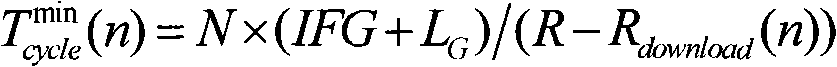Dynamic bandwidth allocation method for self-adapting service quality assurance in Ethernet passive optical network
A dynamic bandwidth allocation, passive optical network technology, applied in data exchange networks, digital transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as reducing bandwidth utilization, failing to achieve optimal system performance, and unfixed polling cycle length.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing.
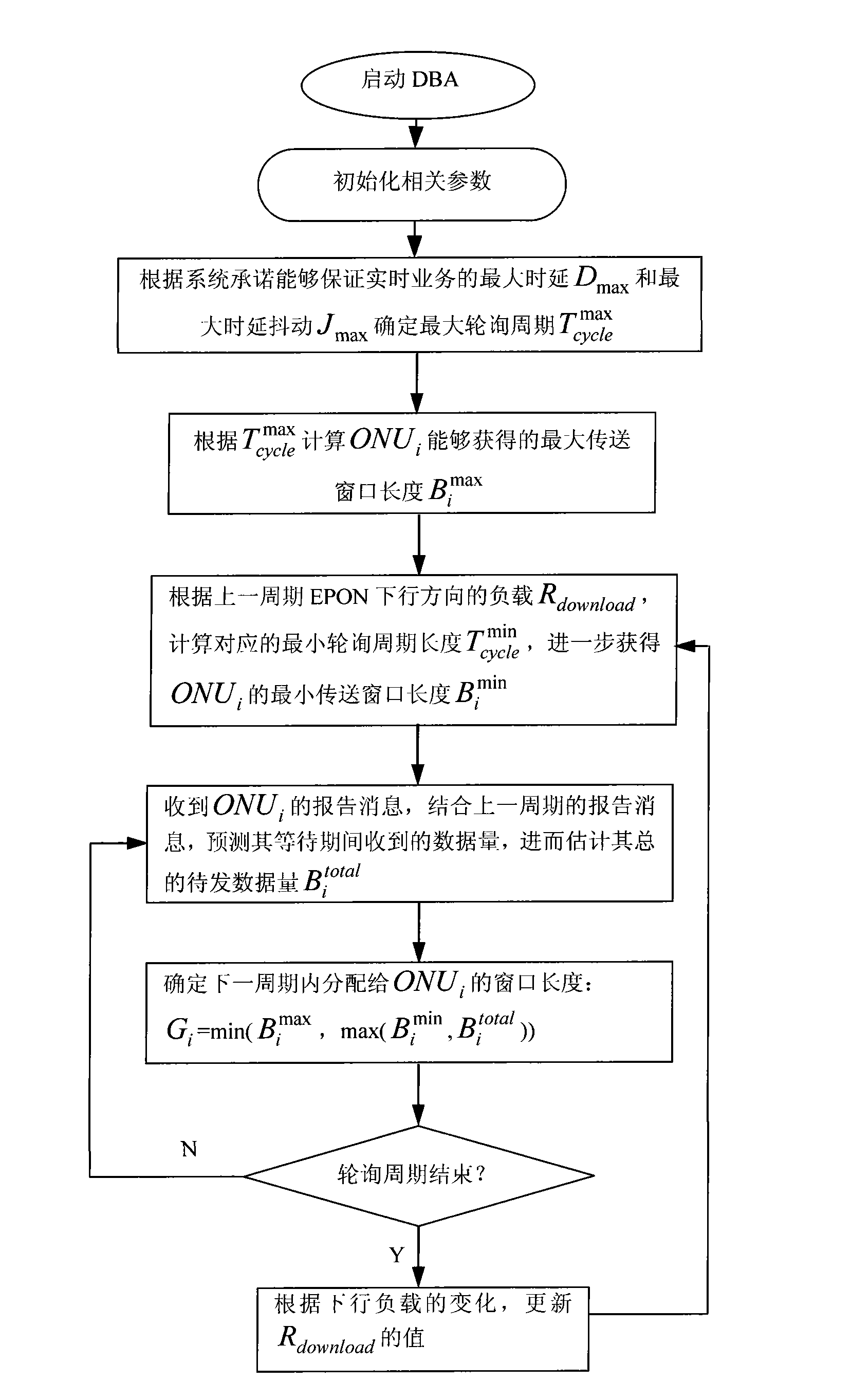
[0044] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention is a dynamic bandwidth allocation method for self-adaptive guarantee of quality of service in an Ethernet passive optical network, and its specific implementation method is:
