A method for producing a hybrid seed using plant of novel cytoplasmic-genic male sterility raphanus sativus line and DNA markers for selecting the plant of said raphanus sativus line
A technology of DNA markers and radish, applied in botany equipment and methods, angiosperms/flowering plants, plant products, etc., can solve the problems of limited sample analysis and high cost of markers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0119] Example 1: Development of a new type of D-CGMS radish line and research on its characteristics
[0120] Breeding of new D-CGMS
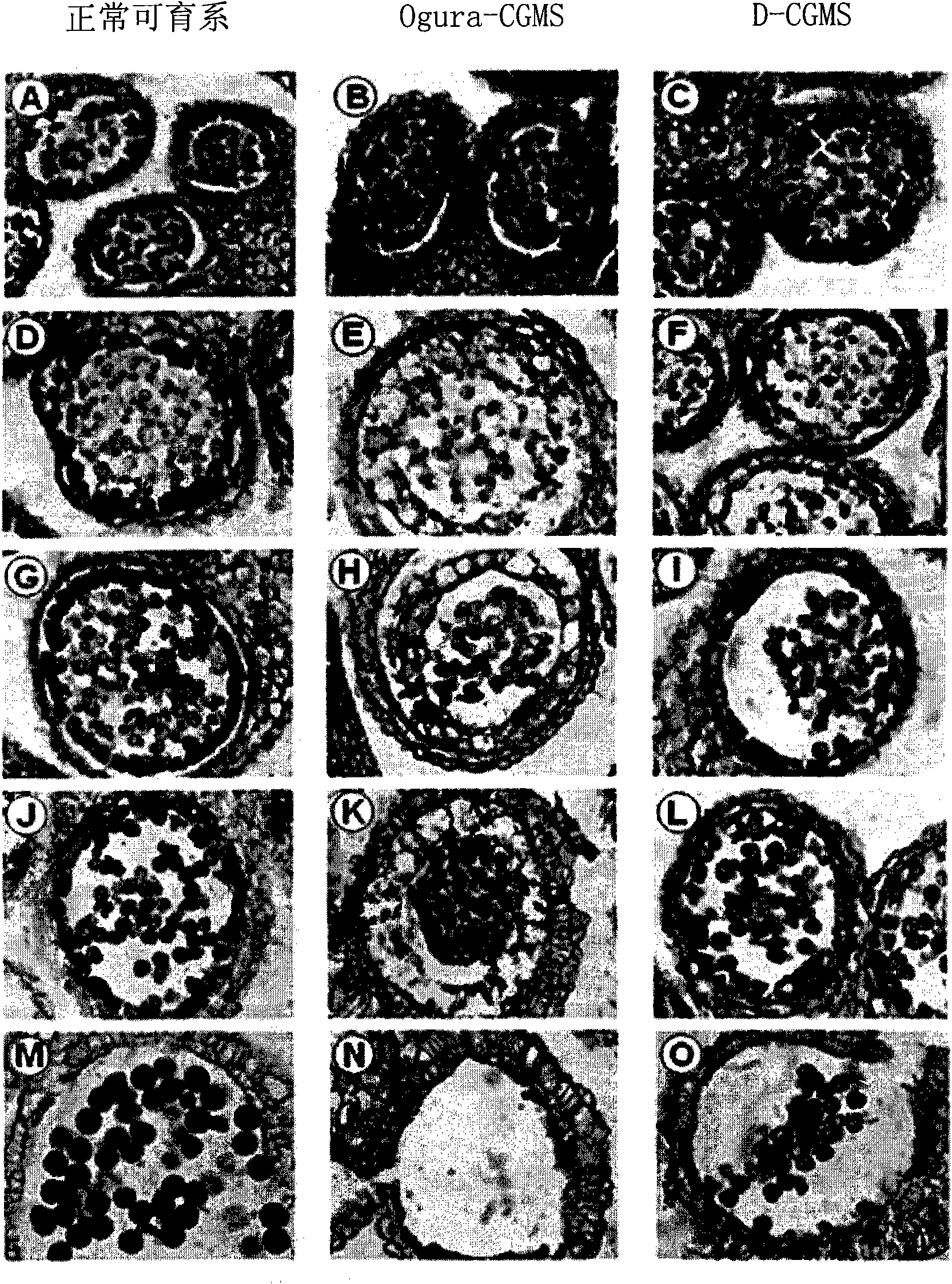
[0121] The inventor has collected novel male sterility resources in order to improve F 1 Production capacity of hybrid seeds. Then, the present inventors studied organ tissues and pollen development of flowers of 20 plants of the radish line collected from Uzbekistan and the like distributed at the National Institute of Horticulture in Korea.
[0122] As a result, a line exhibiting male sterility (nucleoplasmic sterility: CGMS) by inhibiting pollen development was selected and named "D-CGMS (radish variety D-CGMS)".
