Non-woven surface covalent bonding gelatin adsorption material and preparation method thereof
An adsorption material and surface covalent technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, alkali metal compounds, etc., can solve the problems of limited durability of materials, slow washing speed, high price, etc., and achieve simple and convenient manufacturing process. The effect of small column resistance and wide range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Preparation and refining of embodiment 1 (1) polyepichlorohydrin (PECH)
[0035] A three-neck flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, a nitrogen conduit, and a condenser was installed in a water bath. Add 4 mL of refined 1,2-dichloroethane and 0.4 mL of 1,2-propanediol in sequence, start stirring and blow dry nitrogen. 0.5 mL of anhydrous SnCl 4 Inject it under the liquid surface, and then add 65mL of epichlorohydrin (ECH) dropwise within 40min. The polymerization reaction was stirred at 30° C. for 24 h. After the reaction is completed, add 40-50 mL of dichloromethane for dilution, transfer to a separatory funnel and wash with 5% hot brine for several times until the aqueous phase is pH neutral. After static separation, the lower organic phase was placed in a beaker with molecular sieves, and dried in a silica gel desiccator for 24 hours. Then it was filtered, and the filtrate was distilled under reduced pressure in an oil bath at 150°C for 1 h to remove volatile ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: Put 8 g of sodium azide and 0.17 g of tetrabutylammonium bromide into a beaker, add 25.3 mL of distilled water to dissolve to obtain an aqueous solution of sodium azide.
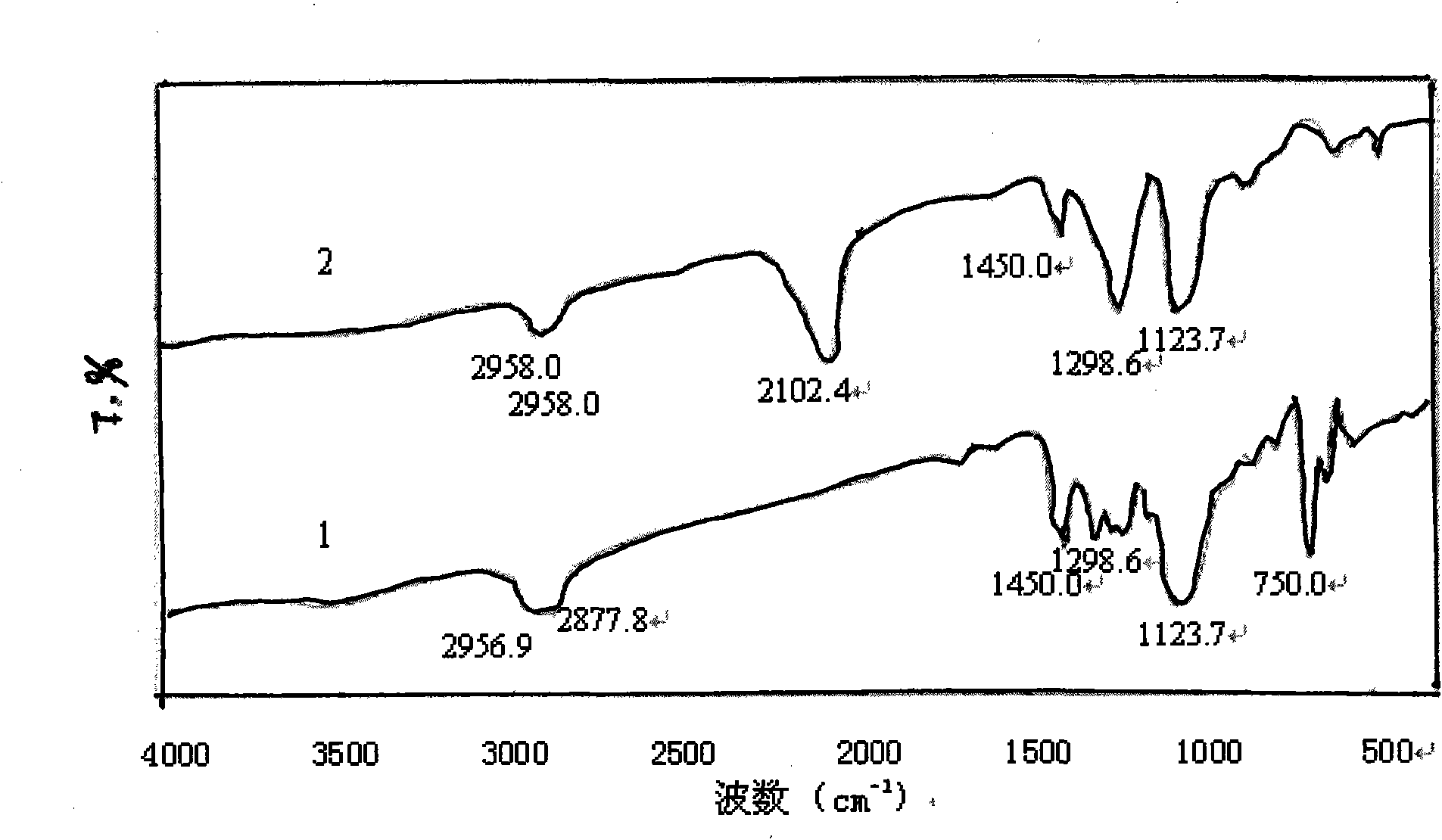
[0039] Add 0.2 g of polyvinyl chloride (commercially available type 5) into a three-necked flask, add 16.7 mL of the above sodium azide aqueous solution, stir and react in an oil bath at 80 ° C for 4 h, then wash and filter with a large amount of distilled water and 10 mL of methanol respectively, and the filter residue is It is a crude product of azide polyvinyl chloride. The crude product was first dissolved in 10 mL of tetrahydrofuran, then precipitated with 30 mL of methanol, and then suction-filtered, repeated three times and dried in the air to obtain the purified azide product, which was stored in a refrigerator at 5°C in the dark for future use. Its FTIR spectrum is shown in figure 2 Spectrum line 2, the characteristic absorption is consistent with the literature value, the FTIR s...
