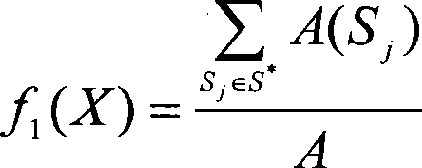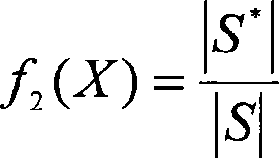Wireless sensor network node coverage optimization method based on genetic algorithm
A wireless sensor and genetic algorithm technology, applied in the field of wireless sensor network node coverage optimization based on genetic algorithm, can solve problems such as complex algorithm process, limited algorithm and protocol promotion and use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
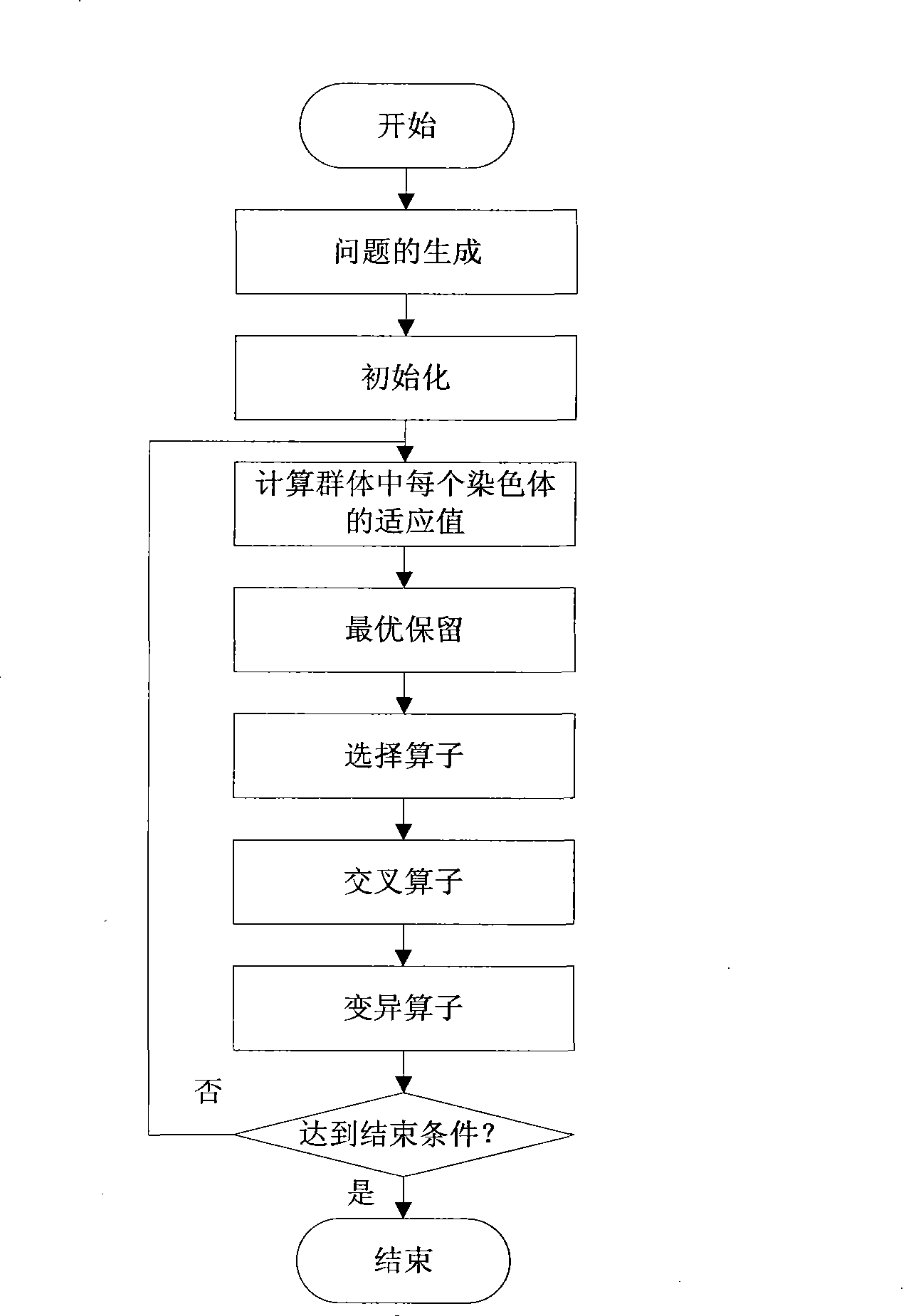
[0024] The method of the invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0025] The model of the wireless sensor network coverage problem is usually established as follows: Assume that N sensor nodes with the same parameter configuration are placed in the monitoring area A. Sensor node set C={c 1 , c 2 ,...,c N}, where c i ={x i ,y i , R}, (x i ,y i ) is the node distribution coordinates, R is the monitoring radius. A is a two-dimensional plane, which is often discretized into m×n grid points, and then the grid point (x, y) is calculated by the following formula, 1≤x≤m, 1≤y≤n, whether the node c i Coverage (where 1 means covered and 0 means not covered).
[0026]
[0027] For any pixel point (x, y), as long as there is an integer i∈[1,...,N] such that P(x, y, c i )=1, that is, the point exists in a sensor node c i within the monitoring range, it is considered to be covered. From this, the total number of covered nodes D...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com