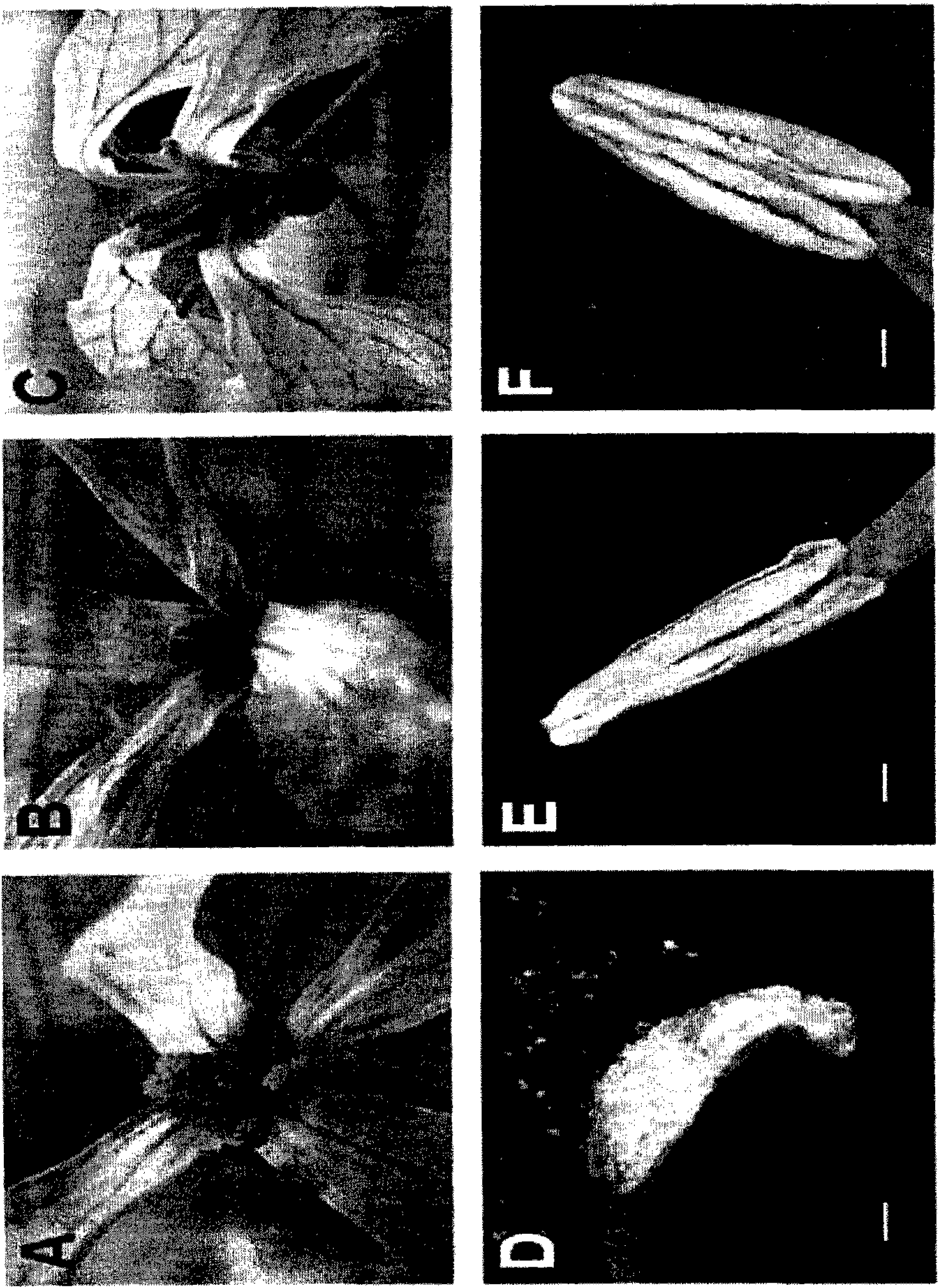
[0123] The flowers and stamens of selected D-CGMS, normal fertile lines and Ogura radish line (Ogura-CGMS) were observed under a dissecting microscope. Ogura-CGMS is generally used to produce hybrid seeds, so it was used here as a control.
[0124] As a result, pollen development was very weak in the novel male sterile line ...
Embodiment 2
[0136] Example 2: Induction of D-CGMS radish male sterility and production of F 1 Proof of Generation Hybrid Seed
[0137] The D-CGMS radish line plant selected from Example 1 is used as the female parent to cross the male fertile line plant to produce the CGMS radish line F with nucleoplasmic interaction sterile type 1 generation hybrid seeds. To compare the CGMS induction rate of the D-CGMS radish line with that of the Ogura-CGMS radish line, male fertile plants for crossing with the D-CGMS radish line were crossed with Ogura-CGMS as the female parent. Pollen development and viability were studied to confirm that the F 1 Whether male sterility is introduced in hybrid seeds. Male fertile line plants (male line) are selected from lines isolated from "JungSangYeoreum" (DB002), HannongYeoreum (DB003), lines isolated from "HannongYeoreum" (DB111), SamYang (DB021), DeaBuRyeongYeoreum (DB084), Lines isolated from "HaChu" (DB092), and plants of those male-fertile lines collected...
Embodiment 3
[0142] Example 3: Development of male fertility restoration gene resources of D-CGMS radish lines
[0143] In order to screen male fertile restorer lines selected from the D-CGMS radish line in Example 1, 10 male fertile lines collected from Uzbekistan and Russia were crossed with D-CGMS radish line plants as female parents. Those 10 male-fertile lines as male lines were collected from foreign countries (Uzbekistan and Russia), so the names of their variants are unknown, so only the names of their lines are given in this paper. To study in F 1 Pollen development and vigor were studied to determine whether male sterility was introduced in the first generation hybrid seeds.
[0144] As a result, among the 10 combinations with male-fertile lines, two hybrid combinations confirmed the emergence of male-fertile offspring. In the F produced by the hybridization of D-CGMS and DB112 1 Male sterile and male fertile progenies were segregated from hybrid seeds of the first generation,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com