Embodiment 3
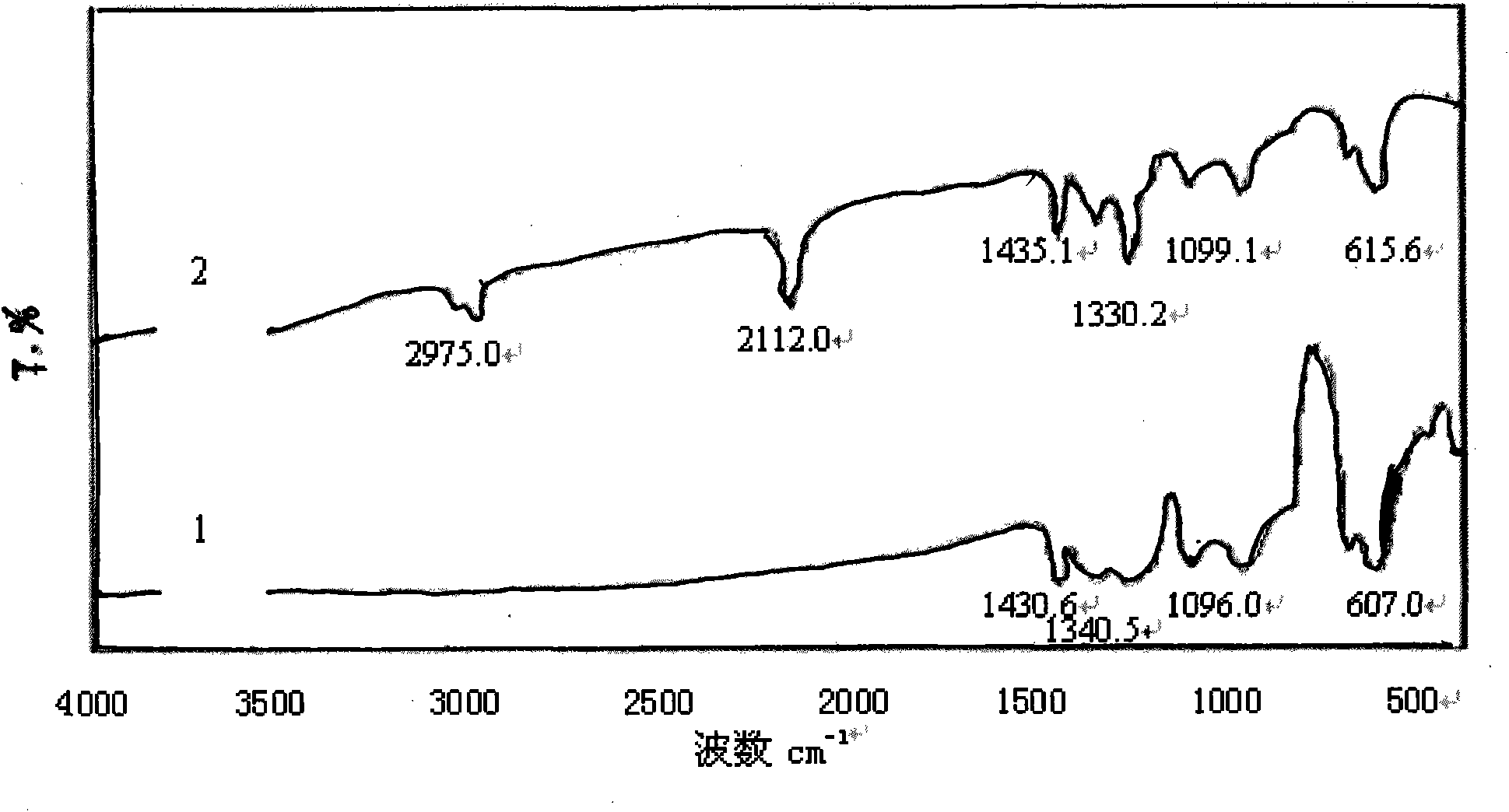
[0040] Embodiment 3: repeat embodiment 2 and only change polyvinyl chloride into vinyl chloride resin (commercially available CM1133 type), its FTIR spectrogram is shown in image 3 Spectrum line 1, the characteristic absorption is consistent with the literature value, and the FTIR spectrum of vinyl acetate resin is shown in image 3 Spectrum 2.
