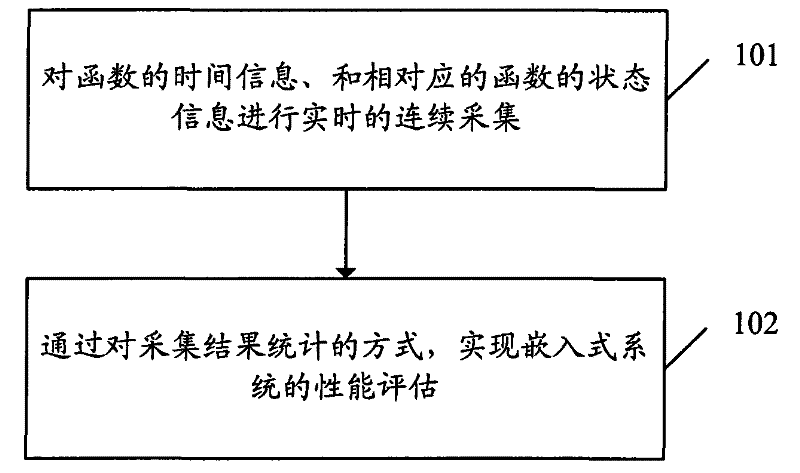
Method and system for estimating property of embedded type system
An embedded system and performance technology, applied in the evaluation method and system field of embedded system performance, can solve the problems that cannot be counted, embedded system performance evaluation, running time and running status cannot be accurately counted, and achieve accuracy high effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
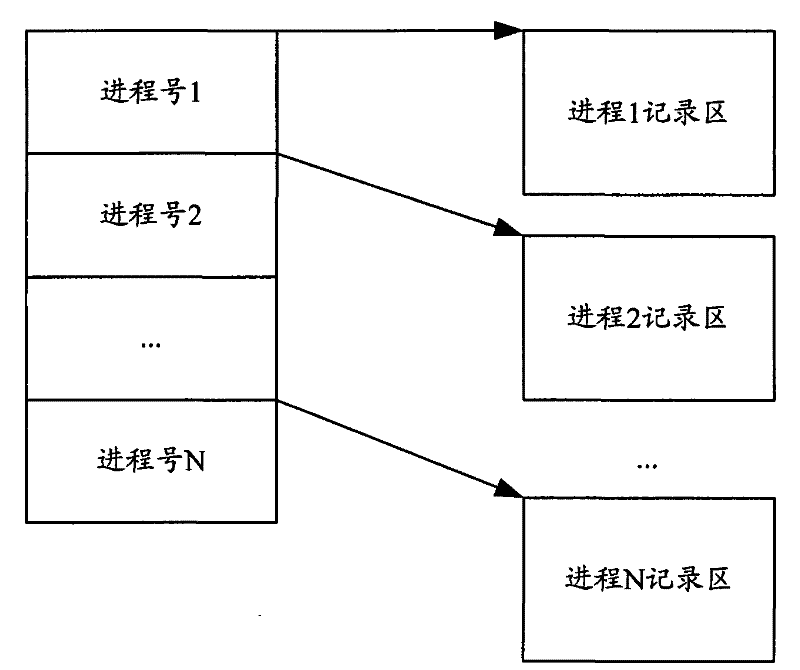
[0104] Example 1: The corresponding relationship between the process number and the index of the recording area.
[0105] Such as figure 2 Shown is a schematic diagram of the recording area corresponding to the process number in the present invention. After the system is powered on, the corresponding recording area is initialized for each process, and the corresponding relationship between the process number and the index of the recording area is established. When the stub function including the stub function and the stub function is called by the current process, the stub The function can index to the corresponding record area according to the process number of the current process.
example 2
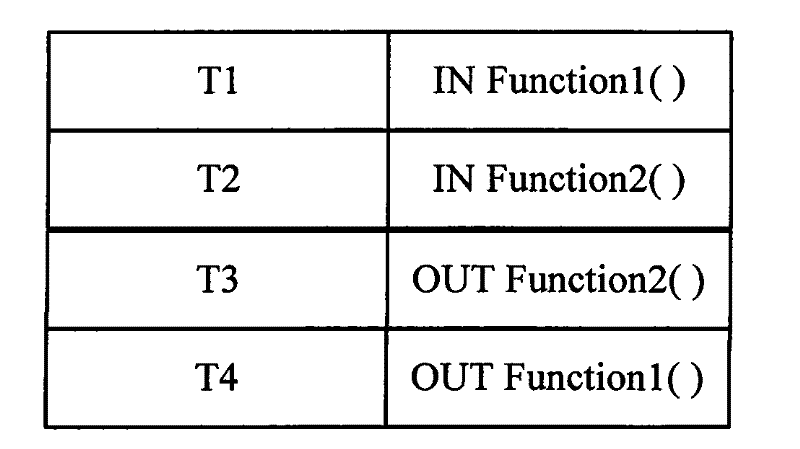
[0106] Example 2: Use the records in a record area to count the running time of each function in a process. At this time, only the pile-in function and the pile-out function are included.
[0107] Such as image 3 Shown is a schematic diagram of a timestamp record of a process calling a function. Since the call of the function Function1 is recorded at the time T1; the call of the function Function2 is recorded at the time T2; the call of the exit function Function2 is recorded at the time T3; the call of the exit function Function1 is recorded at the time T4. It can be known that the call relationship between functions is as follows:
[0108] void Function1()
[0109] {
[0110] Function2();
[0111]}
[0112] Therefore, it can be calculated that the running time of the function Function1 is T4-T1; the running time of the function Function2 is T3-T2.
example 3
[0113] Example 3: Use the records in a record area to count the running time of each function in a process. At this time, in addition to including the stub-in function and the stub-out function, a process switching hook function is also included.
[0114] Such as Figure 4 As shown, because in the process recording area, it is different from figure 2 It also records the time point T3 when the operating system schedules the current process to switch out of the running state, and the time point T4 when it switches back into the running state. Therefore, the running time of the function Function1 can be calculated as (T6-T1)-(T4-T3) ; The running time of Function2 is (T5-T2)-(T4-T3).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com