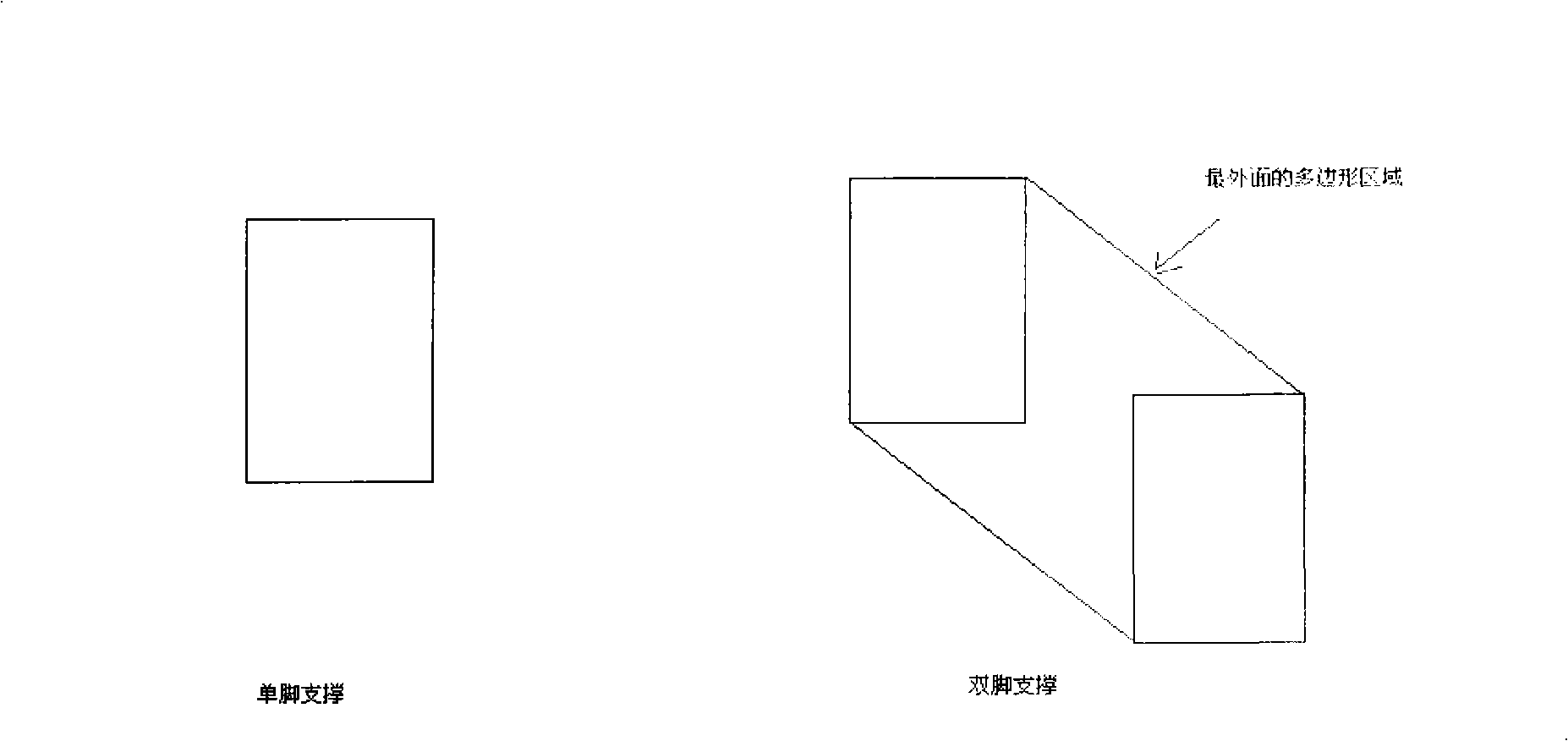
Method and apparatus for movement planning of apery robot ankle
A humanoid robot and motion planning technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, road network navigator, etc., can solve problems affecting the stability of the robot's landing process, increase flexibility, reduce reaction force, and improve stability sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
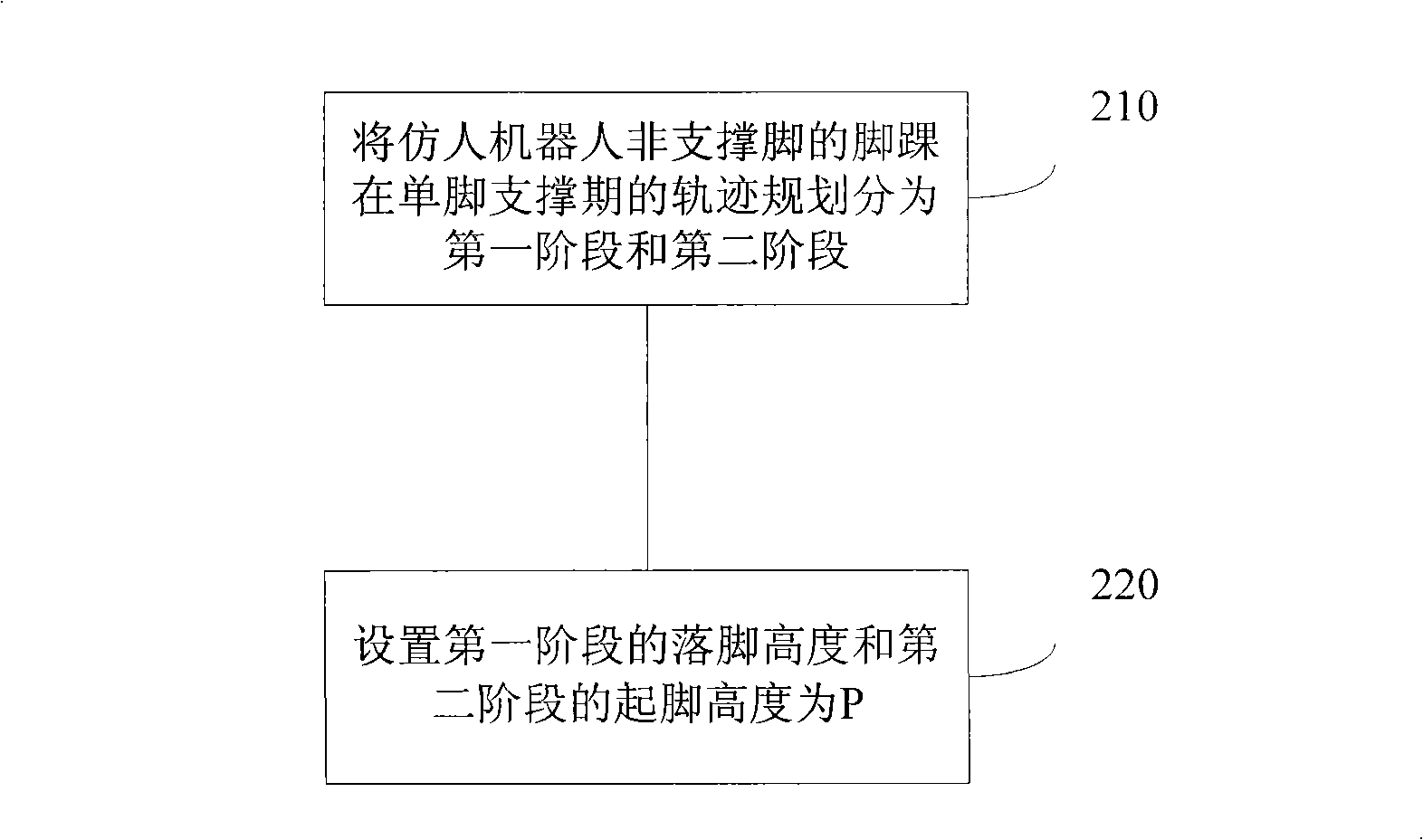
[0030] Embodiments of the present invention provide a motion planning method for the ankle of a humanoid robot, such as figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0031] 210: The trajectory planning of the ankle of the non-supporting foot of a humanoid robot in the single-foot support period is divided into the first stage and the second stage.
[0032] In each of the above-mentioned stages, three key points are respectively included: starting point, middle point, and foothold point. The trajectory planning of the ankle of the non-supporting foot of the humanoid robot in the single-foot support period is based on the above three key points. on the planning.
