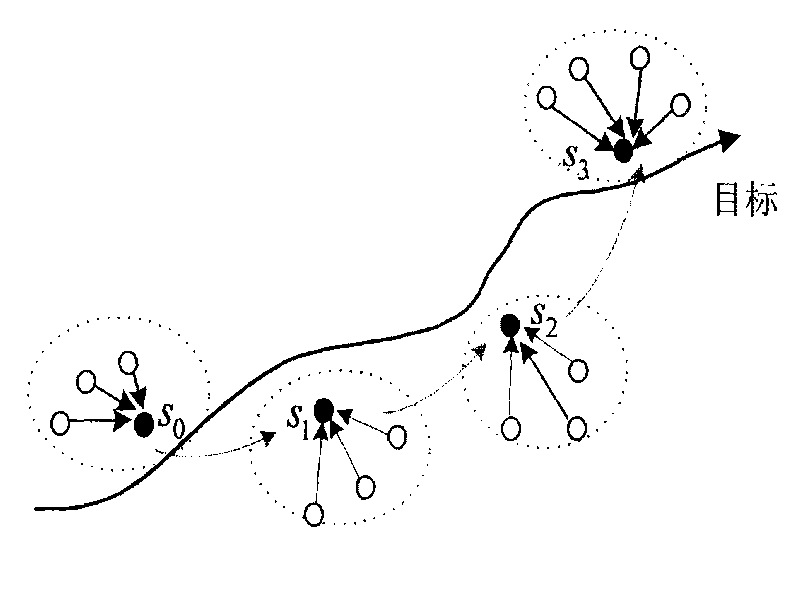
Target predicting and tracking method based on probability graph model
A probabilistic graph model and target tracking technology, which can be used in measuring devices, image analysis, image data processing, etc., can solve problems such as the difficulty of EKF algorithm
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
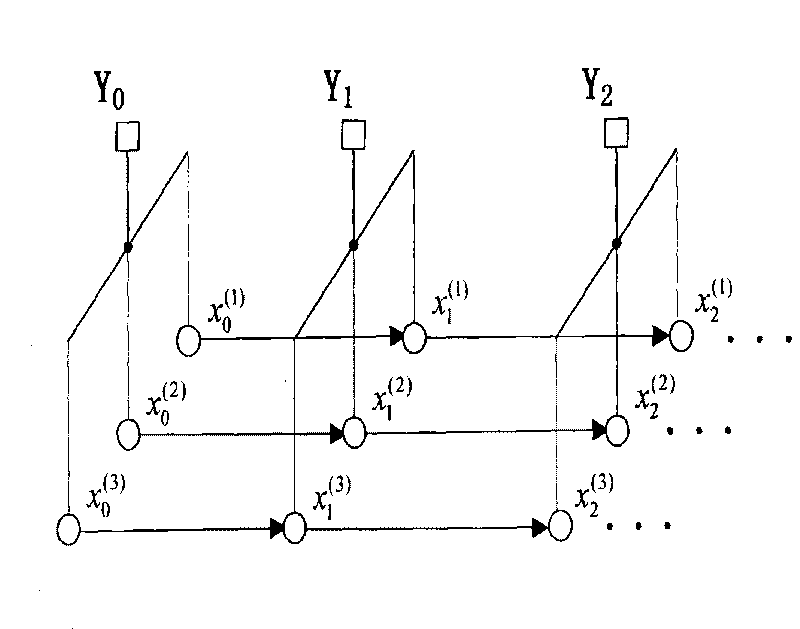
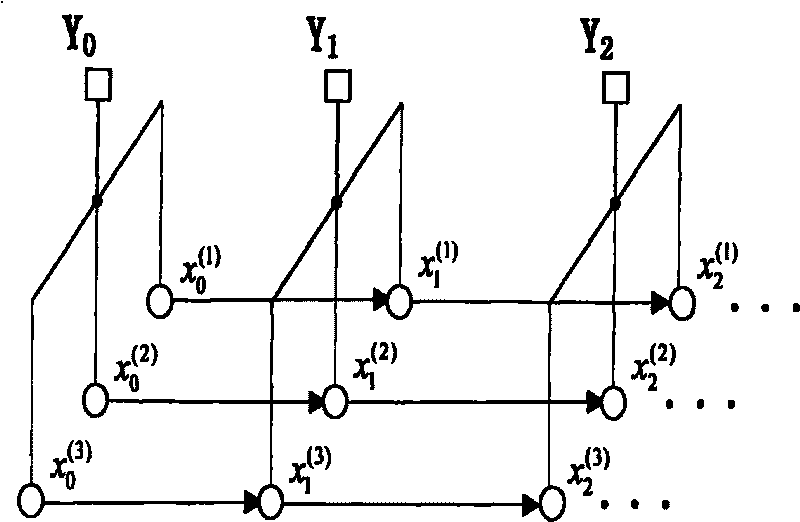
[0037] Probabilistic graphical models:
[0038] An undirected graph model is expressed as G=(V, E), where V represents a set of vertices (nodes), and E represents a set of edges (edges). Such as figure 1 As shown, each vertex s∈V represents a random variable x s , s∈V, the relationship between variables can be represented by the graph model structure. The variables represented by the undirected graph are considered to be discrete, and these variables x are Markov random variables related to the graph structure, and its distribution p(x) is expressed as:
[0039] p(x)=κ∏ s∈V Ψ s (x s )∏ (s,t)∈E Ψ st (x s , x t )
[0040] where κ is a normalization constant: Ψ s (x s ) is a vertex-compatible function that depends on the variable x s ; st (x s , x t ) is an edge compatible function, which depends on the variable x s and x t The connecting line (s, t). In general, the random variable x is an implicit variable to be sought and cannot be observed. Assume that the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com