Structured OLED with micro optics for generating directed light
A lighting equipment and optical collimation technology, which is applied in the directions of optics, nonlinear optics, electroluminescent light source, etc., can solve the problems of expensive and complicated manufacturing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
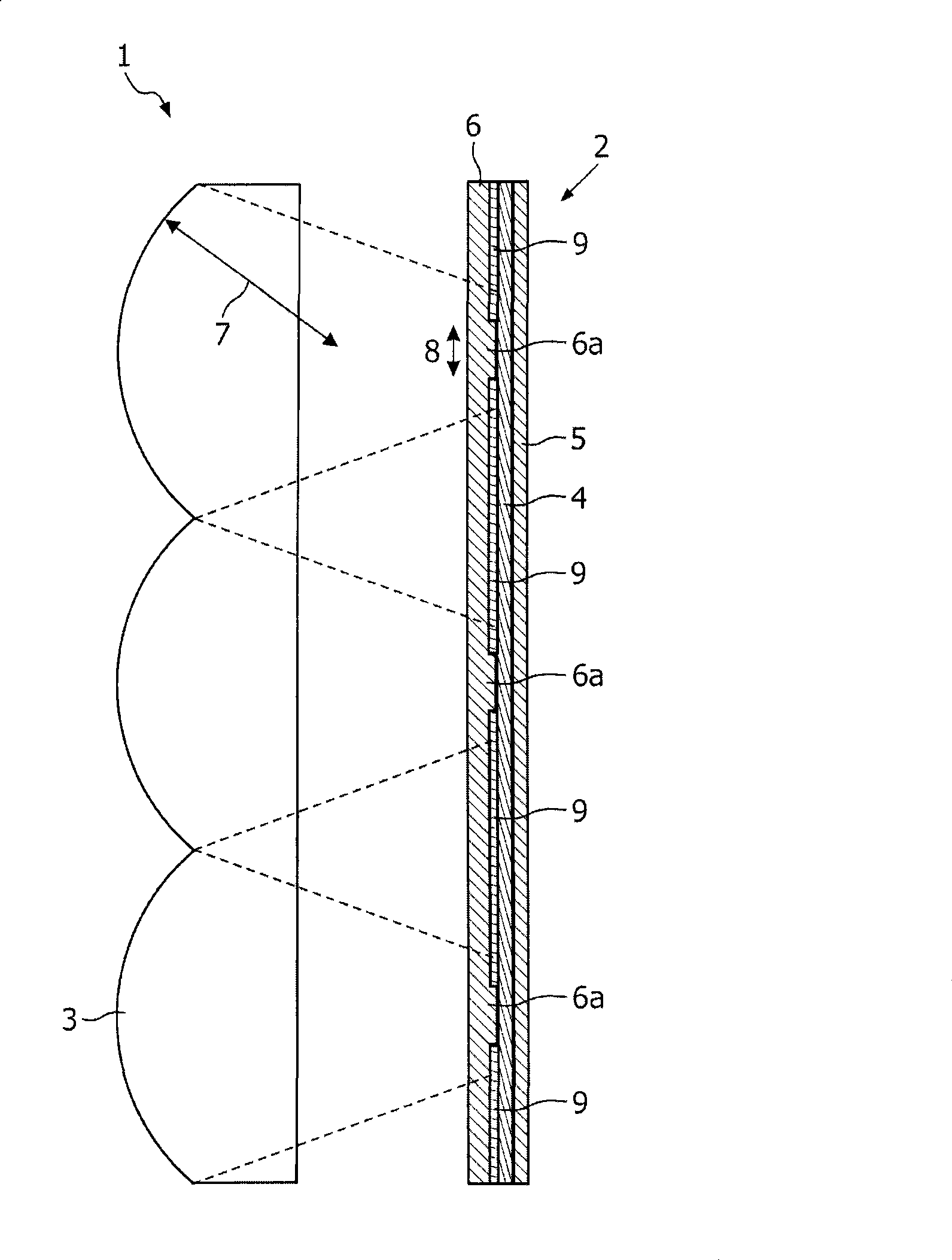
[0030] refer to figure 1 , the lighting device 1 is formed by a stacked OLED 2 and a collimating lens array 3 . The lens array 3 is made of PMMA (polymethylmethacrylate), which is transparent in the visible wavelength range. Each single lens of the lens array 3 exhibits an acceptance angle such as figure 1 Indicated by the dotted line.
[0031] Separated from the lens array 3, the OLED stack 2 is arranged within a prescribed proximity. The OLED stack 2 comprises at least an OLED layer 4 and a first continuous electrode layer 5 arranged on the back side of the OLED layer 4 . A second electrode layer 6 is provided on the front side of the OLED layer 4 .
[0032] The second electrode layer 6 is continuous but is in contact with the OLED layer 4 only in sections 6 a which are within the acceptance angle of the lenses of the lens array 3 . Between these sections there is an insulating layer 9 . For this reason, the generation of light in the OLED layer 4 is only stimulated wi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com