Method for producing alcohol by utilizing cassava as a raw material through applying enzyme preparation production fermenting waste liquid
A technology of fermentation waste liquid and enzyme preparation, applied in the field of fermentation, can solve the problems of increased production cost, pollution of the surrounding environment, low component content, etc., and achieve the effects of large profits, reduced production costs, and waste liquid treatment costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
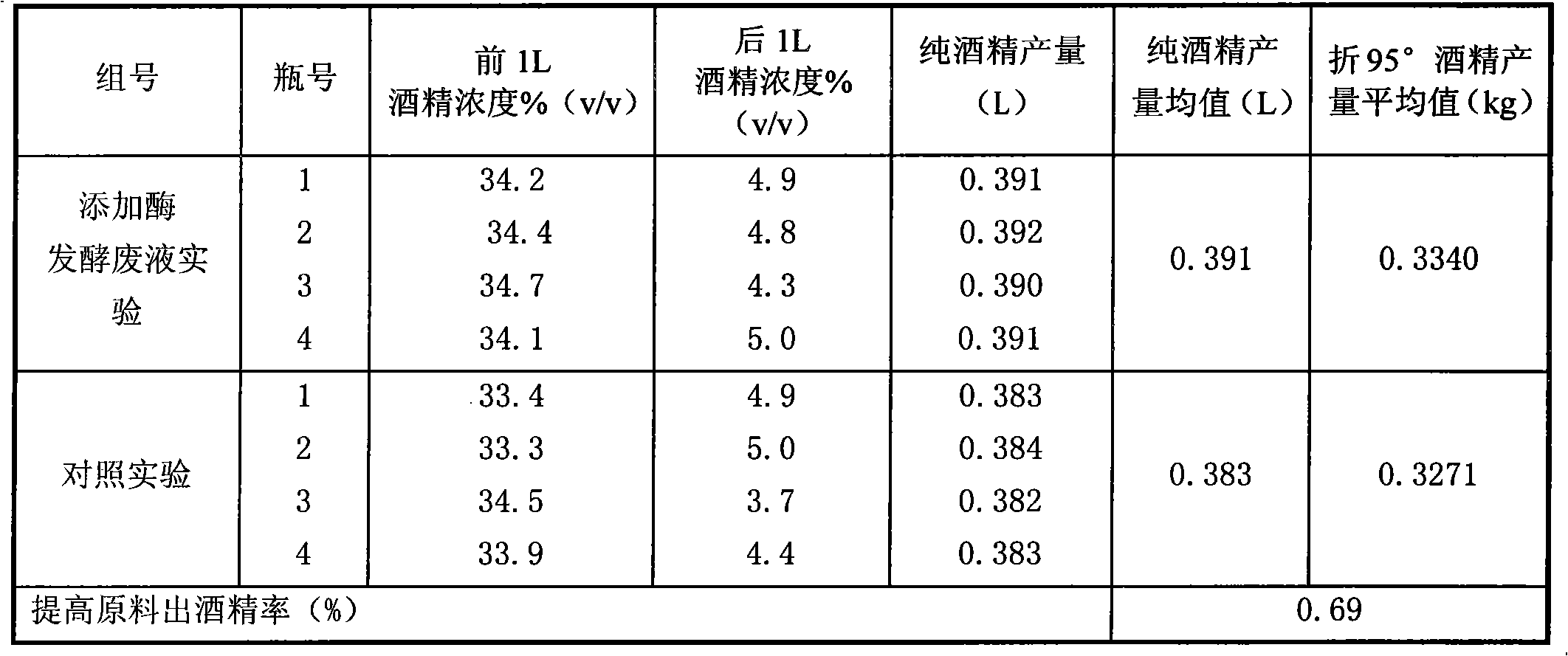
[0023] Example 1 The effect of adding saccharification enzyme fermentation waste liquid on the yield of alcohol
[0024] Enzyme preparation production fermentation waste liquid is applied to cassava raw materials to produce alcohol, including cassava flour slurry, liquefaction, saccharification and fermentation, the steps are as follows:
[0025] The cassava is crushed and passed through the bottom of a sieve with an aperture of 1.8 mm to obtain cassava flour, and then 1 kg of cassava flour is taken, and the cassava flour is mixed with 2.6L of water in a weight-to-volume ratio of 1:2.6, and stirred evenly to obtain a cassava flour slurry; Add 0.04L of amylase diluent (from 20,000 U / mL diluent to 200U / mL) to the powder slurry, mix well, and control the liquefaction at 96°C for 80 minutes to obtain liquefied cassava pulp;
[0026] Cool the liquefied cassava pulp to 60°C, add 0.088L glucoamylase diluent (diluted from 100,000 U / mL to 1000U / mL) and 0.15L glucoamylase fermentation waste li...
