Method for detecting areca-nut yellow leaf disease phytoplasma pathogen and special reagent kit therefor
A phytoplasma and yellowing disease technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of eliminating false positive contamination, simplifying the detection process, and eliminating the spread of seedlings
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
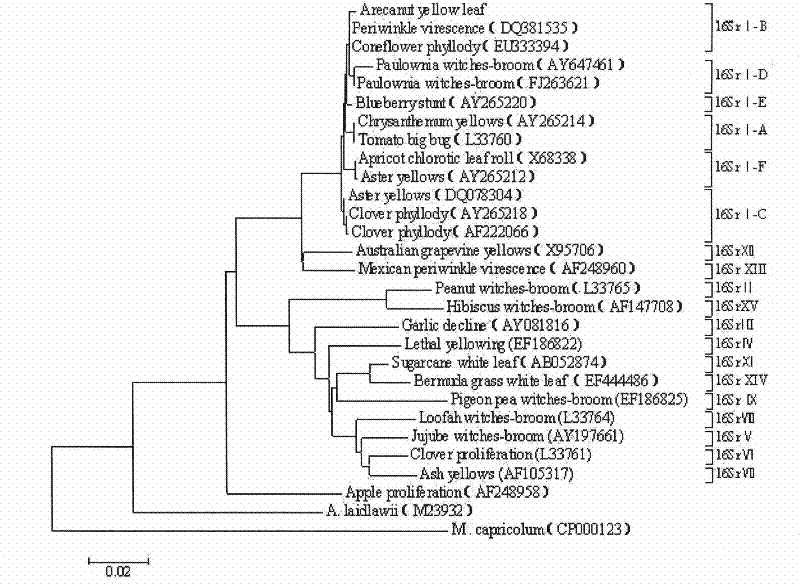
[0026] Example 1. Acquisition of the 16SrDNA sequence of the phytoplasma of betel nut yellowing disease and determination of its taxonomic status
[0027] 1. Extraction of total DNA from betel nut flower buds
[0028] Collect samples of betel nut yellowing plants showing typical yellowing symptoms. The yellowing disease of betel nut is based on Luo Quanquan et al. , 2001, 22 (2): 43-46.) said method identification, wherein, collected from Hainan Tunchang (3 strains): Dc1, Dc2, Dc5; Ding'an (3 strains): Da2,, Da3, Da5; Qiong Hai (3 strains): Qh21, Qh22, Qh23; Wanning (3 strains): Wn1, Wn2, Wn3; Sanya (3 strains): Sy15, Sy21, Sy22; healthy samples were collected from Danzhou, Hainan. Referring to Lee et al. (Lee I M, Davis R E, Hiruki C. Genetic interrelatedness among cloverproliferation mycoplasmalike organisms (MLOs) and other MLOs investigated by nucleic acid hybridization and restriction fragment length polymorph
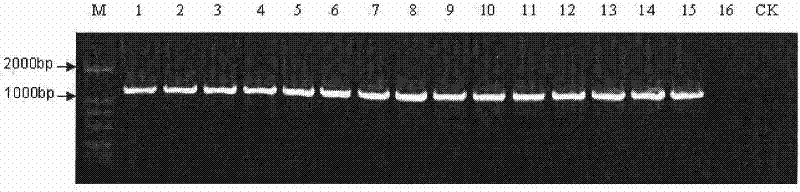
[0029] 2. PCR amplification and electrophoresis detection ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Embodiment 2, the present invention detects the preparation of the probe of betel nut yellowing disease phytoplasma pathogen, kit and their effect verification
[0043] 1. The present invention detects the design of the probe and primer and the preparation of the kit for detecting the phytoplasma pathogen of betel nut yellowing disease