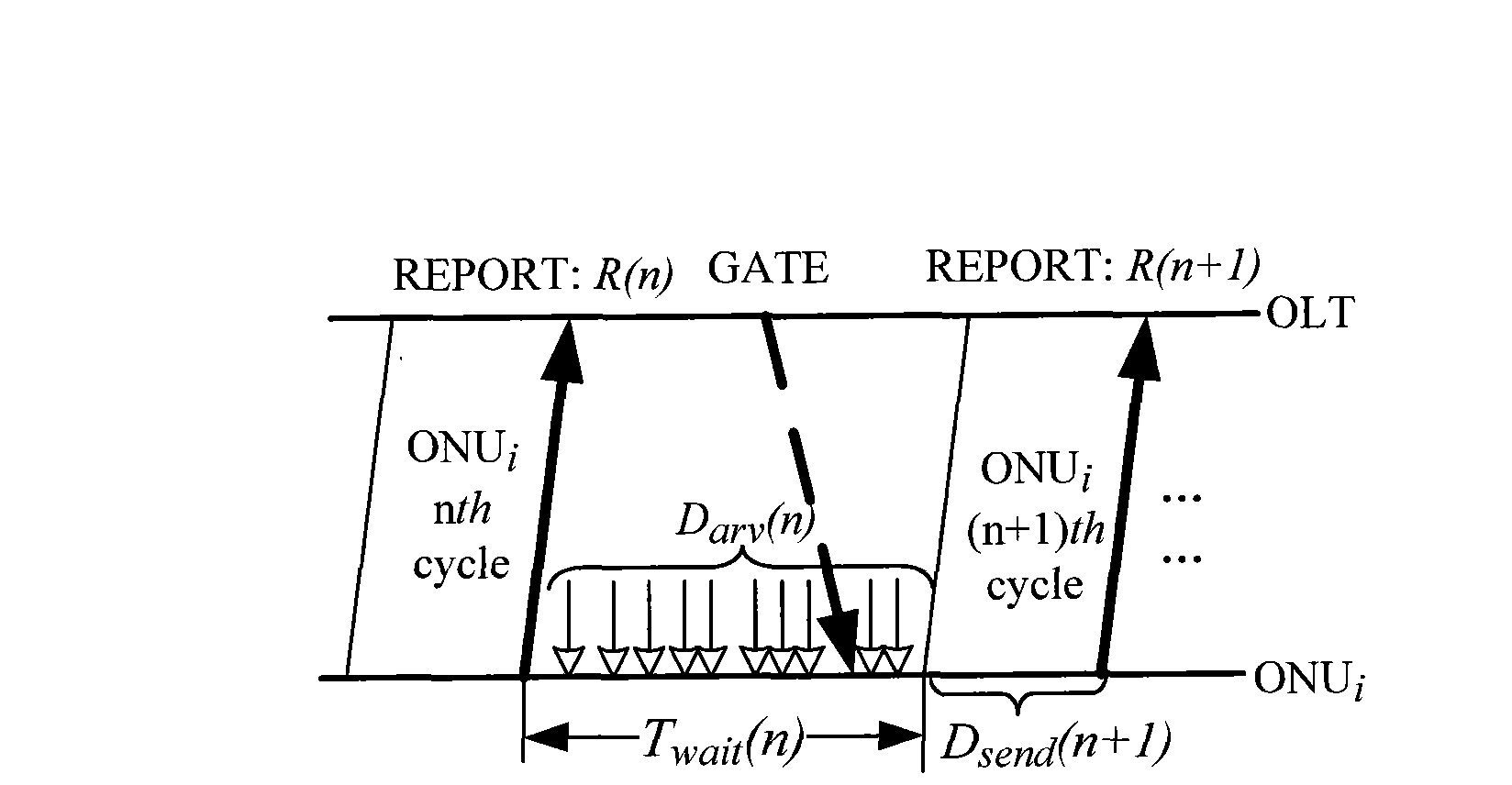
[0045] 1. After the optical line terminal (OLT) works normally, start the dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA) algorithm and initialize some parameters, such as: the maximum delay D of real-time services that the system promises to guarantee max and delay jitter J max And the weight factor w of each ONU i and other fixed parameters (these parameters can be configured through the human-computer interaction interface of the system), and the load R in the downlink direction of the previous cycle download (n), variable parameters such as the amount of reported data R(n) (it may be initialized to 0, because these parameters will continue to be automa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com