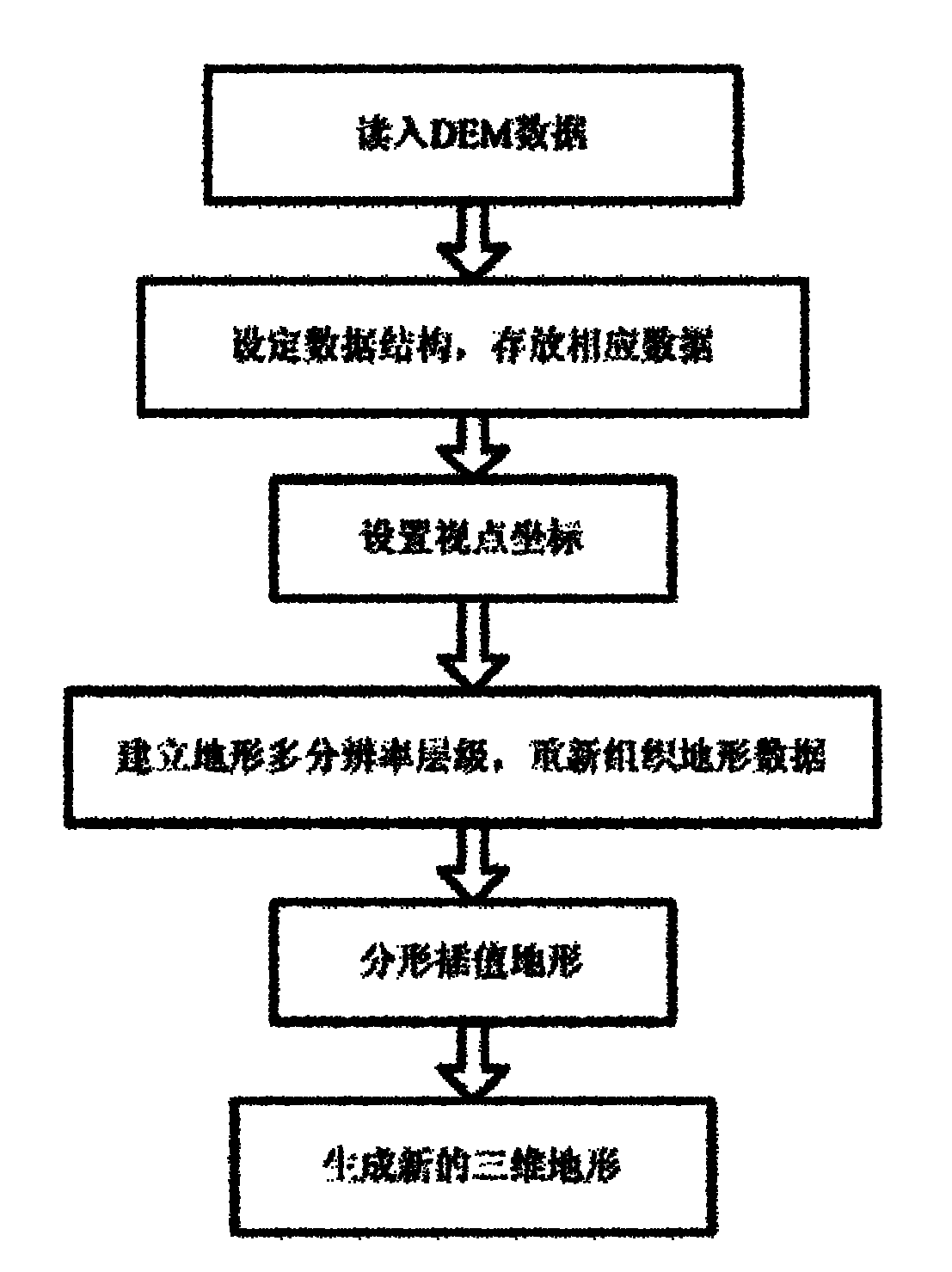
Fractal multi-resolution simplified method used for large-scale terrain rendering
A large-scale terrain and multi-resolution technology, applied in the field of visual simulation, can solve problems such as large-scale complex terrain takes a long time, and it is difficult to achieve real-time display.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
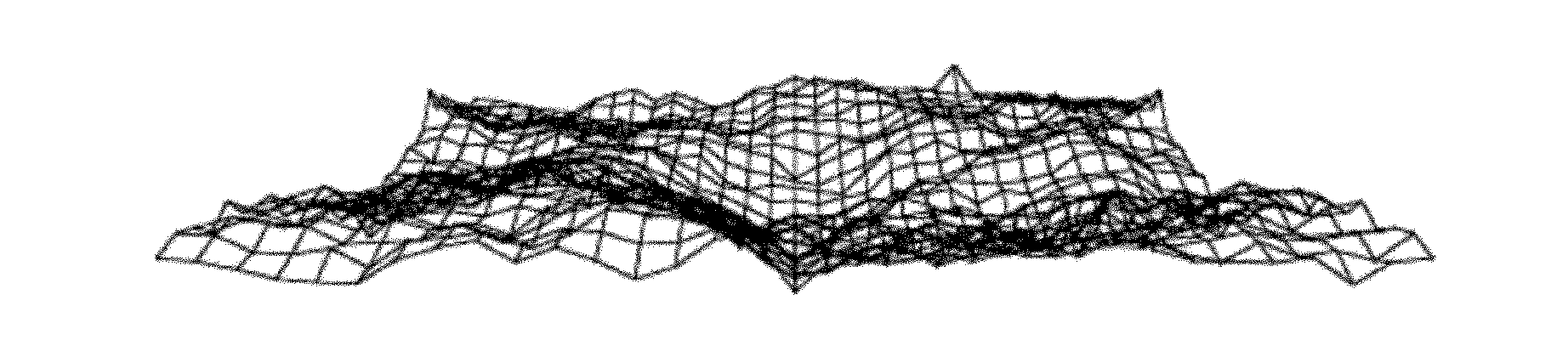
[0033]The rapid generation of large-scale terrain is realized by using the random midpoint displacement method in the fractal representation method. A random perturbation is added to the line segments formed by the vertices of the terrain, and subdivided to produce rich details of the scene. This is done iteratively, bisecting line segments plus random perturbations on every line between vertices in the terrain mesh, until the desired resolution is met. In the process of subdivision, fractal interpolation is performed between two or more points to establish a surface model, and a terrain grid generation method with random midpoint displacement is used to obtain a simulated terrain model with infinite details. The surface features of the terrain are determined by random Offset control. figure 2 is an iterative terrain mesh generated using the random midpoint displacement method.
example 2
[0035] In simulated terrain, the most detailed, high-resolution models give a realistic feel. However, the more complex the model, the greater the computational overhead. In practical applications, it is often not always required to show the most complete details of the model from beginning to end. The fractal multi-resolution simplification method is applied to the real-time rendering of the scene, and the arbitrary polygon representation in the world coordinate system is redescribed in the view coordinate system. Applies view-dependent clipping, projects the mesh polygons onto the view plane, image 3 Indicates the extent of the terrain covered by the projected viewing frustum. Preliminary clipping is performed based on the frustum range to reduce the number of scene polygons that finally enter the graphics pipeline. Based on the multi-resolution level-of-detail model technology, a group of similar models with different precisions is constructed to represent the scene. Eac...
example 3
[0037] According to the different attention levels of different terrain areas, a multi-level model is established. The level of the multi-level model is determined by factors such as the distance of the viewpoint and the complexity of the terrain itself. The adjacent levels are not necessarily continuous. When forming a 3D model, the adjacent levels Cracks may appear between LOD levels. In order to eliminate the crack phenomenon, the boundary point data of the terrain block is intentionally added in the simplification, and the boundary vertices are added for the low-resolution detail level model of the boundary, and it is forcibly split. Experimental results show that the added data points have little effect on the whole, but it can make the terrain continuous in space. The present invention constructs a view-dependent terrain multi-resolution framework. However, the level of detail of the terrain block is only determined from the perspective of visual correlation, and the inf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com