Uplink synchronous control method and device
A technology of synchronous control and control unit, applied in the directions of synchronous devices, electrical components, wireless communication, etc., can solve the problems of high implementation complexity, inability to accurately adjust the transmission time of different carriers, etc., and achieve the effect of precise adjustment and reduction of processing complexity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
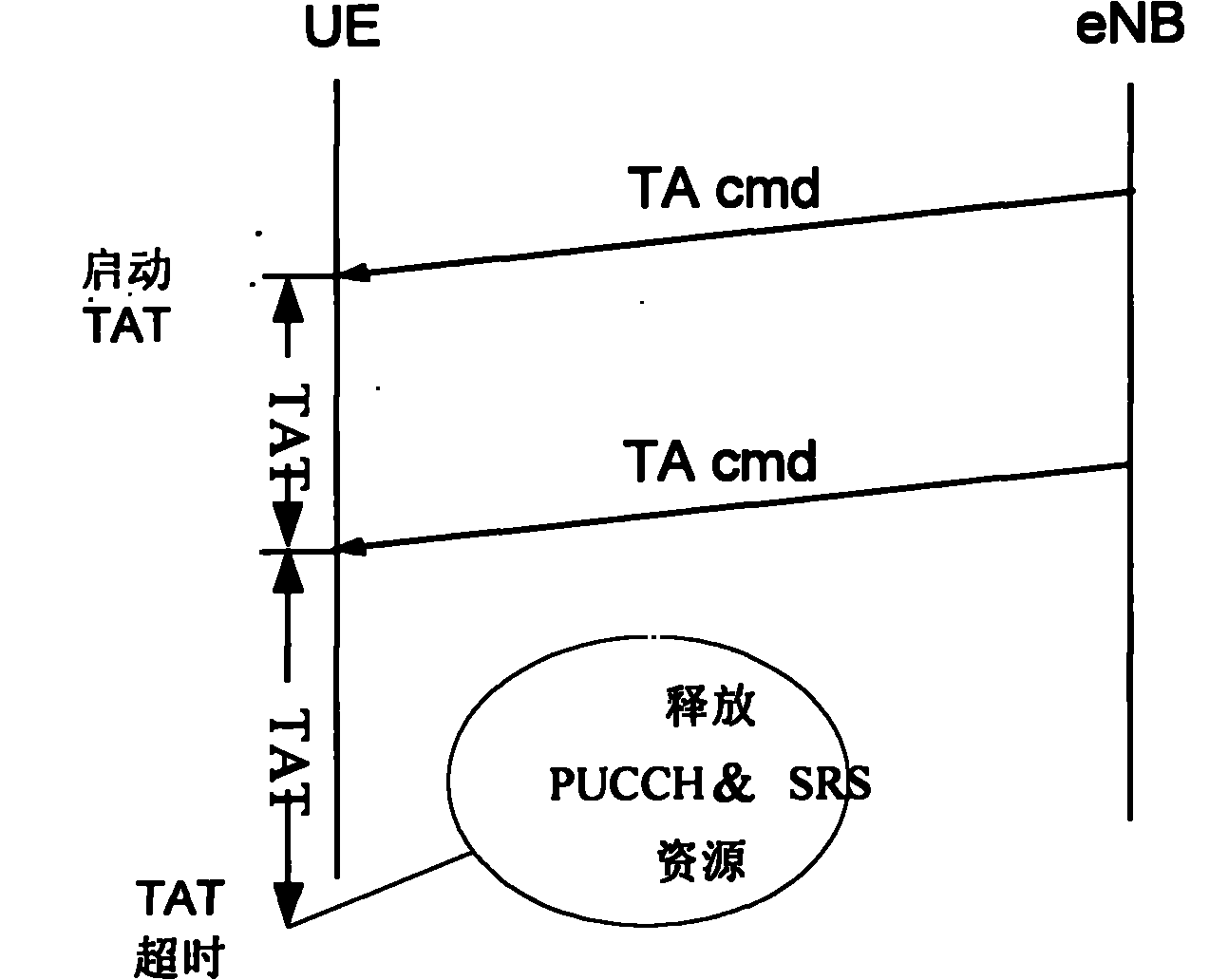
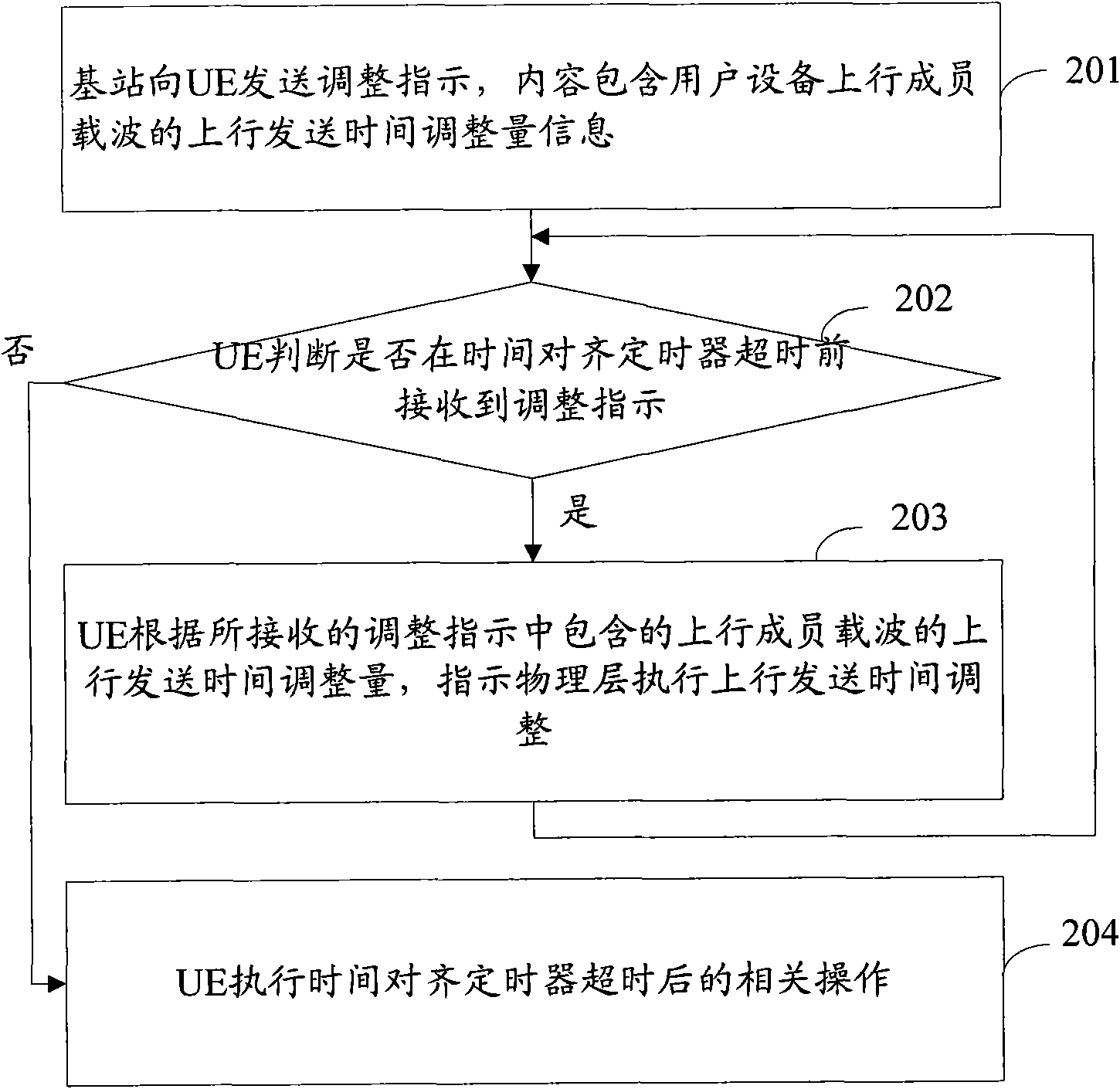
[0107] The application scenario of Embodiment 1 is: N carriers correspond to N sets of transmitters, and the TAC performs uplink transmission time adjustment based on the carriers. Its uplink synchronization control process is as follows: Image 6 shown, including the following steps:
[0108] Step 601: At regular intervals (less than the TAT time), the base station obtains the uplink transmission time adjustment amount of each uplink component carrier from the physical layer, and according to the uplink transmission time adjustment amount, the base station uses the TA format ( 1), format (4), format (5) or format (6) to construct N TA MAC CEs, or construct a TA MAC CE based on TA format (2) or format (3), and all TA MAC CEs are encapsulated into one transmission piece;
[0109] Step 602: the base station selects a downlink component carrier and sends an adjustment instruction including the transport block to the UE.
[0110] Step 603: After the UE receives the adjustment ins...
Embodiment 2
[0111] The application scenario of the second embodiment is that N carriers correspond to M sets of transmitters (N>M), the base station knows the corresponding relationship between the UE's uplink component carrier and the transmitter, and the TAC performs TA adjustment based on the transmitter. Its uplink synchronization control process is as follows: Figure 7 shown, including the following steps:
