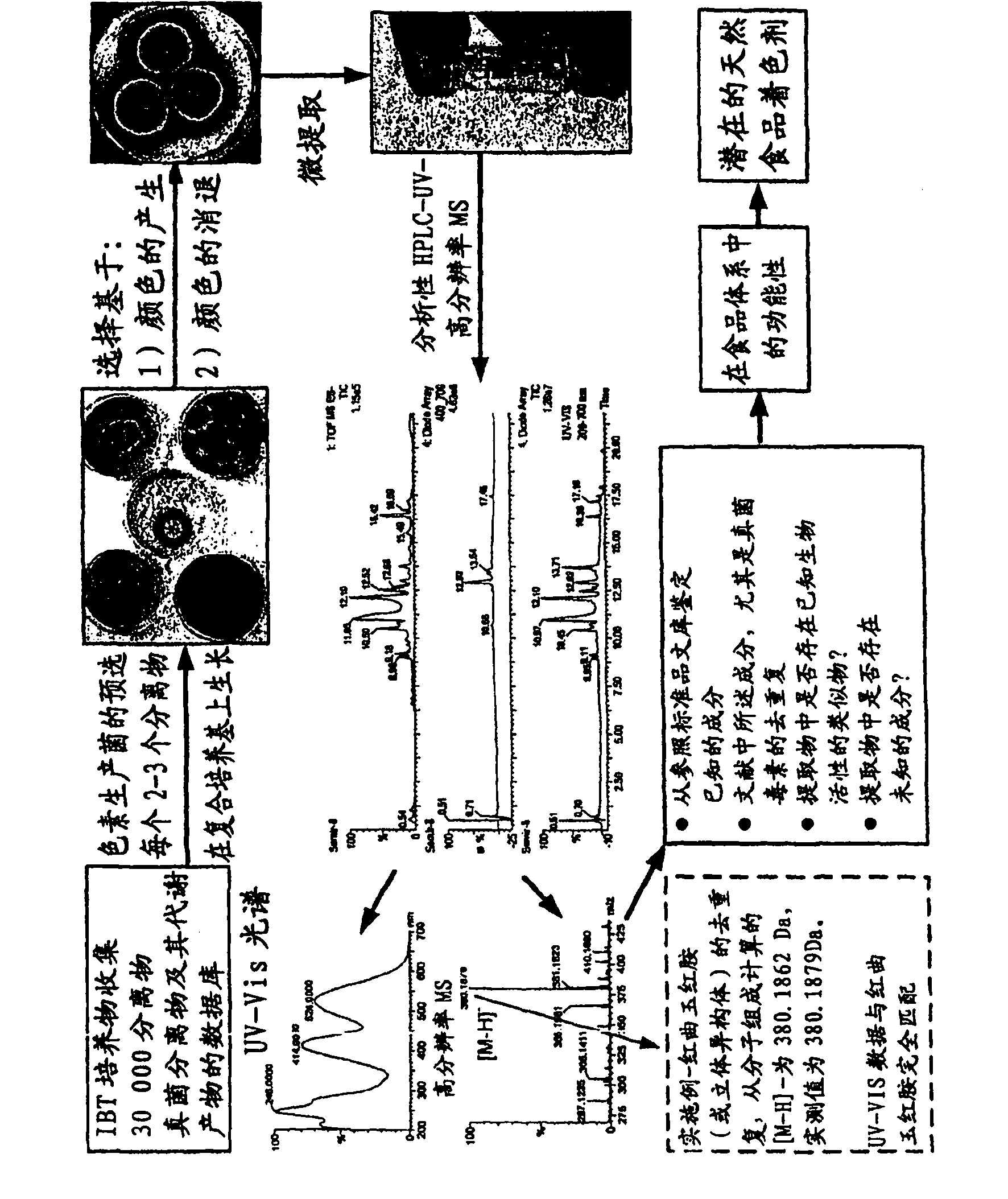
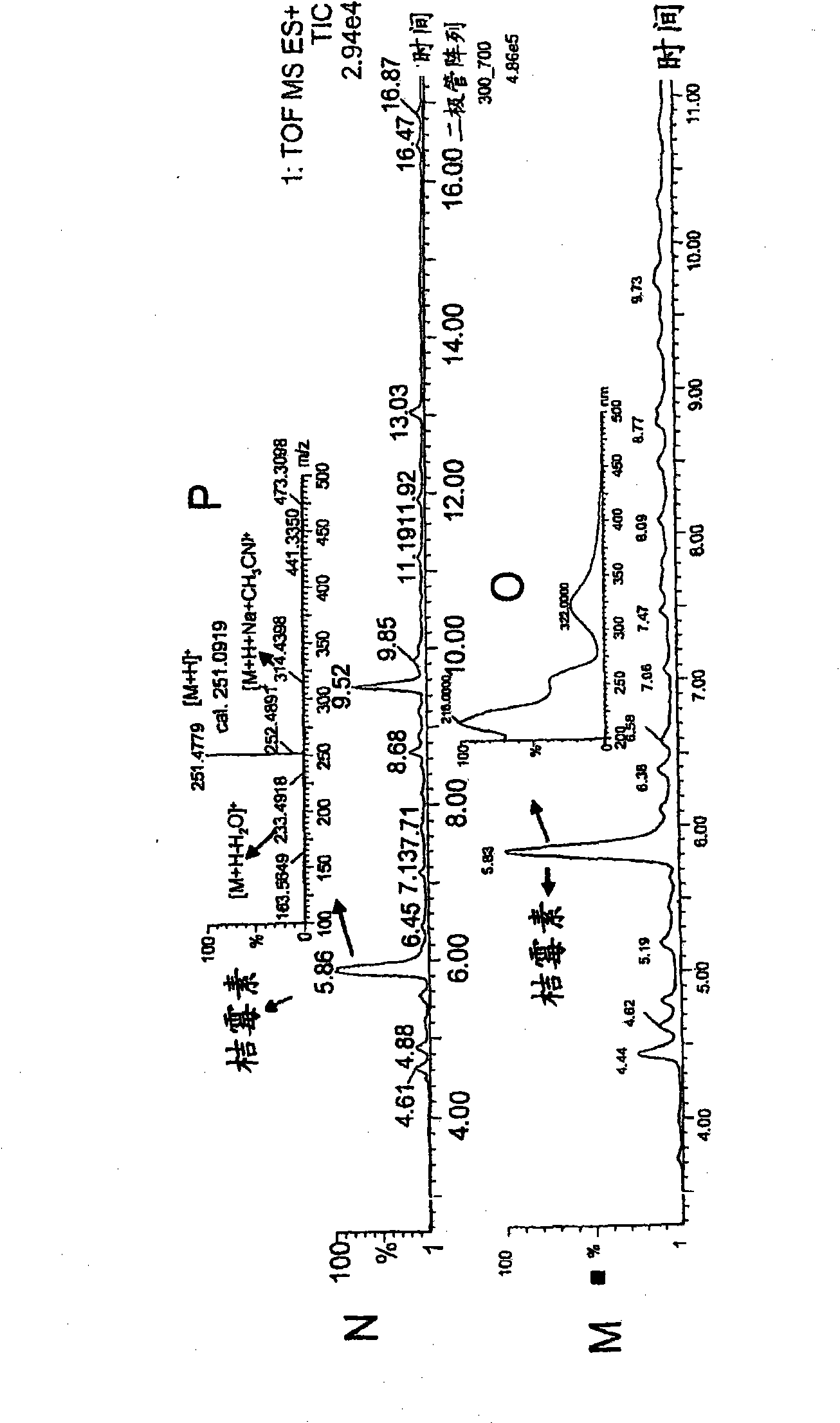
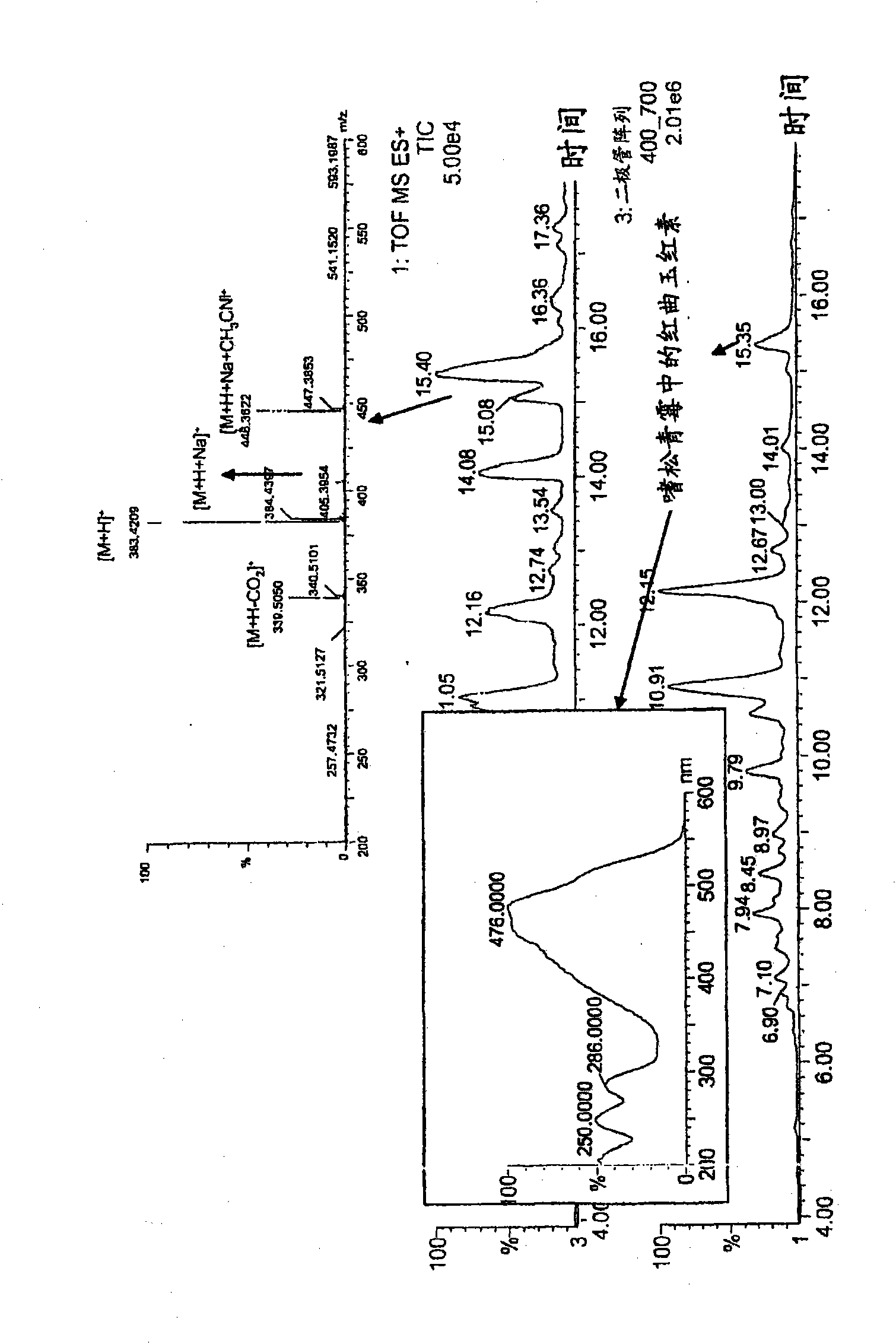
Production of monascus-like azaphilone pigment
A technology of Monascus and pigments, applied in the field of colorants, can solve problems such as instability to light, and achieve the effect of increasing light stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0181] The selection of embodiment 1. fungus, culture medium and culture condition
[0182] All fungal isolates used in this study were produced from Biocentrum-DTU, Technical University of Denmark, Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark. Fungal isolates are listed by IBT number. All fungi were grown on any of four different solid media, Yeast Extract Sucrose (YES) Agar; Malt Extract Agar (MEA), Potato Dextrose (PD) Agar and Czapek-Dox Yeast Autolysate (CYA) agar (Frisvad, J.C.; Thrane, U. Mycological media for food-and indoor fungi. See Introduction to Food-and Airborne Fungi. Introduction), 6th ed.; Samson, R.A., Hoekstra, E.S., Frisvad, J.C., Fitenborg, O., eds.; Royal Netherlands Biotechnology Institute Culture