Embodiment 2
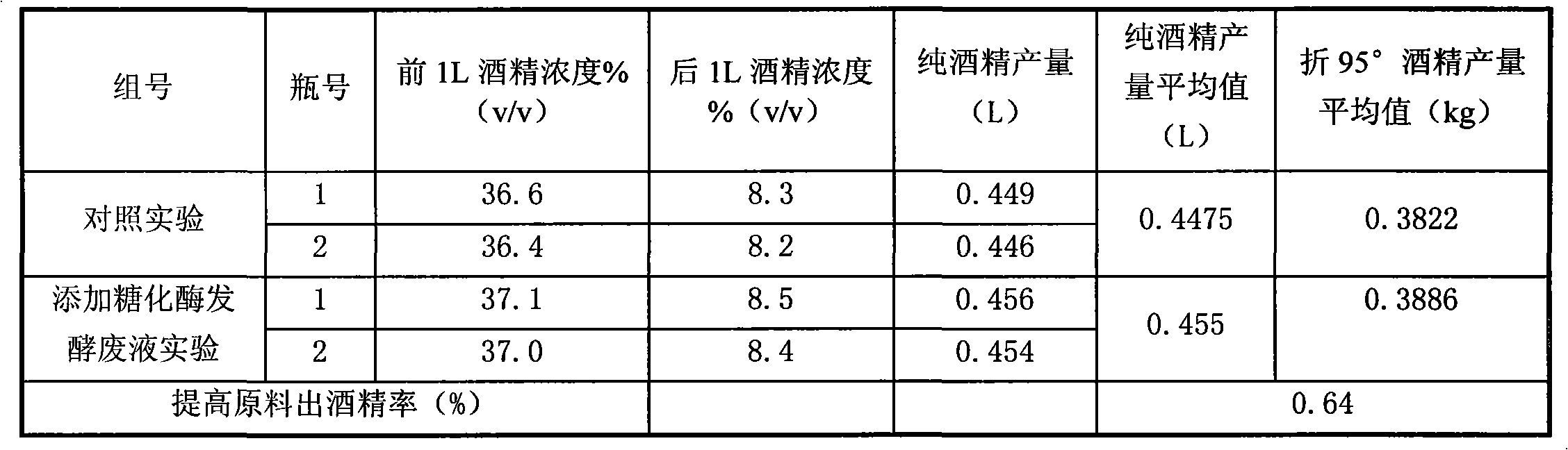
[0036] Example 2 The effect of adding amylase fermentation waste liquid alone on alcohol production
[0037] The enzyme preparation production fermentation waste liquid described in Example 1 is applied to the method for producing alcohol from cassava raw materials. The difference is that only 0.1L of amylase fermentation waste liquid is added to the cassava pulp during the liquefaction process; Add 0.1L of glucoamylase diluent to the liquefied cassava pulp at 60°C, without adding glucoamylase fermentation waste liquid.
[0038] At the same time, do comparative experiments, as shown in the following table:
[0039]
Group No
Raw material quantity (kg)
+
Water (L)
Liquid (L)
Amylase hair
Waste liquid (L)
Glucoamylase
(L)
Nutrients
(g)
Activated yeast
/ L
Control experiment
1+2.6
0.04
0
0.10
1
0.02
Add alpha-amylase
Fermentation waste liquid experiment
...
Embodiment 3
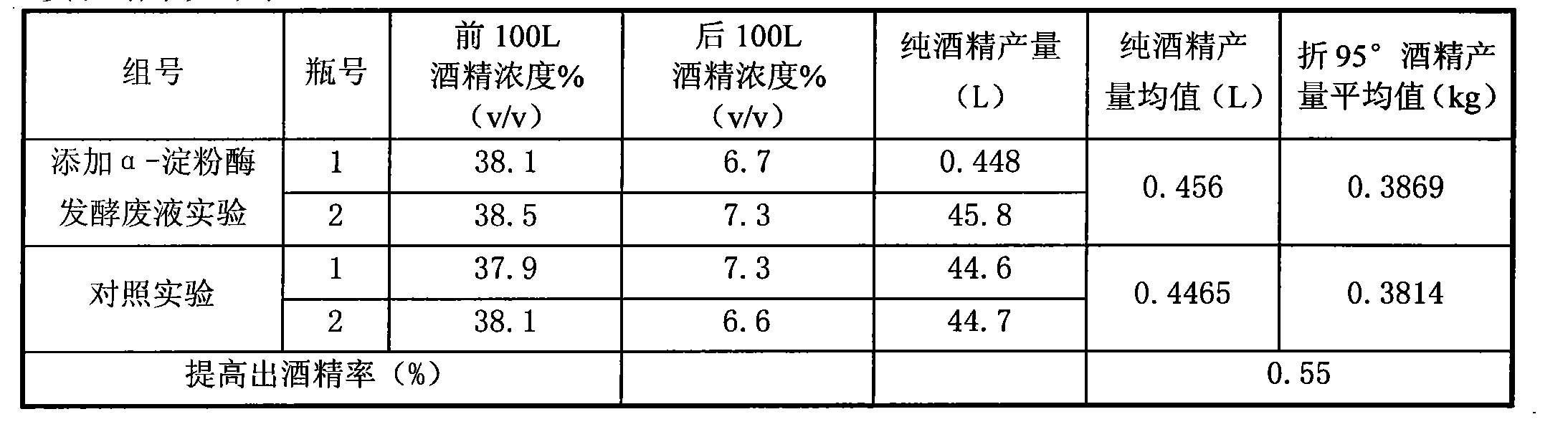
[0045] Example 3 The effect of simultaneous addition of α-amylase fermentation waste liquid and saccharification enzyme fermentation waste liquid on alcohol yield
[0046] The enzyme preparation production fermentation waste liquid as described in Example 1 is applied to the method for producing alcohol from cassava raw materials. The difference is that 0.05L amylase fermentation waste liquid and 0.02L amylase diluent are added to the cassava pulp during the liquefaction process. In the saccharification process, 0.092L of diluent of saccharification enzyme and 0.1L of saccharification enzyme fermentation waste liquid are added to the liquefied cassava pulp cooled to 60°C, 0.5g of nutrient salt is added in the process of saccharification, and 0.02L of activated Saccharomyces cerevisiae is added.
[0047] At the same time do a comparative test, as shown in the following table:
[0048]
Group No
Raw material quantity (kg)+
Water (L)
Amylase thin
Release (L)
Amylase ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com