[0112] Step 701: every certain time interval (less than TAT time), the base station adjusts the uplink synchronization time based on the UE transmitter:
[0113] If a carrier corresponds to a set of transmitters, the physical layer of the base station measures the carrier directly; if multiple uplink component carriers correspond to a set of transmitters, the uplink time measurements of multiple uplink component carriers supported by the transmitter are selected for averaging , the obtained average value is used as a time adjustment amount for each uplink component carrier supp...
Embodiment 3
[0116] The application scenario of the third embodiment is that N carriers correspond to M sets of transmitters (N>M), and the base station does not know the corresponding relationship between UE carriers and transmitters, and performs measurement based on carriers. Its uplink synchronization control process is as follows: Figure 8 shown, including the following steps:
[0117] Step 801: At regular intervals (less than the TAT time), the base station obtains the uplink time adjustment of each uplink component carrier from the physical layer, and the base station constructs N TA MAC CEs based on TA format (1) for N uplink component carriers or based on TA Format (2) or format (3) constructs a TA MAC CE, and all TA MAC CEs are encapsulated into a TB transmission block;
[0118] Step 802: the base station selects a downlink component carrier to send an adjustment instruction to the UE.
[0119] Step 803: After the UE receives the adjustment instruction, the MAC layer adjusts t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com