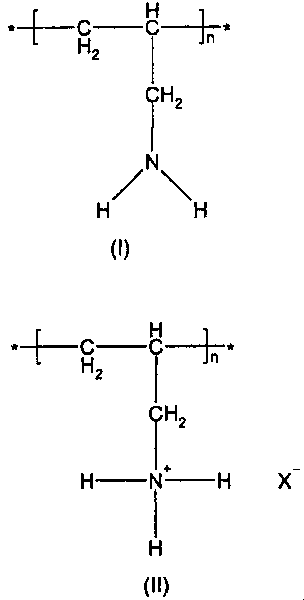
Novel one step process for preparing cross-linked poly(allylamine) polymers
A technology of cross-linking polymer and allylamine, which can be used in pharmaceutical combinations, medical preparations containing active ingredients, metabolic diseases, etc., and can solve the problems of poor efficiency and expensive purification of cross-linking agents.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0100] In another embodiment, the present invention provides a process for the preparation of a carbonate salt of a crosslinked poly(allylamine) polymer comprising:
[0101] a) dissolving sodium carbonate in water at a temperature of 30-40°C;
[0102] b) adding the hydrochloride salt of the cross-linked poly(allylamine) polymer dropwise to the solution;
[0103] c) stirring the mixture obtained in b);
[0104] d) recovering the solid by filtration and resuspending it in water;
[0105] e) Filtration, washing and drying of the carbonate salt of the cross-linked poly(allylamine) polymer.
[0106] Sodium carbonate is dissolved in water at a temperature of about 30-40°C. Preferably, the sodium carbonate / water ratio is about 50-85 wt / vol, preferably 62.5 wt / vol.
[0107] The hydrochloride salt of the cross-linked poly(allylamine) polymer was added dropwise to this solution. Preferably, the crosslinked poly(allylamine) polymer / sodium carbonate ratio is about 1.5-1.6 weight / weig...
Embodiment 1
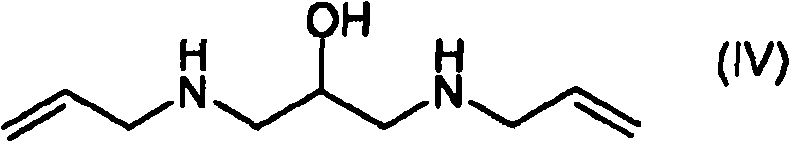
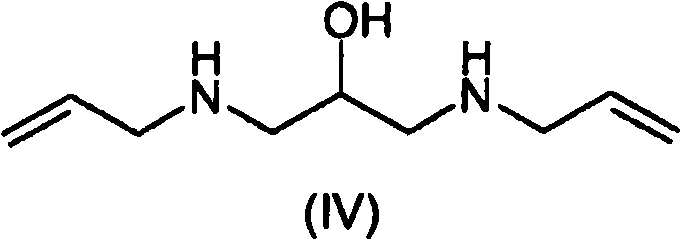
[0162] 1,3-Bis-allylamino-2-propanol (IV), preparation of dihydrochloride
[0163] Allylamine (321 g, 5.62 mol) and water (46 mL) were added to a 1 L four-necked flask equipped with a mechanical stirrer, temperature probe, dropping funnel, and condenser with a nitrogen inlet on top. The resulting mixture was heated to 57 °C and a solution of glycidyl tosylate (Va) (128 g, 0.561 mol) in THF (128 mL) was added dropwise while maintaining vigorous stirring. When the addition of (Va) was complete, the reaction was allowed to stand at 62°C for 45 minutes. The progress and / or completion of the reaction was monitored by TLC according to the disappearance of (Va) (eluent: n-hexane / ethyl acetate 7:3 v / v). The reaction mixture was concentrated to a residue under reduced pressure, isopropanol (700 mL) was added and the pH of the solution was adjusted to 1-1.5 by adding aqueous hydrochloric acid (37%, 148 mL). While stirring, the mixture was cooled to 5 °C, and the solid was filtered a...
Embodiment 2
[0169] Preparation of Sevelamer Hydrochloride (III)
[0170] Method A
[0171] To a 250 mL jacketed reaction vessel equipped with a mechanical stirrer, temperature probe, dropping funnel and condenser with a nitrogen inlet on top was added 37% hydrochloric acid (27.6 g, 0.280 mol) and the solution was cooled to 0 °C. Allylamine (16 g, 0.280 mol) was added dropwise with stirring while maintaining the temperature at 5-10°C. After the addition was complete, acetonitrile (52.2 mL) and 1,3-bis-allylamino-2-propanol dihydrochloride (IV) (8.3 g, 0.034 mol) were added. The solution was heated to 50°C and the azo-initiator VA-044 (1.15 g) was added. The reaction was allowed to stir at 50°C for 24 hours. Additional VA-044 (1.15 g) was added and heating and stirring continued for a further 18 hours. The solid was then filtered off, washed with methanol (150 mL) and dried under reduced pressure at 40°C to give a granular pale yellow solid (27 g) with a phosphate binding capacity o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com