Testing simulation system for generation process of diffusion hydrates in precipitates and testing method thereof
A hydrate generation and experimental simulation technology, applied in chemical/physical processes, methods of chemically changing substances using atmospheric pressure, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of hydrate sample collection and in-situ measurement difficulties, etc. Achieve the effect of fast reaction rate, simple operation and convenient data collection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
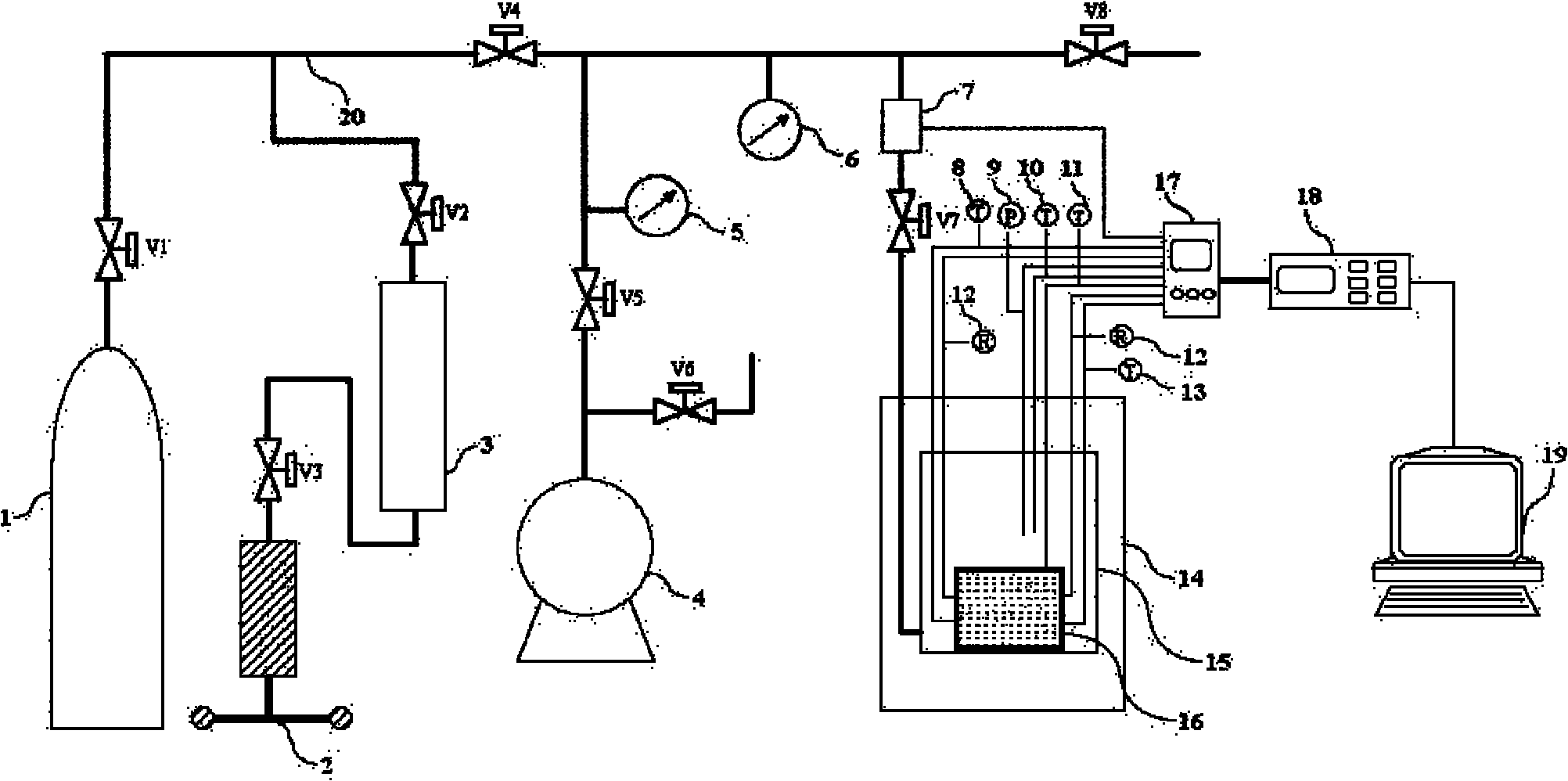
[0054] Using quartz sand, methane, and brine as experimental materials, the experiment system of the present invention is used to conduct an experiment on the formation of natural gas hydrate in sediments to simulate the formation process of natural gas hydrate in sediments.