Collection, Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; p378), or Cultivation in a specific combination of media on which it was found produces the largest pigments with interesting shades in the red to yellow spectral range. The cultures were grown in the dark at 25°C for 7 days.
[0183] P...
Embodiment 2
[0184] Example 2. Extraction of fungal pigments
[0185] Extraction was performed by a modified form of Smedsgaard's micro-extraction method (J. Chromatogr.A 1997, 760, 264-270), in which 6 mm plugs were extracted for 30 minutes in two steps in 2 ml vials, first using 1 ml containing 0.5 % formic acid in ethyl acetate to break down cell walls and extract relatively nonpolar metabolites. The extract thus obtained was then transferred to a new 2 ml vial and evaporated under vacuum. Based on our initial results showing maximal pigment extraction from specific pigment-producing fungi, a second extraction was performed using 1 ml of methanol or isopropanol. Because the extract chemistry of pigments varies from fungus to fungus, an appropriate solvent needs to be used for a particular strain. By doing this, we can extract maximum pigment. However, the same solvent system was used to extract the same strains grown in different media. A second extract was then added to the vial al...
Embodiment 3
[0187] Example 3. Analysis of pigments
[0188] 3.1 Colorimetric method: Adjust the absorbance value of the pigments in the filtered fermentation broth at the respective maximum absorption points with pure water as a diluent, which is obtained from a Milli-Q system (Millipore, Bedford, MA) in order to measure the Beer-Lambert's law The absorbance within the linearity of . The dilution factor was then taken into account to calculate yields based on volumetric production of Absorbance Units (AU) per 100 ml of broth. The absorbance maximum was determined by scanning the absorbance spectrum of the extract in the range of 350-700 nm using a spectrophotometer (Agilent HP 8453, Agilent technologies, Palo Alto, USA).
[0189] Absorbance is also used to determine color quality. The absorbance values recorded at the pigment absorption maxima are two characteristic absorption peaks in the visible range of the spectrum, the first at approximately 495 nm and the other in the 407-420 nm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com