Method for rapid degradation of triphenylmethane dye waste water
A technology for triphenylmethane and dye wastewater, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, textile industry wastewater treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve the problems of high energy demand and complex reaction equipment requirements, and achieves strong applicability and operating costs. Low, inexpensive effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
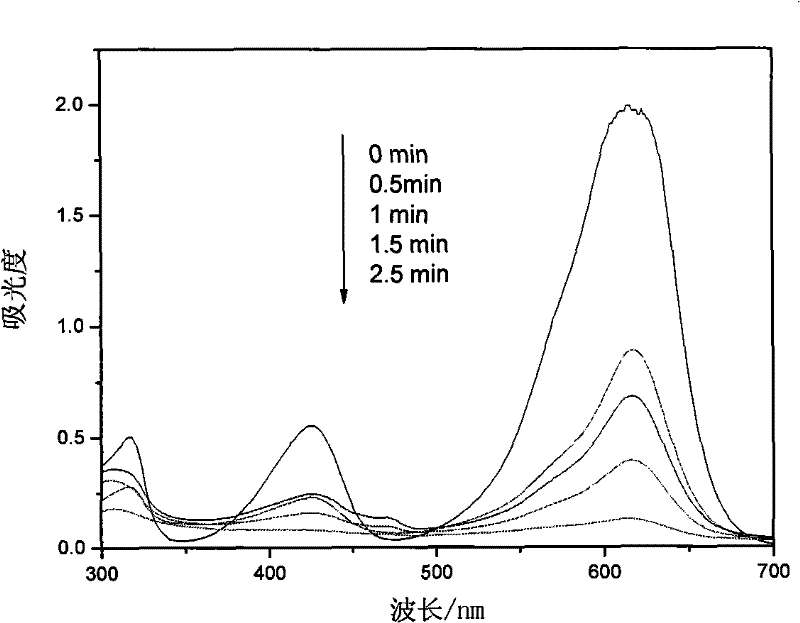
[0027] Prepare 20mg / L rhodamine B aqueous solution to simulate dye wastewater, and measure 100mL dye solution into the reaction bottle. A stirring bar was placed in the bottle, and the solution was stirred under the action of the stirrer. Weigh 200mg NaBiO 3 and 50mg AgNO 3 Add the above solution and start the reaction under the action of stirring. Subsequently, the variation of rhodamine B concentration with the reaction time was measured, and the experimental results showed that within 14 minutes, the concentration of rhodamine B decreased by 99%, and after 15 minutes, TOC decreased by 54%. For details, see figure 1 .
Embodiment 2
[0029] Prepare a 20mg / L malachite green aqueous solution to simulate dye wastewater, and measure 50mL of the dye solution into a reaction bottle. A stirring bar was placed in the bottle, and the solution was stirred under the action of the stirrer. Weigh 100mg NaBiO 3 and 200mg AgNO 3 Add the above reaction solution. When the reaction starts, the concentration of malachite green changes with the reaction time. The experimental results show that the decolorization rate of malachite green exceeds 95% within 8 minutes, and the TOC drops by 21% after 15 minutes. For details, see figure 2 .
Embodiment 3
[0031] Prepare 40 mg / L methyl violet aqueous solution to simulate dye wastewater, and measure 100 mL of dye solution into a reaction bottle. A stirring bar was placed in the bottle, and the solution was stirred under the action of the stirrer. Weigh 300mg NaBiO 3 and 100mg AgNO 3 Add the above solution and start the reaction under the action of stirring. Subsequently, the change of the concentration of methyl violet with the reaction time was measured. The experimental results showed that the concentration of methyl violet decreased by 92% within 4 minutes, and the TOC decreased by 75% after 15 minutes. For details, see image 3 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com