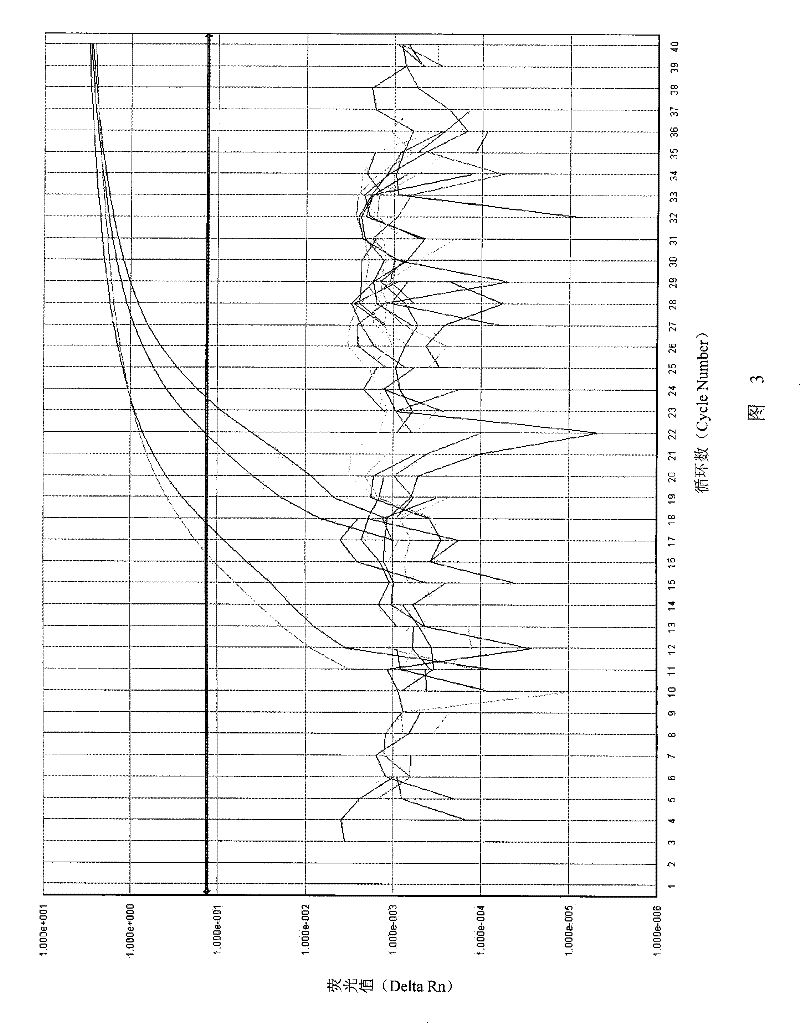
[0044] In this study, phytoplasma 16SrDNA was used as the target gene to design primers and probes, and the 16SrDNA sequences of all known phytoplasmas were downloaded from NCBI, and compared with ClustalX1. The region with a stable mutation in the sequence, and then use Primer Express Real-time fluorescent PCR primers / TaqMan MGB probes were designed with version3.0 software, and the forward and reverse primers were compared using the Blast program in NCBI (http: / / blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / Blast). No species other than the 16Sr I group could pair with this pair of primers and cause amplification was found. The sequence looks like this: ...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3, the test kit for detecting the phytoplasma pathogen of betel nut yellowing disease of the present invention is verified for the detection accuracy effect of sampling from different parts of betel nut
[0090] Cutting 30 plants infected with betel nut yellowing disease on the east and south lines of Hainan Island, according to Luo Quanquan et al. Acta Crops Sinica, 2001, 22 (2): 43-46.) said method identification, get flower bud, heart leaf, blade respectively (get the vein of the 2nd, 3rd, 5th leaf successively from the bottom leaf of lower betel nut plant) ), root as the detection site, respectively extracting total DNA as a template sample, all using the kit prepared in step 1 of embodiment 2, and detecting according to the real-time fluorescent PCR detection method described in step 3 of embodiment 2.
[0091] The test results are as follows:
[0092] (1) Test results of flower bud samples
[0093] The total DNA extracted from the unexpanded betel nut bu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com