Snake simulating method in protein folding emulation
A protein folding and protein technology, which is applied in the field of simulation of protein folding, can solve the problem that the protein folding process cannot be simulated, and achieve the effect of reducing manpower
Inactive Publication Date: 2010-12-01
HARBIN ENG UNIV
View PDF1 Cites 0 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
However, due to ignoring a large number of specific details of the folding process, the simulated folding process has a large deviation from the actual process, and the folding process of many proteins cannot be simulated.
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment Construction
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
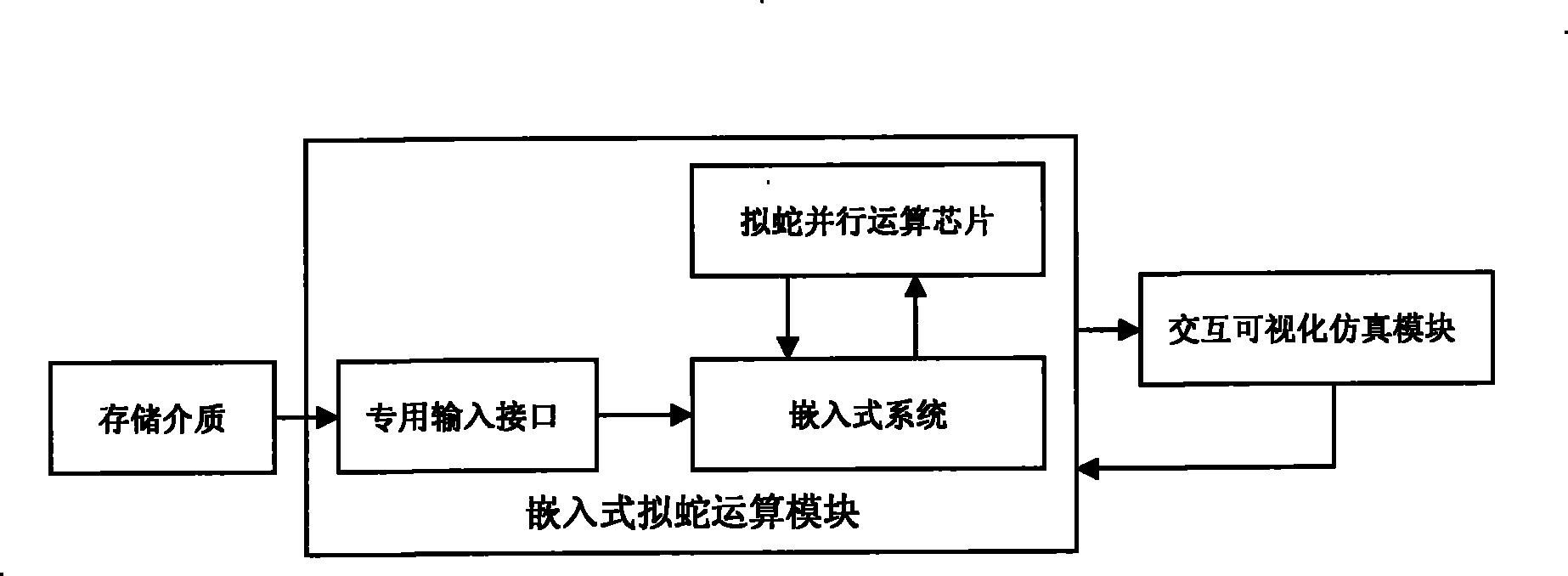
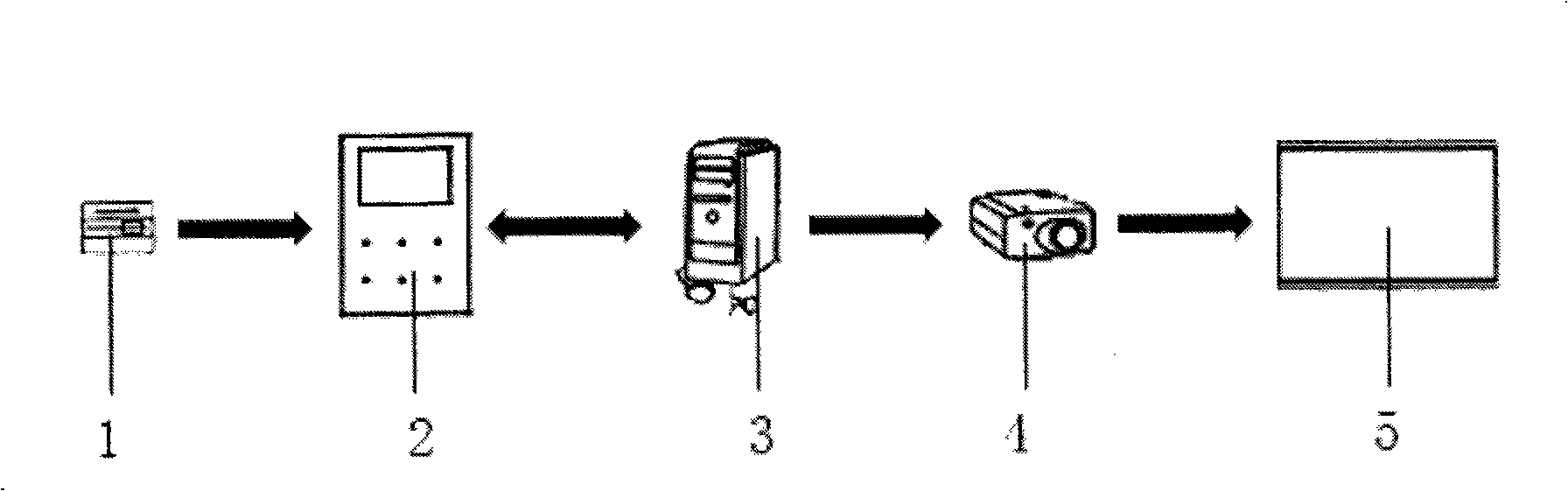
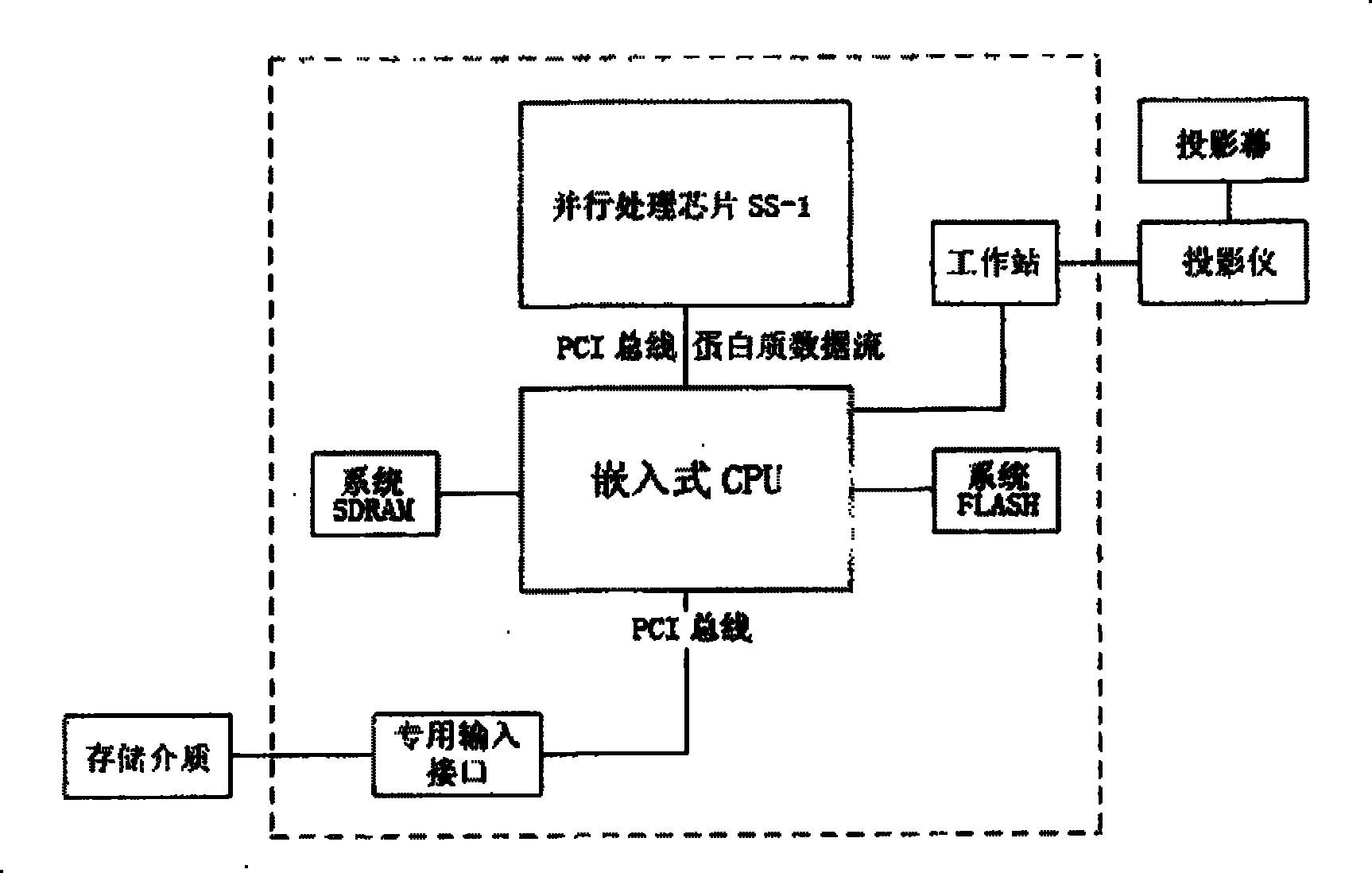
The invention provides a snake simulation method in protein folding simulation. (1) an initial state: serving as a straight protein sequence; (2) starting of folding: making wave motion and expressing by a function of sin(t); (3) later stage of folding: making temporary rectilinear motion and expressing by a function that x is equal to x plus t; and (4) end of folding: making coiling motion, and expressing by a function that x(t) is equal to (C<1>cos(omega t) plus C<2>sin(omega t)), wherein C and omega are coefficients and related to self characteristics of protein. For the protein with unknown space structure, by the snake simulation algorithm, an intermediate body and final space structure of a protein chain are predicted, thereby reducing human and material resources consumed in the process of measuring the space structure of the protein, and simultaneously providing folding analysis for theory researchers to refer.
Description
Model Snake Method in Protein Folding Simulation (1) Technical field The invention relates to a protein computer folding method. (2) Background technology The research on protein folding began in the early 1960s. Professor Anfinsen of the National Institutes of Health and his colleagues found that ribonucleases that were inactive due to the addition of denaturants could spontaneously fold into The native conformation thus becomes physiologically active again, and this process can be repeated. In 1968, Levinthal pointed out in a paper that the number of possible conformations that protein molecules can adopt is an astronomical number, and its natural conformation has only one, which makes some scientists believe that there must be a special folding pathway, Proteins fold along this pathway, rapidly folding into their native conformation through a series of specific intermediates. Since the 1970s, several research groups have successively found signs of the existence of ...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Patents(China)
IPC IPC(8): G06F19/00G06F19/16
Inventor 张菁陈怀友李艳波李松赵明王立伟王海玲于思亮温乃锋刘波
Owner HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com