Catalytic conversion method for preparing lower olefins and aromatics
A technology for low-carbon olefins and aromatic hydrocarbons, which is applied in the field of catalytic conversion and can solve the problems of underutilized potential content of low-carbon olefins, low yields of propylene and aromatic hydrocarbons, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0049] The preferred technical solution of this embodiment comprises the following steps:
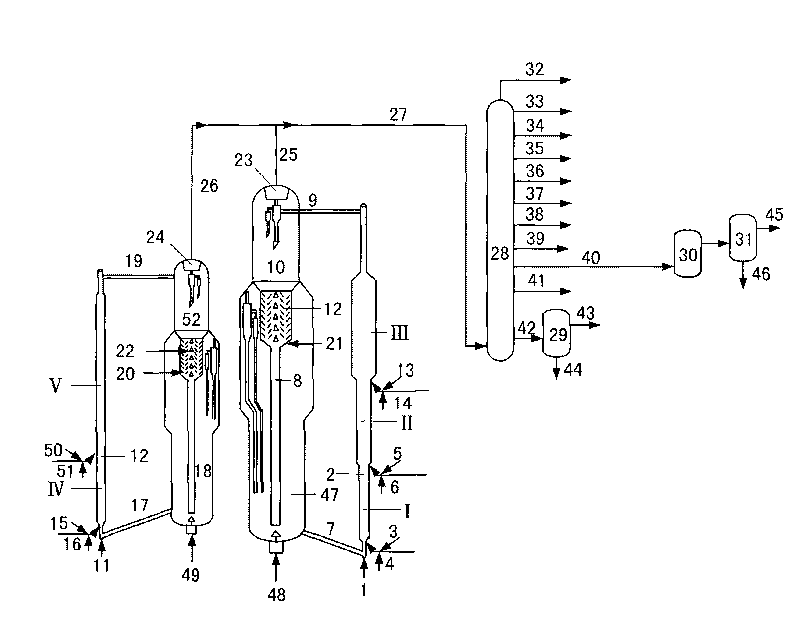
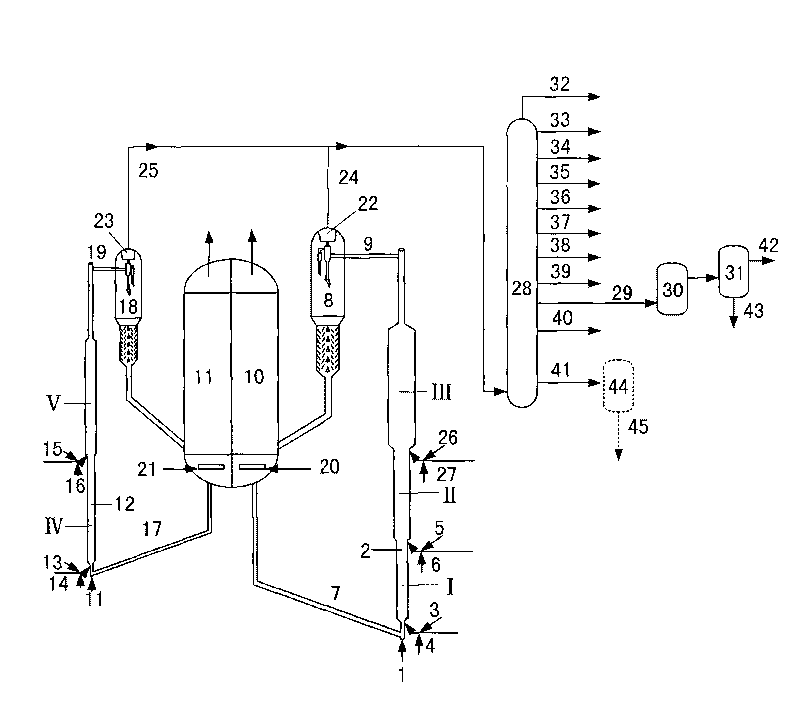
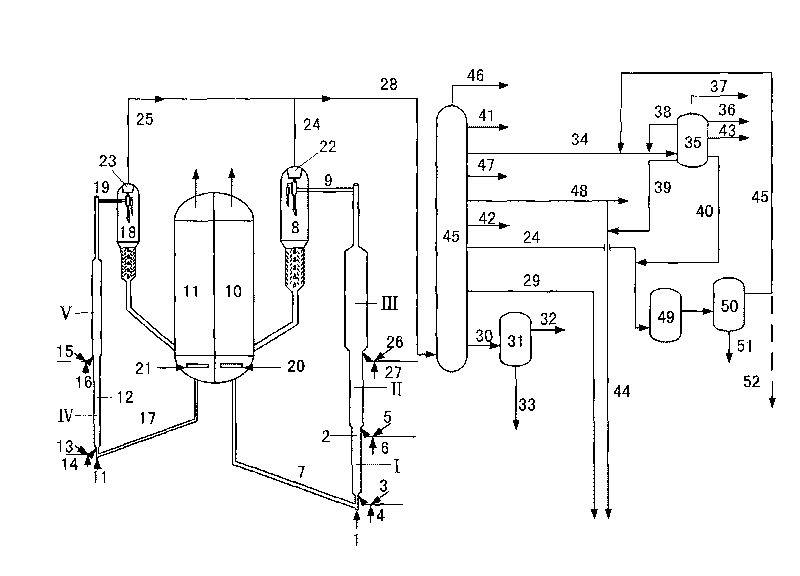
[0050] (1) The difficult-to-crack raw oil enters the bottom of the first riser reactor and contacts with the thermally regenerated catalytic cracking catalyst. -1 -800h -1 , the reaction pressure is 0.10MPa-1.0MPa (absolute pressure), the weight ratio of catalytic cracking catalyst and raw material is 30-150, and the weight ratio of water vapor and raw material is 0.05-1.0 to carry out the cracking reaction;
[0051] (2) The reaction effluent is not separated from the oil agent, and is mixed with the easily cracked raw material oil. -1 -100h -1 , the reaction pressure is 0.10MPa-1.0MPa (absolute pressure), the weight ratio of catalytic cracking catalyst to raw material is 2-30, and the weight ratio of water vapor to raw material is 0.05-1.0 to carry out the cracking reaction;
[0052] (3) The reaction effluent is mixed with one or more of optional difficult-to-crack raw material oil,...
Embodiment approach 2
[0058] The preferred technical solution of this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0059] (1) The difficult-to-crack raw oil enters the bottom of the first riser reactor and contacts with the thermally regenerated catalytic cracking catalyst. -1 -800h -1 , the reaction pressure is 0.10MPa-1.0MPa (absolute pressure), the weight ratio of catalytic cracking catalyst and raw material is 30-150, and the weight ratio of water vapor and raw material is 0.05-1.0 to carry out the cracking reaction;
