Japonica rice three-factor nutrition management method
A management method and nutrient technology, applied in the field of agriculture, can solve the problems of insignificant yield increase effect, difficulty in achieving high yield, high quality, efficient use of nutrients, and few researches on field nutrient management technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
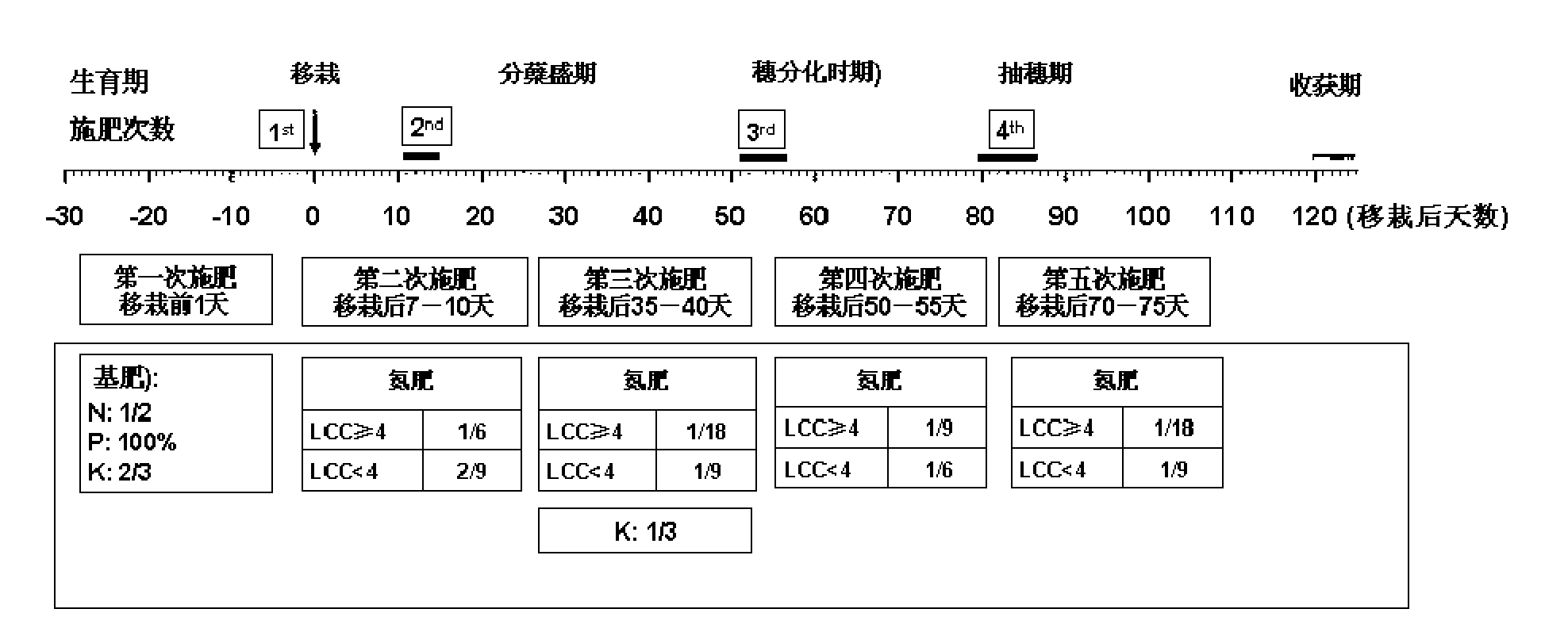
[0025] Embodiment 1: Fertilization management of japonica rice varieties (yield target > 9t / ha)
[0026] The soil foundation is moderately fertile (the output of nitrogen fertilizer blank area is ≥4.95t / ha)
[0027] 1. The total amount of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium application
[0028] (1) Total amount of nitrogen fertilizer (N) = (target yield - basic soil yield) / agronomic utilization rate of nitrogen fertilizer = (9-4.95) / 15 = 270kg / ha
[0029] (2) Phosphate fertilizer (P 2 o 5 ) total amount:
[0030] N:P 2 o 5 =1:0.3; Phosphate fertilizer (P 2 o 5 )=270×0.3=90kg / ha
[0031] (3) Potassium fertilizer (K 2 O) Total amount:
[0032] N:K 2 O=1:0.5; potassium fertilizer (K 2 O)=270×0.5=135kg / ha
[0033] 2. Fertilization period and fertilizer amount
[0034] 1) Base fertilizer (applied 1 day before transplanting)
[0035] The basal fertilizer nitrogen fertilizer accounts for 50% of the total nitrogen application rate (120kgN / ha), and all the phosphate fe...
Embodiment 2
[0136] Embodiment two: the japonica rice high-yield " three causes " nutrient management method of establishment has carried out field comparative test in southern Jiangsu, central Jiangsu and northern Jiangsu 30 peasant households, and half of field is local high-yield fertilization method (contrast, figure 1 Right), the other half of the application embodiment one "three reasons" nutrient management method, see figure 1 Left). Other cultivation measures are the same as:
[0137] 1. Machine transplanting technology
[0138] Technical points: (1) Precise sowing and uniform sowing, floppy disk dry seedling raising. Sow 100 grams of dry grain per plate, and the seedling-to-field ratio is 1:80; (2) The seedling age is controlled within 20 days, and the basic seedlings are planted, with a row spacing of 30cm×11.7cm, 1.6-18,000 holes per mu, and 3-4 seedlings per hole. About 70,000 to 80,000 basic seedlings per mu.
[0139] 2. The technology of returning full amount of wheat st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com