Photovoltaic concentrators based on non-imaging optics
A non-imaging optics and concentrator technology, applied in the field of photovoltaic concentrators, which can solve the problems of low concentration multiple, large aspect ratio and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
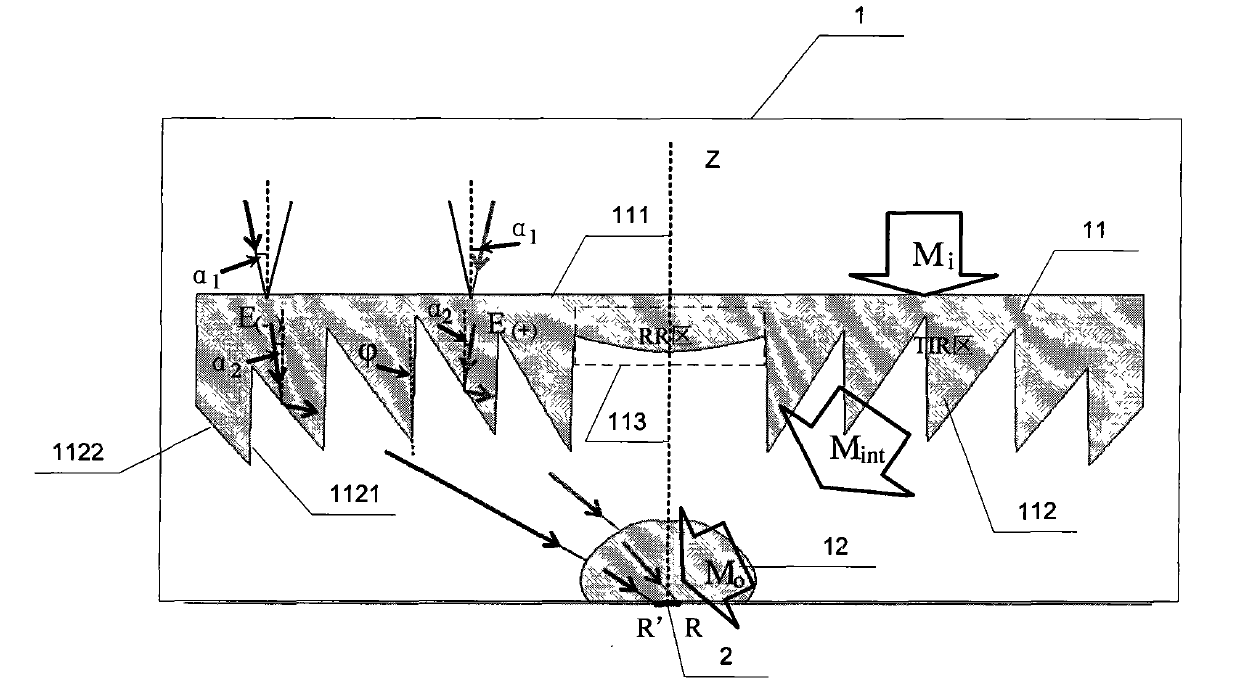
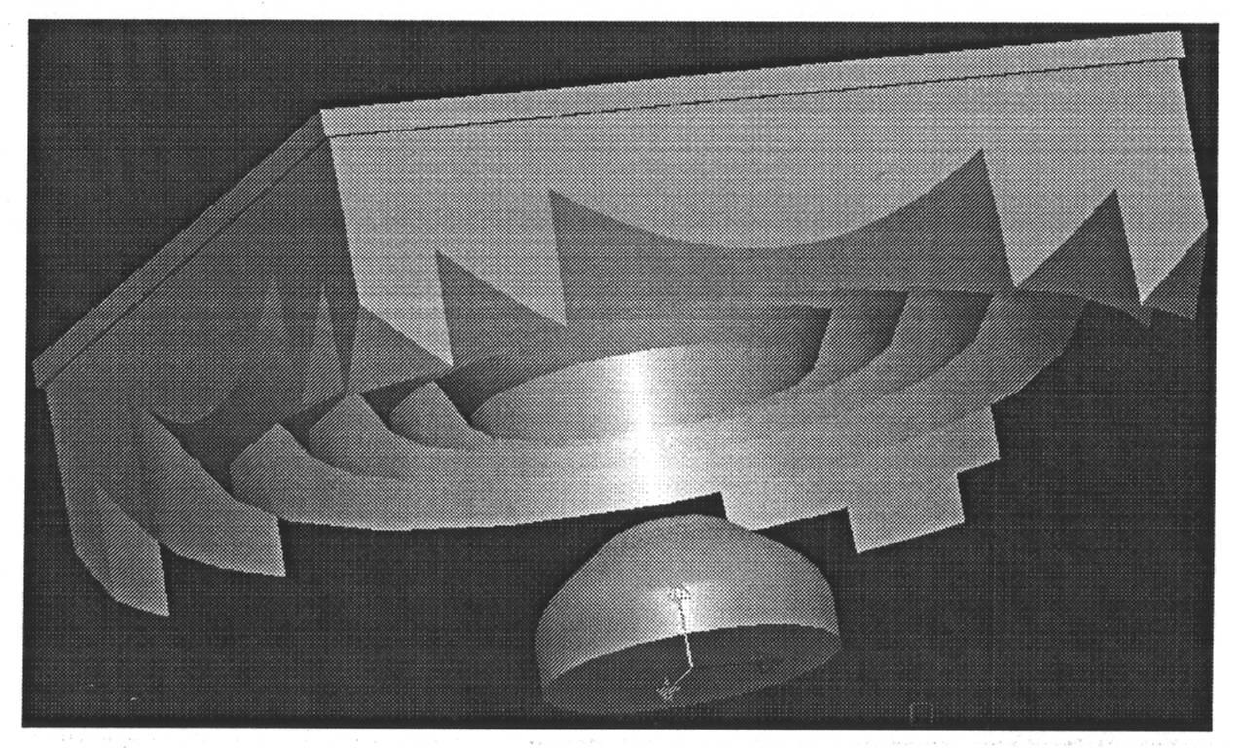
[0034] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 and figure 2Describe this embodiment, the photovoltaic concentrator based on non-imaging optics, it is made up of concentrator 1 and solar cell 2, and described concentrator 1 is made up of main lens 11 and secondary lens 12, and main lens 11 and secondary lens The lens 12 is an axisymmetric structure, the upper surface 111 of the main lens 11 is a plane, and the lower surface of the main lens 11 is divided into two parts, one part is the TIR region, and the other part is the RR region 113, and the RR region 113 is in the TIR region. In the center of the TIR zone, there are N Fresnel teeth 112 in the TIR zone, each Fresnel tooth 112 in the TIR zone is composed of a refraction surface 1121 and a total internal reflection surface 1122, and the refraction of the Fresnel teeth 112 in each TIR zone is The included angle between the surface 1121 and the axis of symmetry of the main lens 11 is The material refractive index...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0064] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further description of step 1 in specific embodiment 1: C described in step 1 g =A i / A o is obtained according to the following method: the upper surface 111 of the main lens 11 receives the light beam M i , the gathering angle of the incident ray is a 1 , the light beam M received by the surface of solar cell 2 o , the upper surface 111 receives the light beam M i The boundary ray dM i The angle between each point of the receiving surface and the normal line of the point is a 1 angle of light, the receiving beam M i The light beam refracted by the upper surface 111 is M int , a 2 Beam M int The maximum angle with the z axis, a 2 It is called the inner collecting light angle of the main lens 11, and its calculation formula is:
[0065] sin(a 1 )=n·sin(a 2 )
[0066] In the above formula, n is the material refractive index of the main lens 11 and the secondary lens 12 of the concentrator 1, and the light beam M r...
