Method for removing cold-embossing residual adhesive layer
A technology of residual glue and embossing glue, which is applied in the field of nano-manufacturing and can solve problems such as removing the residual layer of embossing glue
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] 1. Deposit an adhesive layer TiN and an opaque material layer Cr on the surface of 0.5 mm thick 2-inch quartz glass in sequence, with thicknesses of 20 nm and 1 μm, respectively.
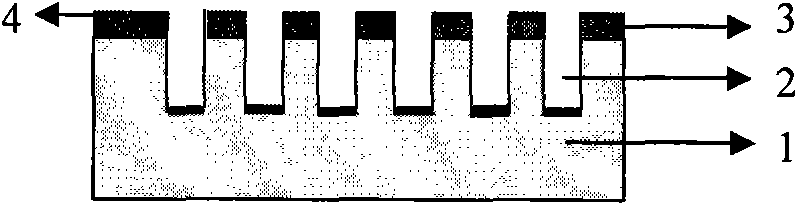
[0020] 2. Use electron beam exposure, etching and other semiconductor processing techniques to pattern the TiN and Cr layers, so that the bottom of the pattern is exposed to the surface of the quartz glass ( figure 1 ).
[0021] 3. Use low-pressure spraying method for modification treatment to form a layer of modification film to reduce its surface energy ( figure 2 ). The modifier is CF3-(CF2)7-(CH2)2-SiCl3.
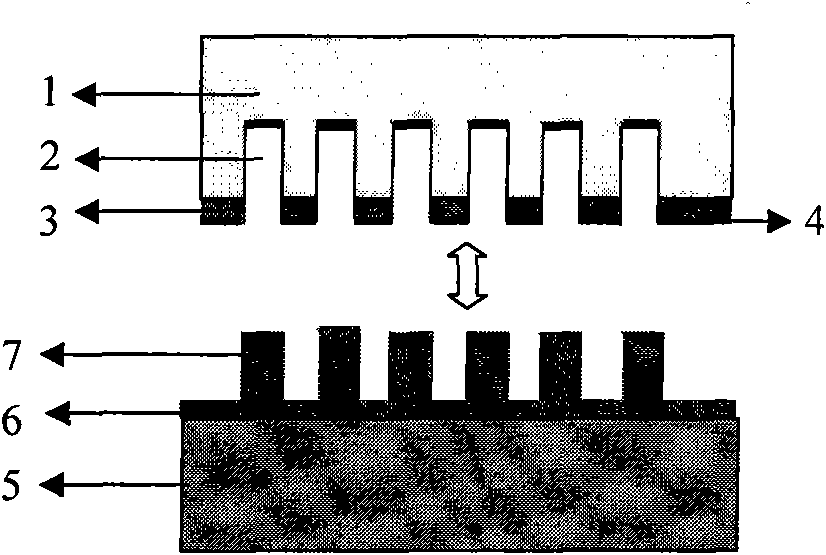
[0022] 4. Use the obtained template for the UV nanoimprinting process, and imprint on the silicon-based surface UV imprinting glue AMONIL04 layer to obtain a template pattern replica structure ( image 3 ).
[0023] 5. Soak the replica structure in acetone for 5s, remove the residual glue layer ( Figure 4 ).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com