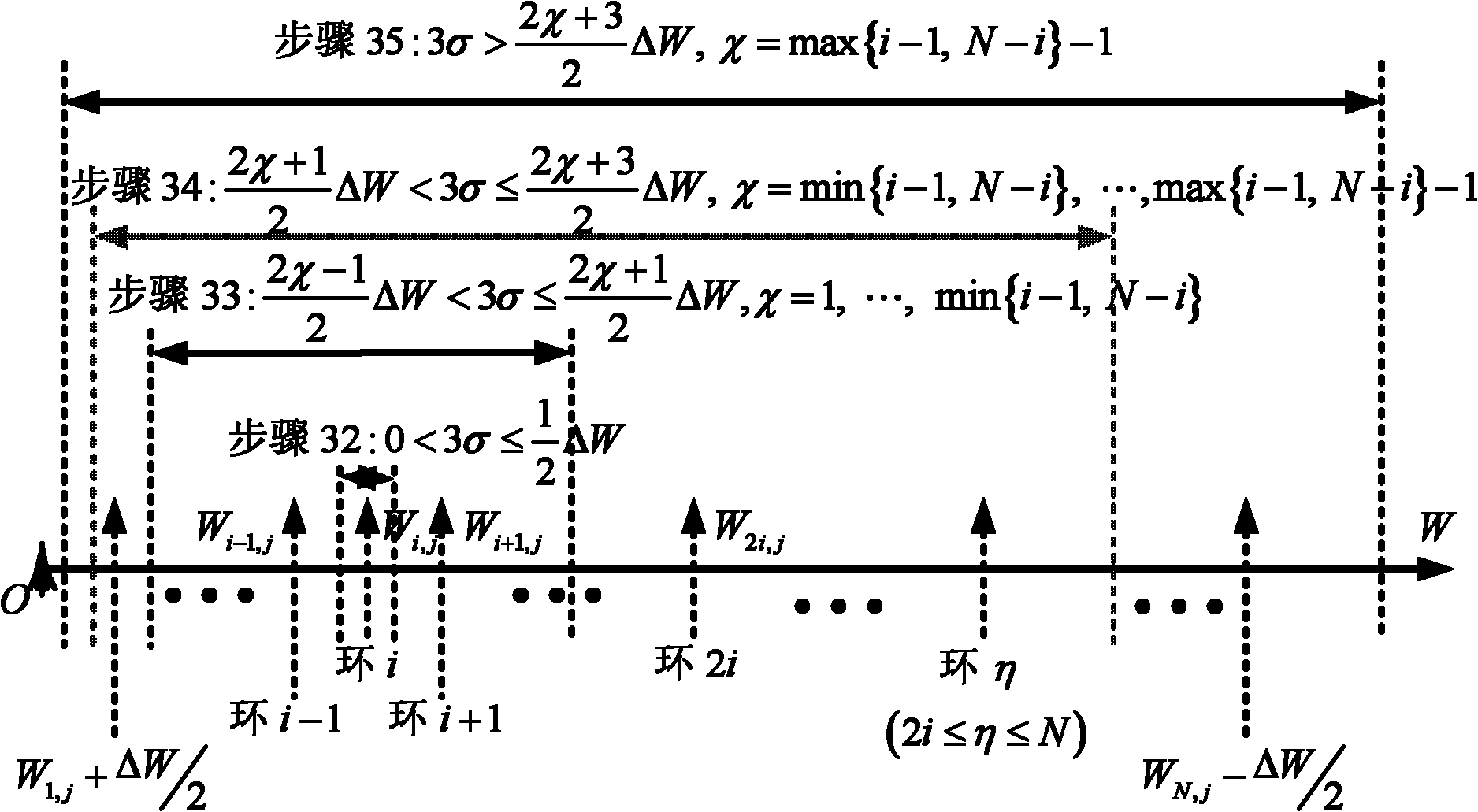
[0029] Step 21: Between the i-th and i+1-th rings of the N′×M′ low-dimensional model, add k n rings, and satisfy ΔW=W i,j -W i+1,j =W s,j -W s+1,j , s=1,...,N-1,
[0030] Among them, W i,j Indicates the reference point R i,j The mean value of the signal strength from the access point AP collected at ;
[0031] Step 22: Add M-M' on the i-th ring i reference points, and the M reference points formed after the increase are required to be evenly distributed on the ring, that is, the argument angle between adjacent reference points on the same ring is 2π / M, and the newly added M-M' i reference point and original M′ i The reference points have the same mean sig...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0040] Specific implementation mode three: this implementation mode further explains implementation mode two, and the newly added k is obtained in step 23 n The process of the average signal strength of a reference point on a ring is:
[0041] The newly added k between the i-th, i+1 and two rings n The rings have similar signal intensity logarithmic attenuation characteristics, that is, the logarithmic attenuation model W i,j =W 0 -[Pl i,j (d 0 )+10α i,j log 10 d i +h(f)], the reference distance d 0 = Free space loss Pl at 1m i,j (d 0 ) and path decay exponent α i,j are constants, where W 0 Represents the transmit power of the access point AP, h(f) represents the attenuation factor related to the transmit frequency of the access point AP, then,
[0042] D. 2,2 P 2,1 =F 2,1 ,
[0043] Among them, D 2,2 represents the reference point location matrix, and D 2,2 = 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com