specific Embodiment approach 3
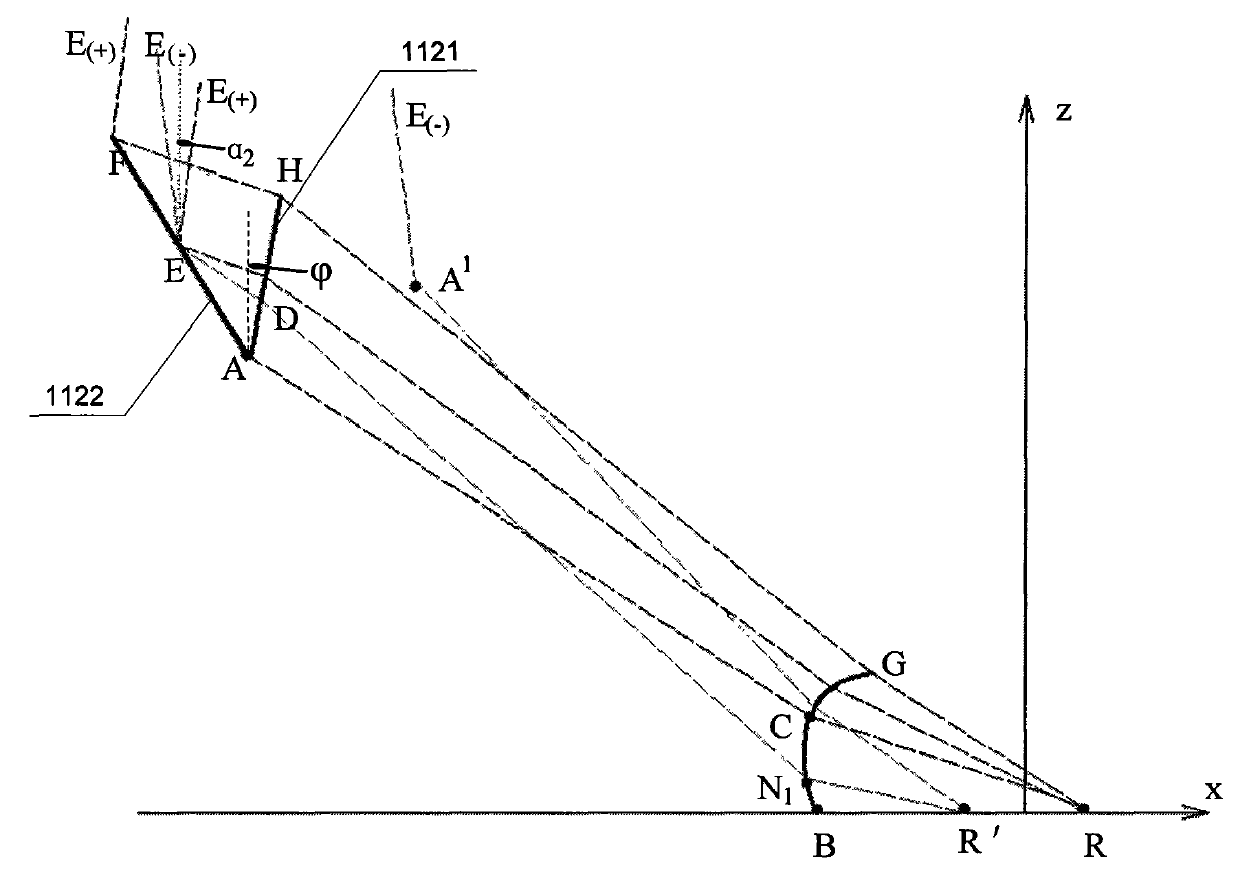
[0081] Specific embodiment three: this embodiment is a further description of step 4 in specific embodiment 1: the coordinates of point A in step 4 are (x A ,z A ), the coordinates of point B are (x B ,z B ), calculate a section of conic curve of the surface boundary of secondary lens 12 according to the coordinates of point A, point B and point R ', described quadratic curve is a Cartesian ellipse, and the curve equation is:
[0082] ( x - x A ) 2 + ( z - z A ) 2 + n · ( x - x ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com