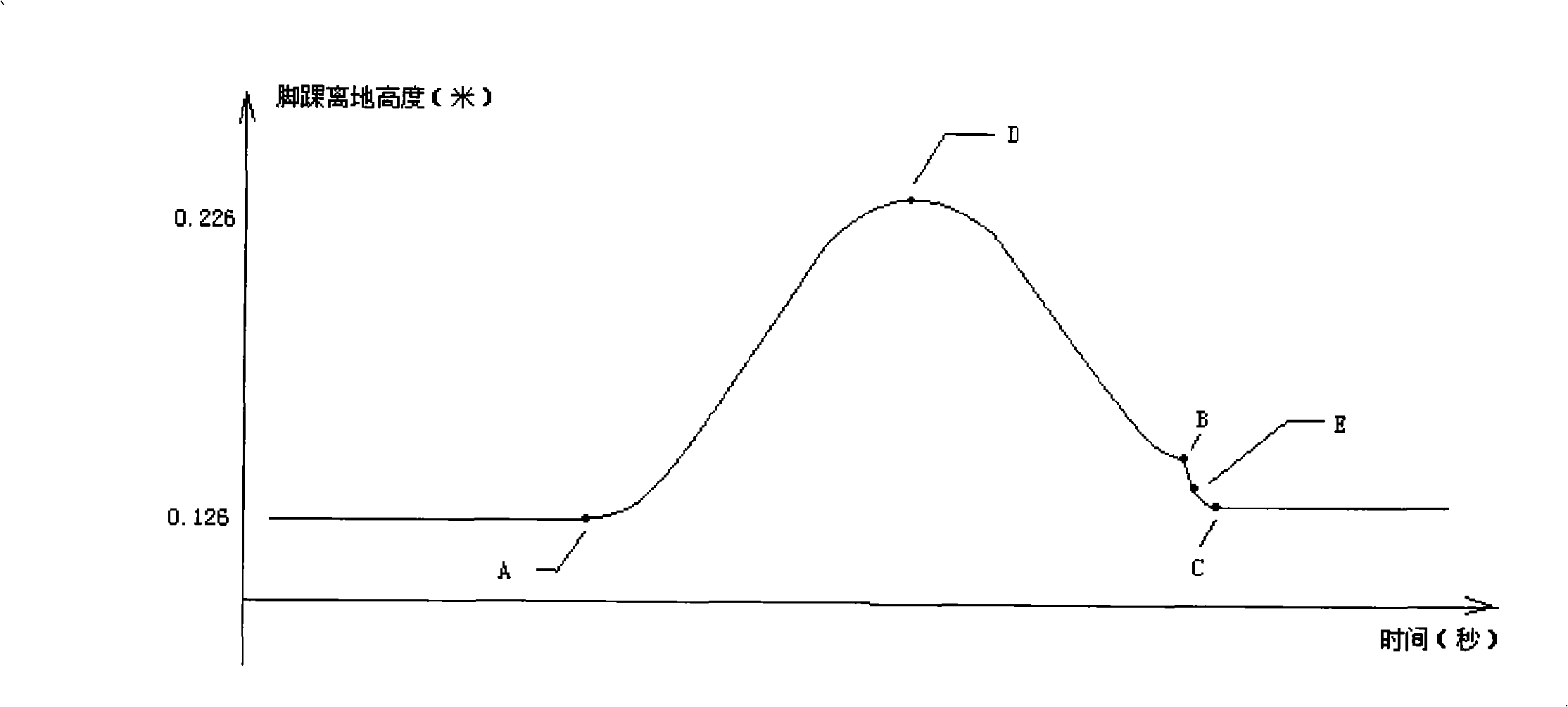
[0033] 220: Set the landing height of the first stage and the kicking height of the second stage as P, where P=L+F, L is the distance between the ankle and the instep, F is the compensation for the height of the ankle from the ground, and L>0, F >0.
[0034] Set the landing height of the first stage and the star...
Embodiment 2
[0040] An embodiment of the present invention provides a motion planning device for a humanoid robot ankle, such as Figure 5 shown, including:
[0041] The phase division module 501 is used to divide the trajectory planning of the ankle of the non-supporting foot of the humanoid robot into the first phase and the second phase during the single-foot support phase.
[0042] The setting module 502 is used to set the landing height of the first stage and the kicking height of the second stage as P, wherein P=L+F, L is the distance between the ankle and the instep, F is the amount of compensation for the height of the ankle from the ground, and L >0, F>0.
[0043] The setting module 502 sets the height of the feet in the first stage and the height of the feet in the second stage to the same value P, that is, L is the distance between the ankle and the instep, F is the compensation for the height of the ankle from the ground, and L>0, F >0.
[0044] The setting module 502 sets t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com