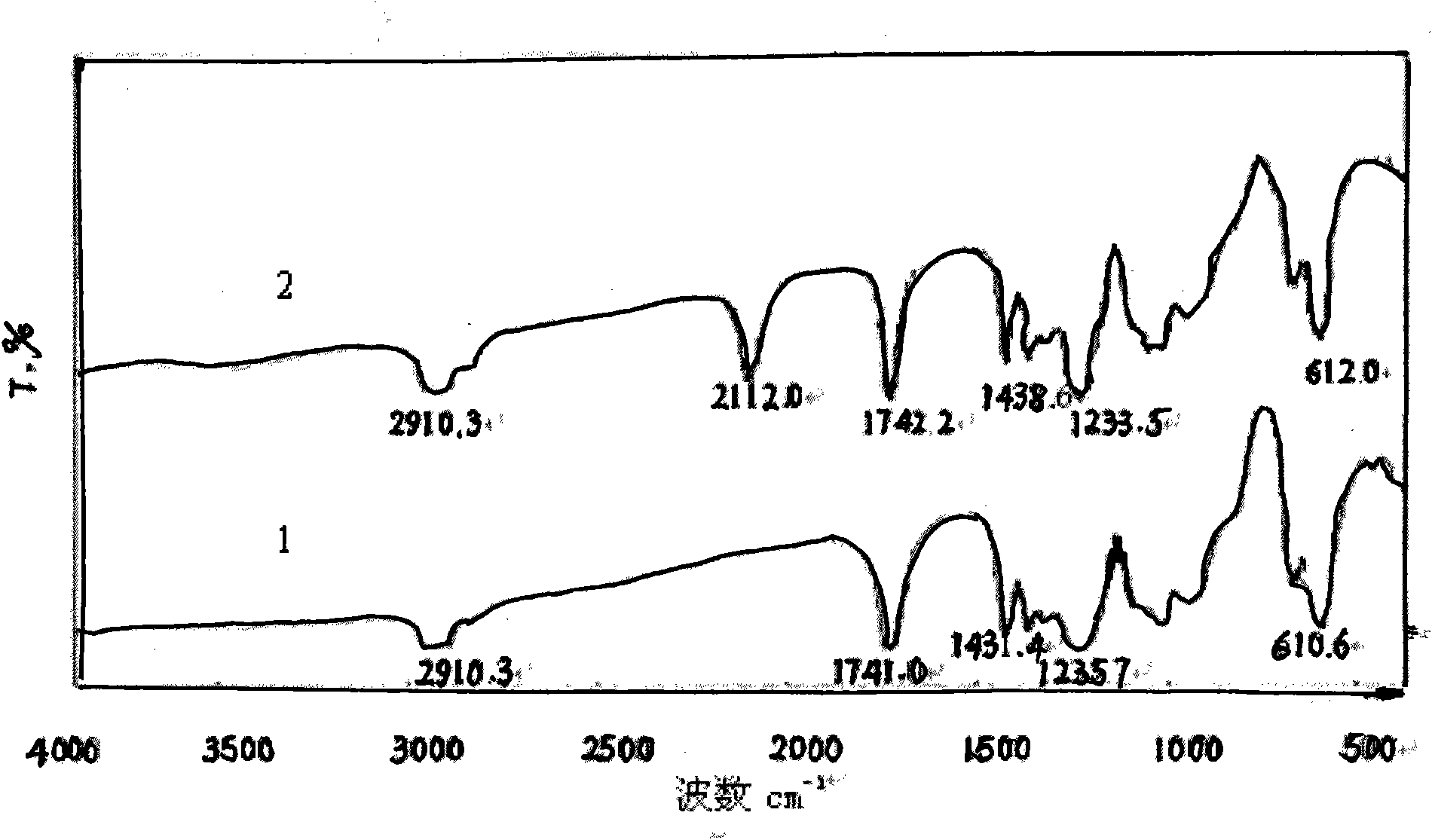
[0041] From the FTIR spectrogram ( Figure 1-Figure 3 In spectral line 2), it can be found that the azidation reaction does not affect the characteristic absorption of the main chain structure of the chlorine-containing polymer resin, only making 700-750.0cm -1 attributable to CH 2 The strong stretching vibration peak of -Cl disappears or weakens, while at 2100-2112cm -1 There is a strong attribution to -N 3 The absorption peak of the asymmetric stretching vibration of the group, the reduction of the chlorine atom and the appearance of the azide characteristic peak confirm that the azide group has replaced the chlorine, -N 3 It ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com