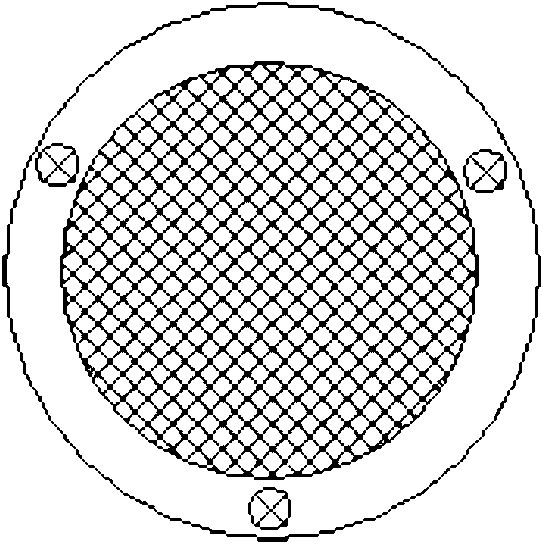
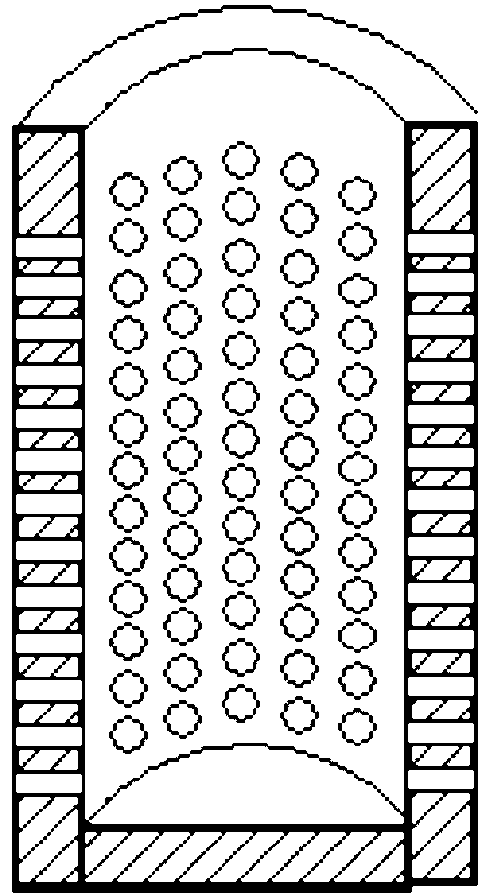
[0055] First, the quartz sand sample obtained from seabed mining was cleaned with distilled water, put into an oven to dry the water, and sieved with 60-mesh and 80-mesh sieves to obtain quartz sand particles with a particle size distribution between 180 μm and 250 μm. The material porosity is 36.7%, and the sand after getting 95g sieving is put into small polytetrafluoroethylene reactor 16. Then prepare brine with a mass fraction of NaCl of 3.5%, and drop it into the sediment with a dropper, and the dropping amount is 16 g. Then cover the small polytetrafluoroethylene reaction kettle cover of screen shape, fix it with screws, put the small polytetrafluoroethylene reaction kettle into the large stainless...
Embodiment 2
[0059] With quartz sand, mixed gas (CH 4 : 91.85%; C 2 h 6 : 5.09%; C 3 h 8 : 3.06%), brine as experimental materials, using the invented experimental system device to carry out the formation experiment of natural gas hydrate in sediments, and simulate the formation process of natural gas hydrates in sediments.
[0060] The quartz sand is sieved with a 40-60 mesh sieve, and the particle size distribution is between 250 μm and 380 μm. The measured porosity of the sediment is 41.9%. Take 95g of the sieved sand and put it into a small polytetrafluoroethylene reaction kettle . Then prepare brine with a mass fraction of NaCl of 3.5%, drop it into the sediment with a dropper, the amount of dropping is 39g, and the pore water will fill the pore space of the sediment. Put the small polytetrafluoroethylene reactor into a large stainless steel reactor, seal it and place it in a water bath for 12 hours, then vacuumize the system, and then enter the air with a gas pressure of 5MPa. A...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Using quartz sand, methane, and distilled water as experimental materials, the invented experimental system device is used to conduct experiments on the formation of natural gas hydrate in sediments to simulate the formation process of natural gas hydrates in sediments.
[0063] The quartz sand is sieved with a sieve of 80-100 mesh, the particle size distribution is between 150μm-180μm, and the porosity of the sediment is measured to be 38.2%. Take 95g of the sieved sand and put it into a small polytetrafluoroethylene reaction kettle . Then drop about 27g of distilled water with a dropper, water accounts for about 75% of the porosity of the sediment. Put the reaction kettle into a large reaction kettle and seal it and place it in a water bath for 12 hours, then vacuumize the system, then take in air, the gas pressure is 12MPa, and carry out the constant volume experiment. Set the temperature of the water bath at 25°C and keep it for 48 hours. Then the temperature of t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com