Method for selecting autonomous navigation signposts of deep space probe based on observing matrix
A deep space detector and observation matrix technology, applied in the direction of integrated navigator, etc., can solve the problem of no navigation road sign independent selection method and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] In order to better illustrate the purpose and advantages of the present invention, the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
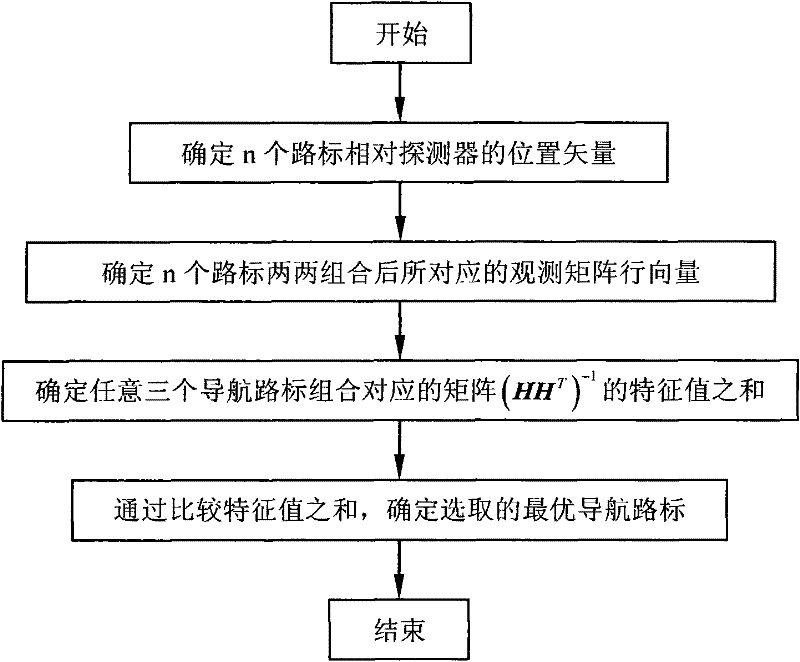
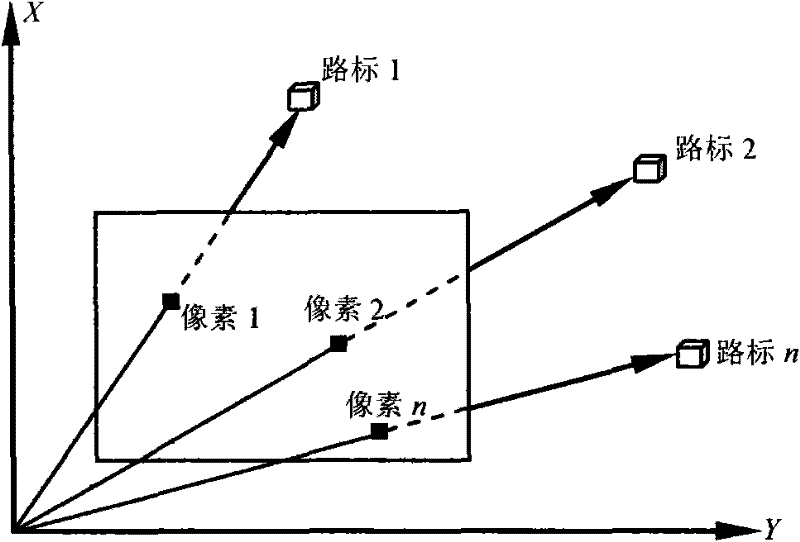
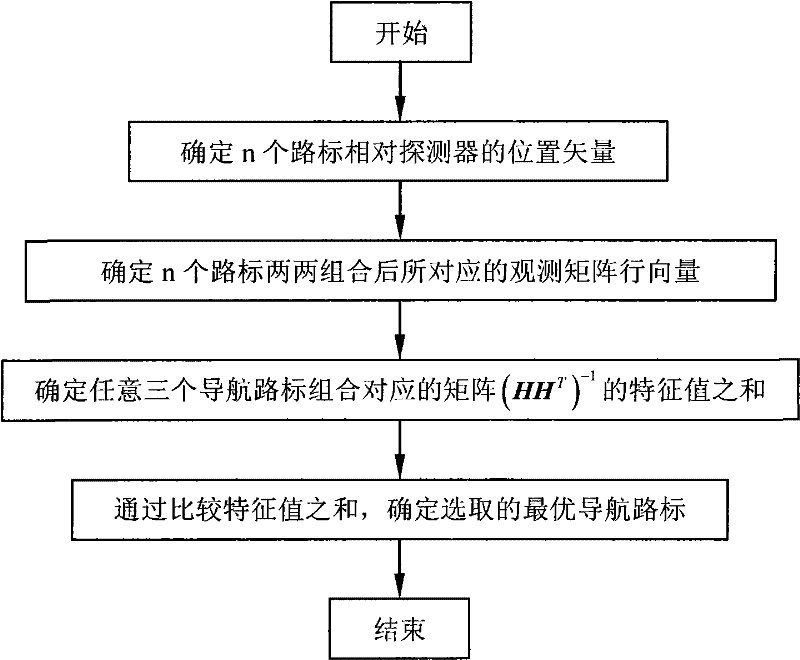
[0032] When the deep space probe is near the target celestial body, it uses an optical camera to take images of the surface of the target celestial body, extracts landmarks with obvious terrain features such as rocks and craters, and uses them as reference points for the autonomous navigation of the deep space probe. The position and attitude of the deep space probe relative to the target celestial body can be determined by using the information of the three landmark points. Therefore, in order to simplify the actual engineering algorithm and reduce the calculation time of the spaceborne aircraft occupied by the algorithm, three navigation algorithms are used in the navigation algorithm. Landmarks are used for autonomous navigation of deep control detectors. Sinc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com