Detecting architectural vulnerability of processor resources
A processor and vulnerability technology, applied in error detection/correction, electrical digital data processing, instrumentation, etc., can solve problems such as power and performance consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
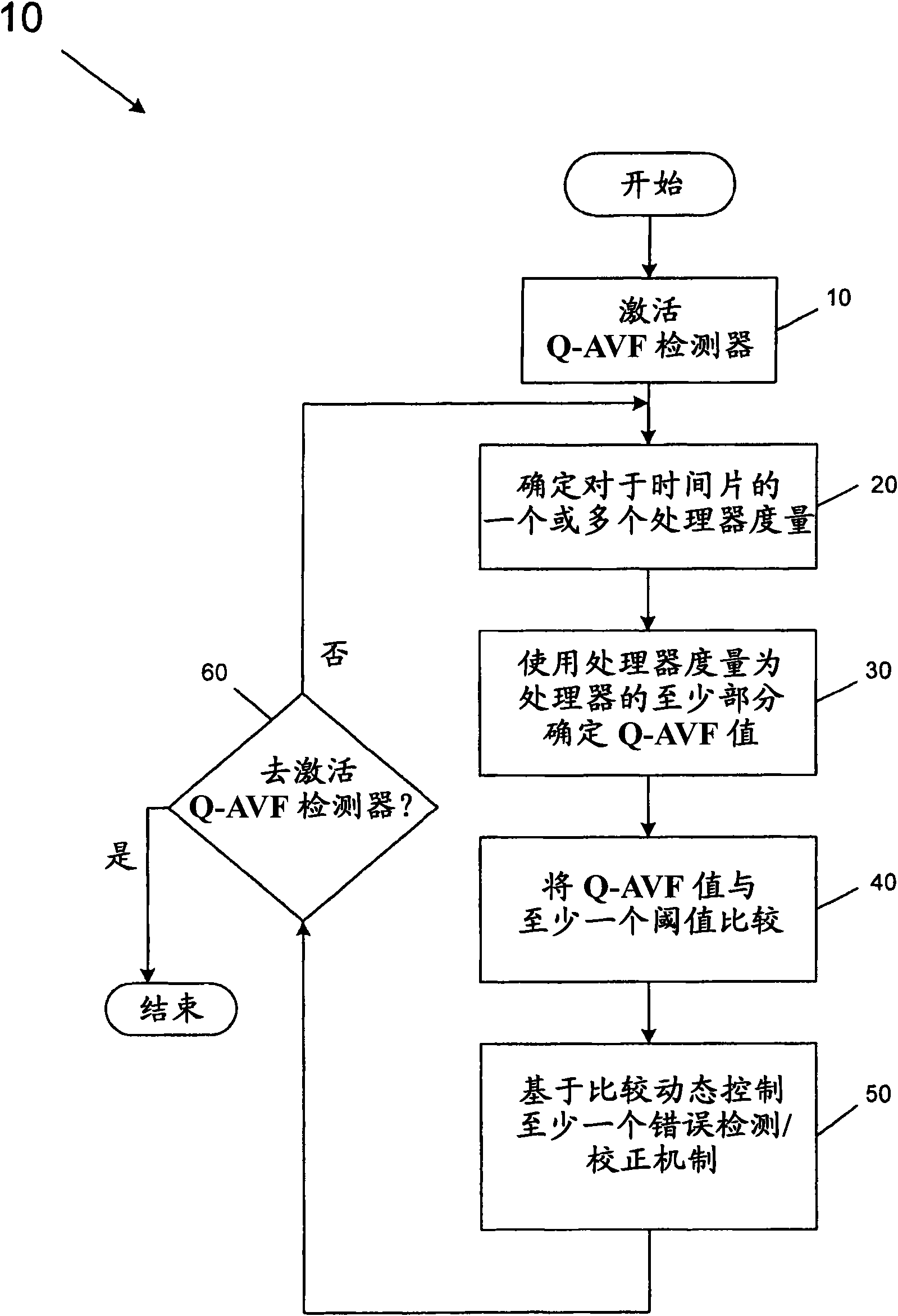
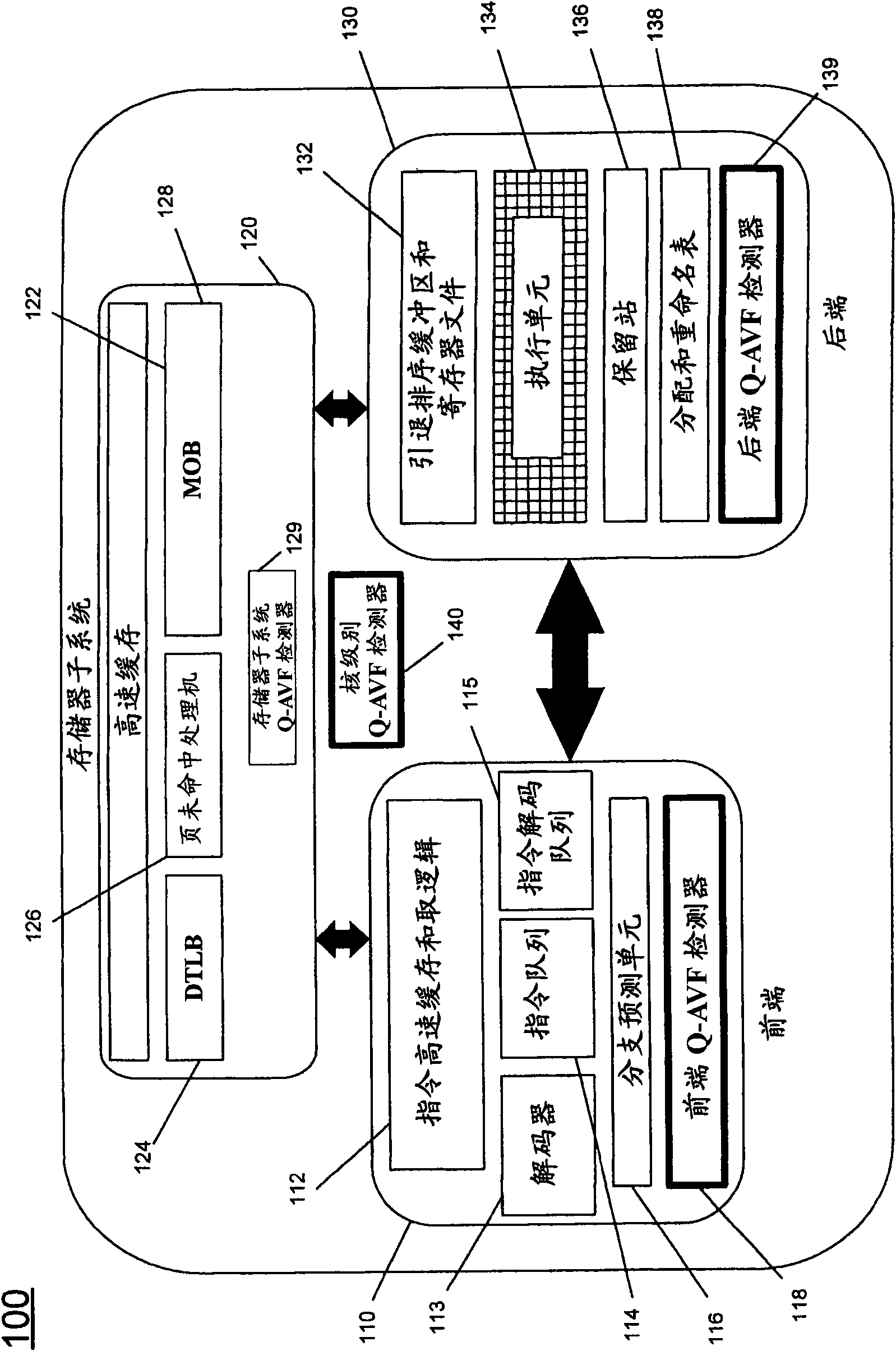
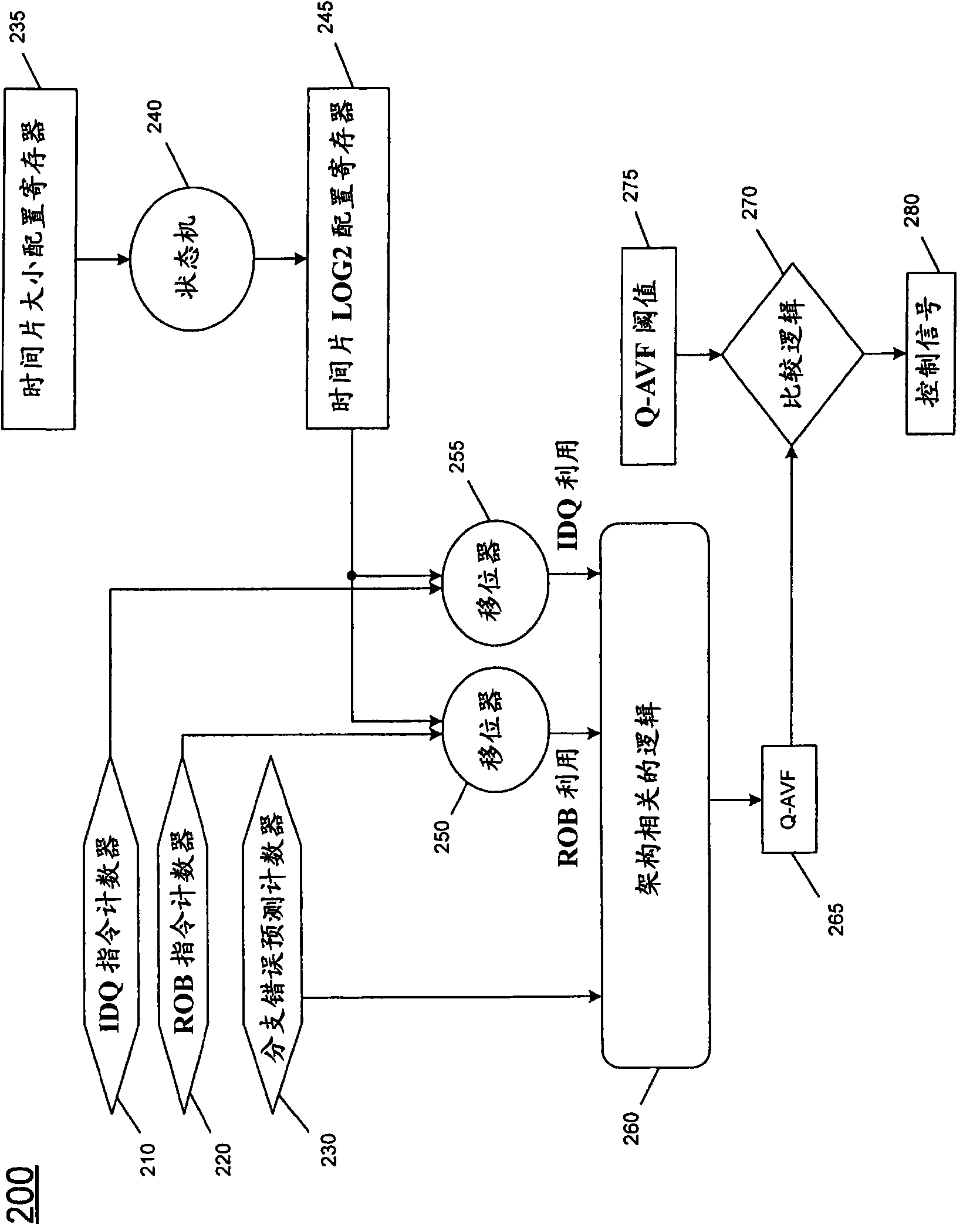
[0016] In various embodiments, quantized AVF (Q-AVF) can provide a real-time indication of architectural vulnerability during processor execution. This Q-AVF can be significantly different from the average AVF. Because Q-AVF is a real-time indicator of architectural vulnerability, embodiments can make full use of this information to control error mitigation hardware. That is, the embodiment can measure the quantified AVF metric and determine whether to use error mitigation hardware based on the measurement, and the degree of such use. For example, one or more thresholds can be set for acceptable vulnerability and mitigation hardware can be activated when Q-AVF exceeds a given threshold. In this way, faulty hardware can be dynamically controlled, thereby saving power and improving performance when the vulnerability is low, and only when the fault vulnerability is actually high will cause these penalties in exchange for increased reliability.
[0017] Some examples of such savings c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com