[0060] (2) The reaction effluent is not separated from the oil agent, and is mixed with the easily cracked raw material oil. -1 -100h -1 , the reaction pressure is 0.10MPa-1.0MPa (absolute pressure), the weight ratio of catalytic cracking catalyst to raw material is 2-30, and the weight ratio of water vapor to raw material is 0.05-1.0 to carry out the cracking reaction;
[0061] (3) The reaction effluent is mixed with one or more of optional difficult-to-crack raw material oil,...
Embodiment approach 3
[0067] The preferred technical solution of this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0068] (1) The difficult-to-crack raw oil enters the bottom of the first riser reactor and contacts with the thermally regenerated catalytic cracking catalyst. -1 -800h -1 , the reaction pressure is 0.10MPa-1.0MPa (absolute pressure), the weight ratio of catalytic cracking catalyst and raw material is 30-150, and the weight ratio of water vapor and raw material is 0.05-1.0 to carry out the cracking reaction;
[0069] (2) The reaction effluent is not separated from the oil agent, and is mixed with the easily cracked raw material oil.-1 -100h -1 , the reaction pressure is 0.10MPa-1.0MPa (absolute pressure), the weight ratio of catalytic cracking catalyst to raw material is 2-30, and the weight ratio of water vapor to raw material is 0.05-1.0 to carry out the cracking reaction;
[0070] (3) The reaction effluent is mixed with one or more of optional difficult-to-crack raw material oil, e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Cell constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com