Permanent magnet rotary motor and compressor using the same
A technology of rotating electrical machines and permanent magnets, applied in the field of permanent magnet rotating electrical machines, can solve the problems of ineffective mid-frequency band noise and incapable of sufficiently reducing the high-order harmonic components of the magnetic flux in the machine, so as to reduce the pulsating torque and improve the The effect of hearing sense of frequency band and reducing high-order harmonic components
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
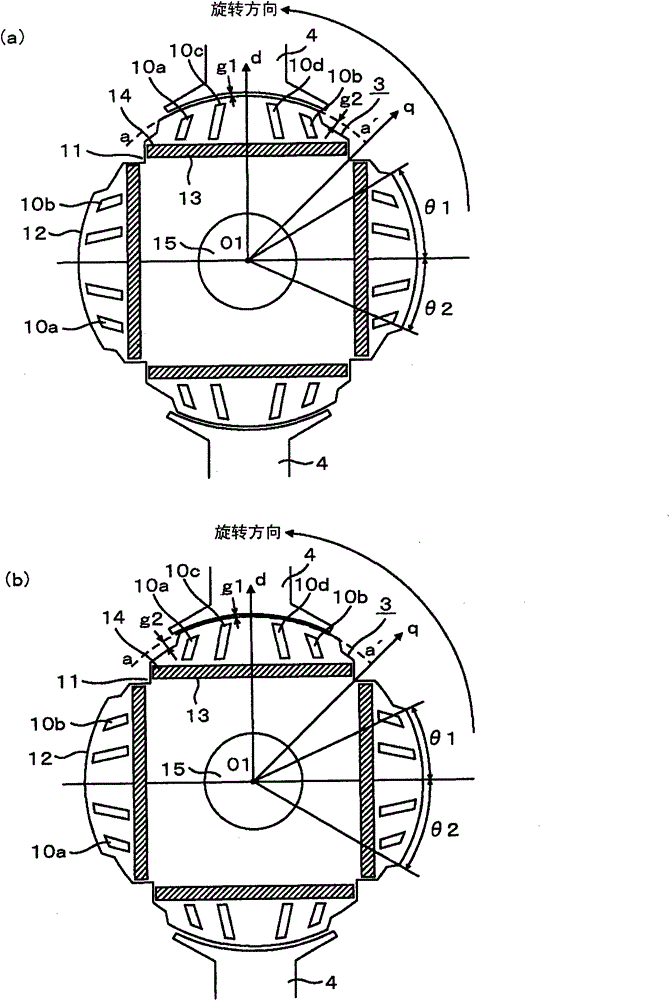
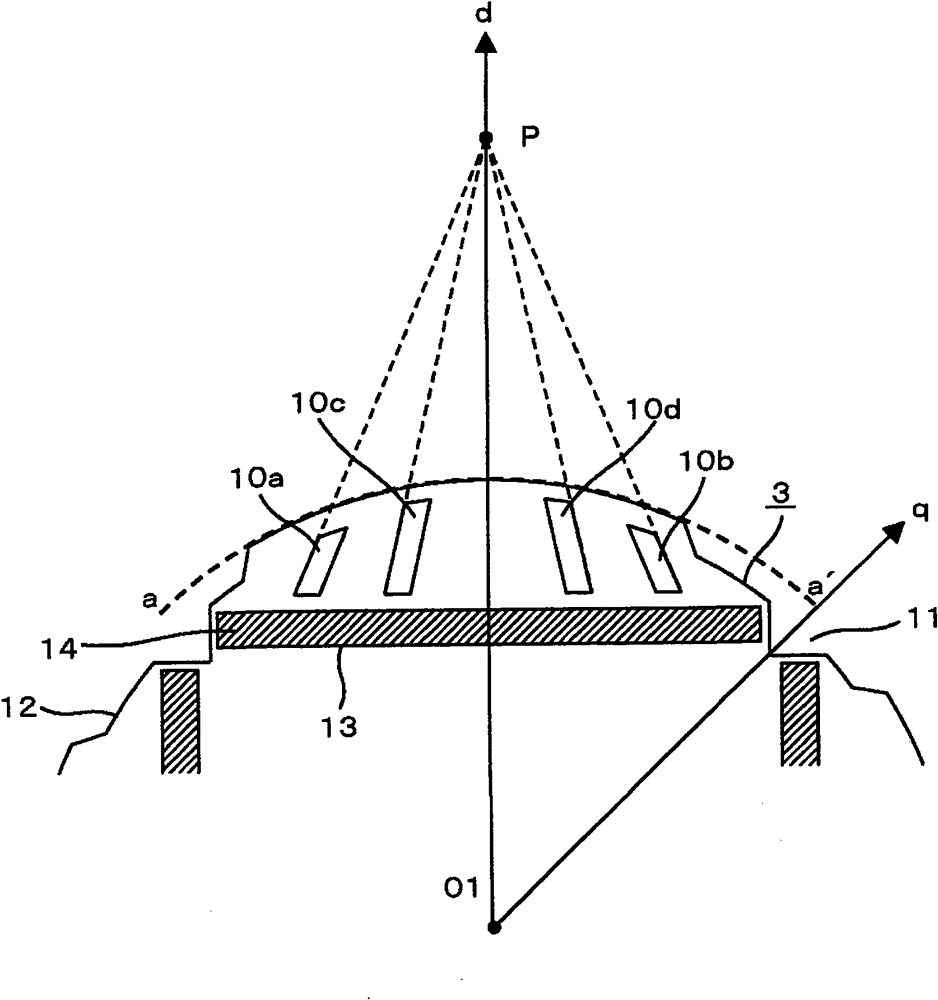
[0076] Figure 7 It is a cross-sectional view showing the shape of the stator core of Embodiment 1 of the permanent magnet type rotating electrical machine of the present invention. Figure 8 It is a figure which shows the shape of the stator core of Embodiment 1 of the permanent magnet type electric rotating machine of this invention. Figure 12 The cross-sectional structure of the compressor of the present invention is shown, and Table 1 shows the results of hearing tests on compressors with various rotating electrical machine structures.
