Method of identifying individuals at risk of thiopurine drug resistance and intolerance
A thiopurine and tolerance technology, applied in the identification of individuals at risk of thiopurine drug resistance and intolerance, can solve problems such as toxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
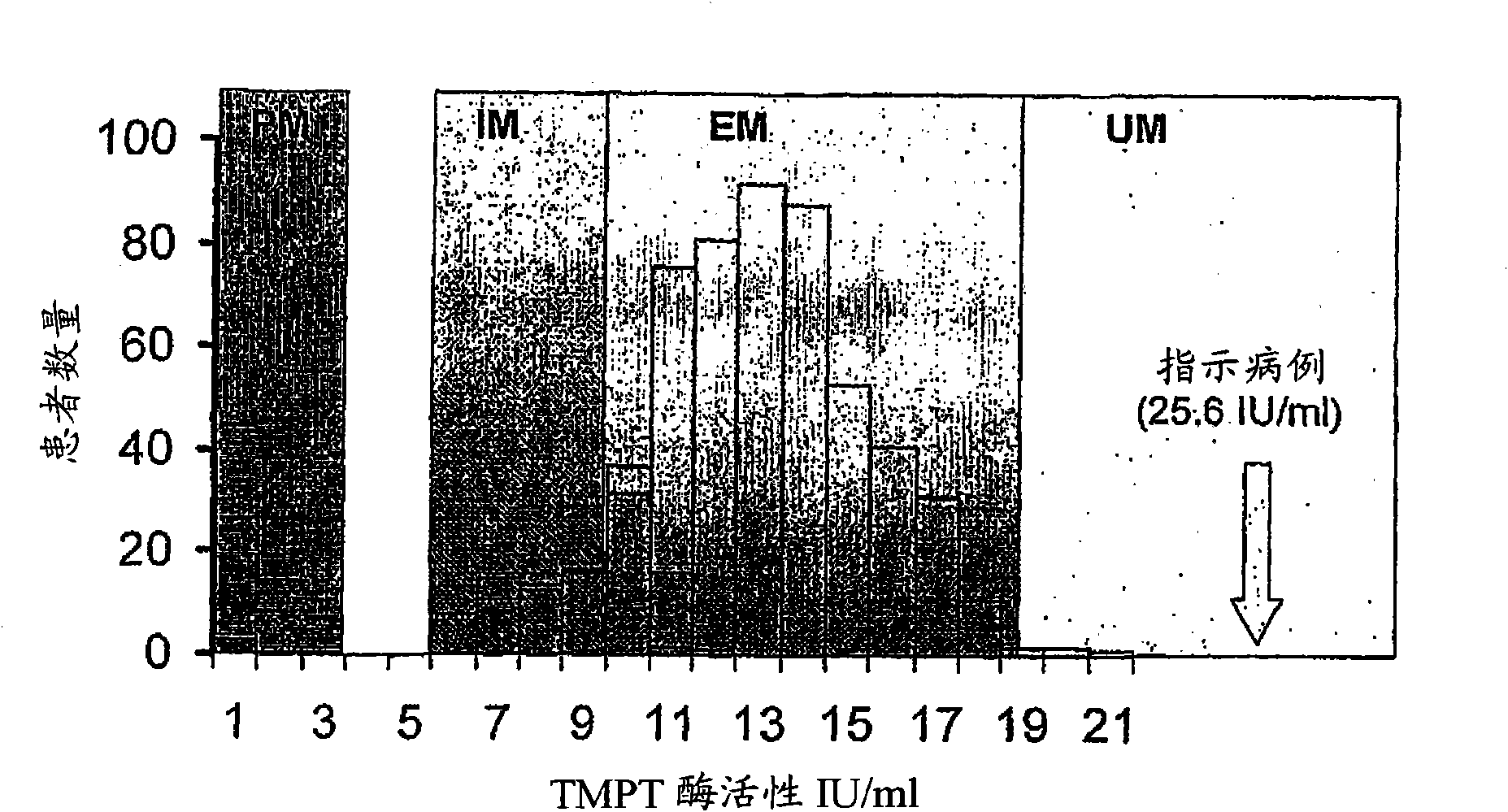
[0130] A 50-year-old Caucasian male (patient A) with indeterminate colitis had RBC TPMT activity found to be as high as 25.6 units / ml RBC (referred to as figure 1 "Indicator Case" in ), using radiochemical analysis (Weinshilboum et al., 1999). TPMT phenotypes were first offered as a clinical service in Christchurch (New Zealand) in 2003 (Sies et al., 2005) and since then over 2000 individuals have been tested. The standard range of TPMT activity, as measured by phenotypic assays, is 9.3 to 17.6 units / ml RBC ( figure 1). The highest available activity previously recorded was 22.5 units / ml RBC (Sies et al., 2005). Since Patient A did not receive any inhibitory drug treatment to induce TPMT activity, it is conceivable that his UM status was due to a mutation within the TPMT promoter. To test this hypothesis, the TPMT promoter was sequenced in this patient, as were nine other individuals with the UM phenotype (18.4-22.5 units / ml RBC).
[0131] Genomic DNA was extracted from 5 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com