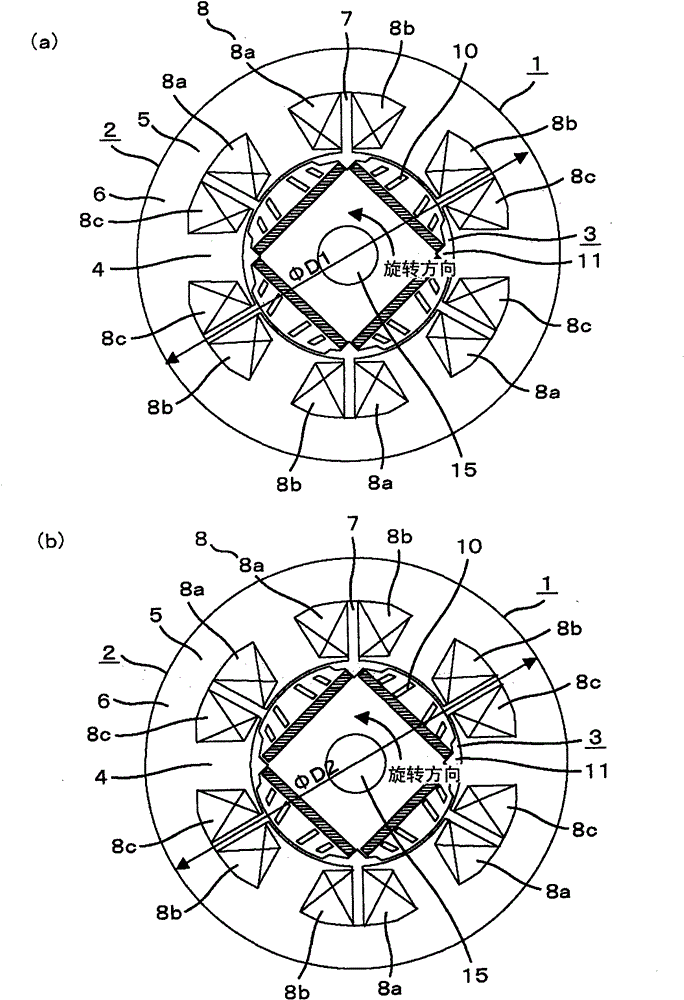
[0077] figure 1 It is a sectional view showing Embodiment 1 of the permanent magnet type rotating electric machine of the present invention.
[0078] exist figure 1 Among them, a permanent magnet rotating electrical machine 1 includes a stator 2 and a rotor 3 . The stator 2 includes a stator core 6 and a concentratedly wound armature winding 8 (composed of U-phase winding 8a, V-phase winding 8b, and W-phase winding 8c of the three-pha...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Next, other embodiments of the present invention will be described.
[0112] Figure 9 Showing the stator core shape of Embodiment 2 of the permanent magnet type rotating electric machine of the present invention, with respect to Figure 7 The same components are given the same symbols. In the figure, with Figure 7 The difference is that two protrusions 80 consisting of 80a and 80b are formed outside the outer circumference of the stator section B, and the outer peripheral surface of the protrusions 80 is the same diameter (ΦD1) as the outermost circumference of the stator section A. Thus, when the stator 2 is formed from the stator section A and the stator section B, since the diameters of the outermost peripheries are the same, stacking can be performed without misalignment using the stator core outer periphery as a reference position. Here, although two protrusions 80 are provided on the outer periphery of each groove 7, one may be provided, and an arbitrary numb...
Embodiment 3
[0114] Figure 10 It is a figure showing the shape of the rotor core of Embodiment 3 of the permanent magnet type rotating electrical machine of the present invention. Figure 4 The same components are given the same symbols. In the figure, with Figure 4 The different part is that the lamination thickness ratio of the rotor section A is configured so that 50%A figure 2 same effect.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com