Multi-label anticollision method based on packet dynamic frame and binary tree search for RFID system
A binary tree and dynamic frame technology, applied in the field of anti-collision, can solve the problems of waste of idle time slots, waste of time slots, and many collision time slots, and achieve the effect of reducing the number of collision time slots, simple structure, and low complexity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0032] (1) The process of the reader to identify all tags
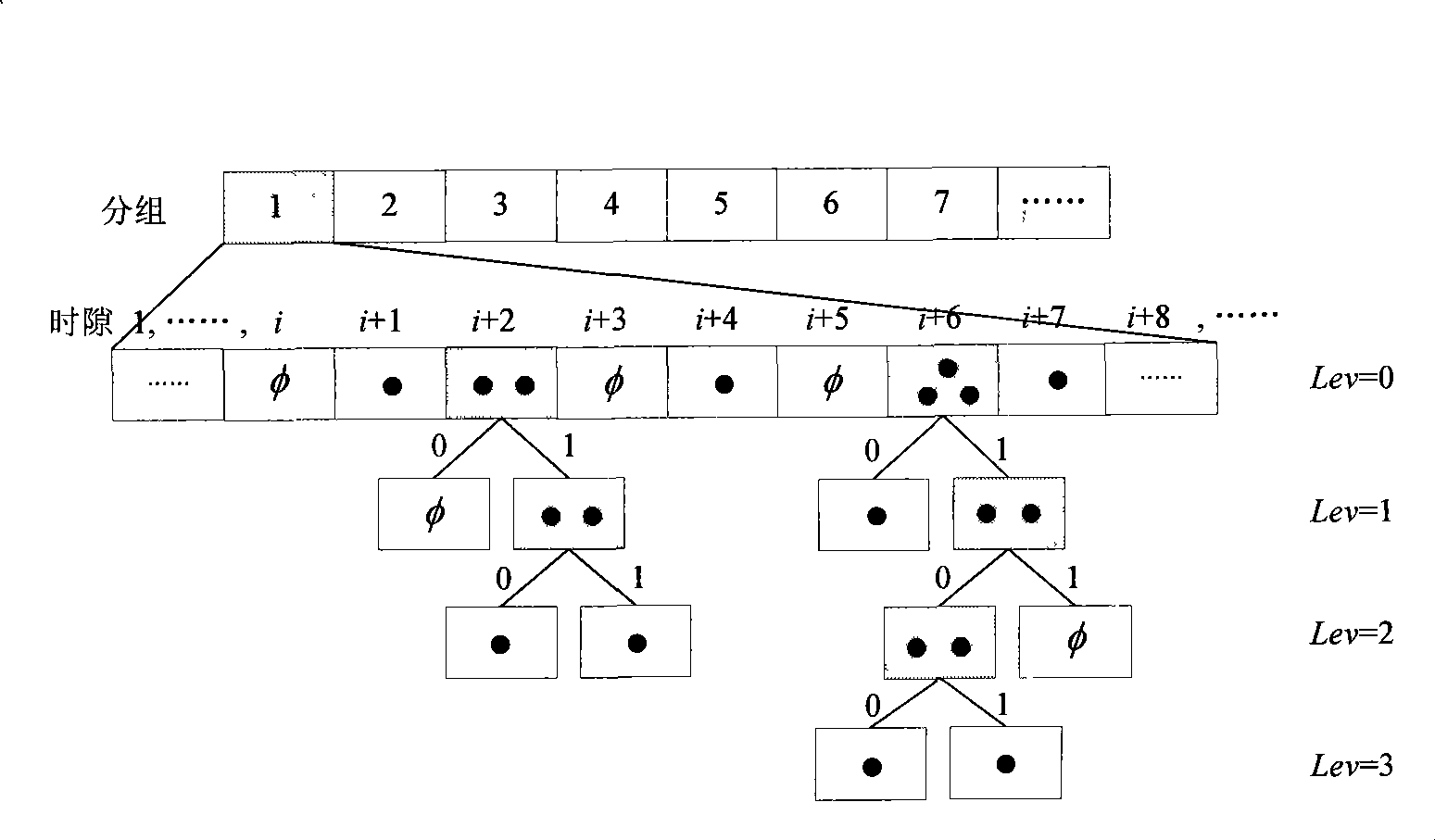
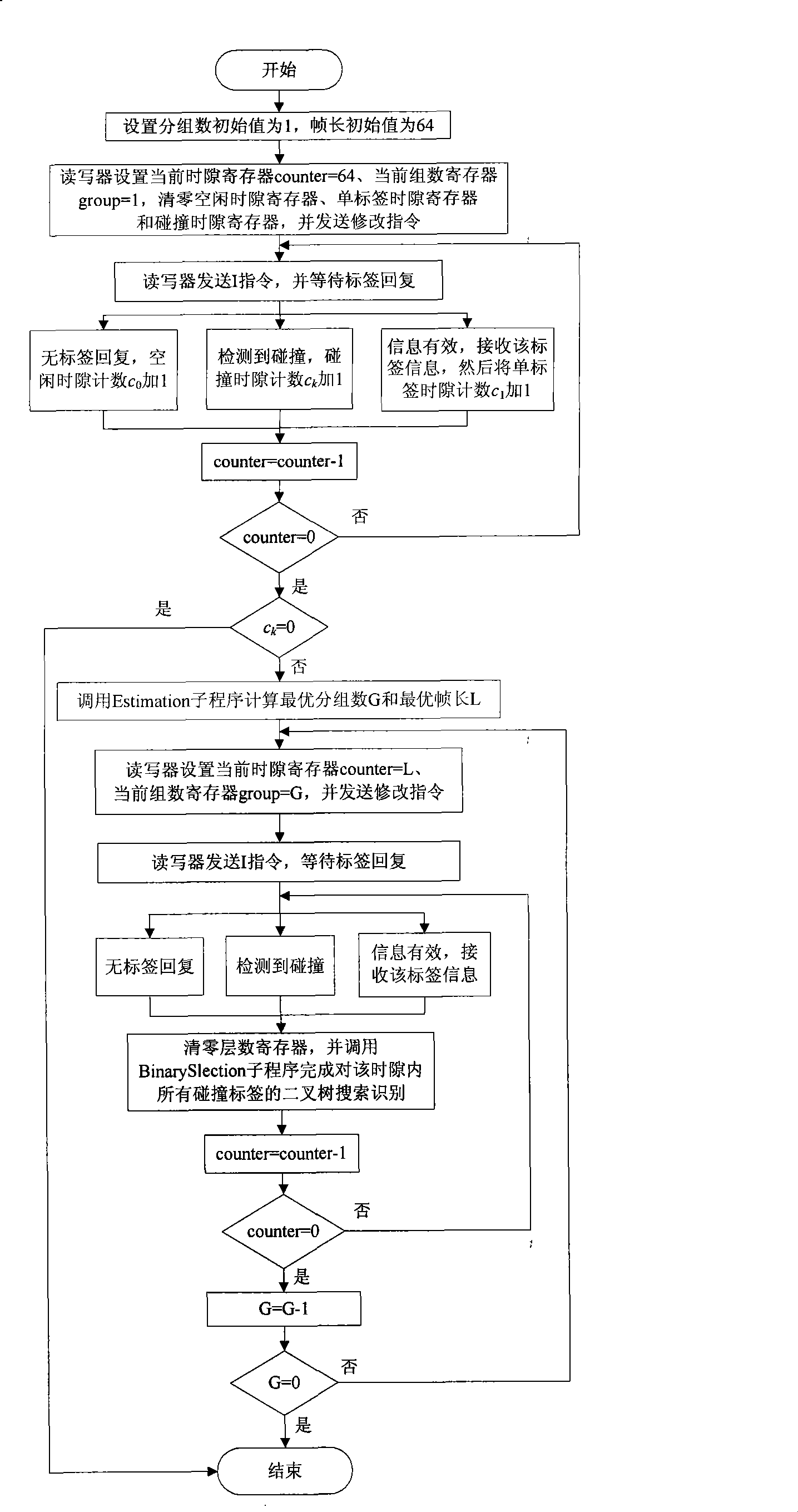
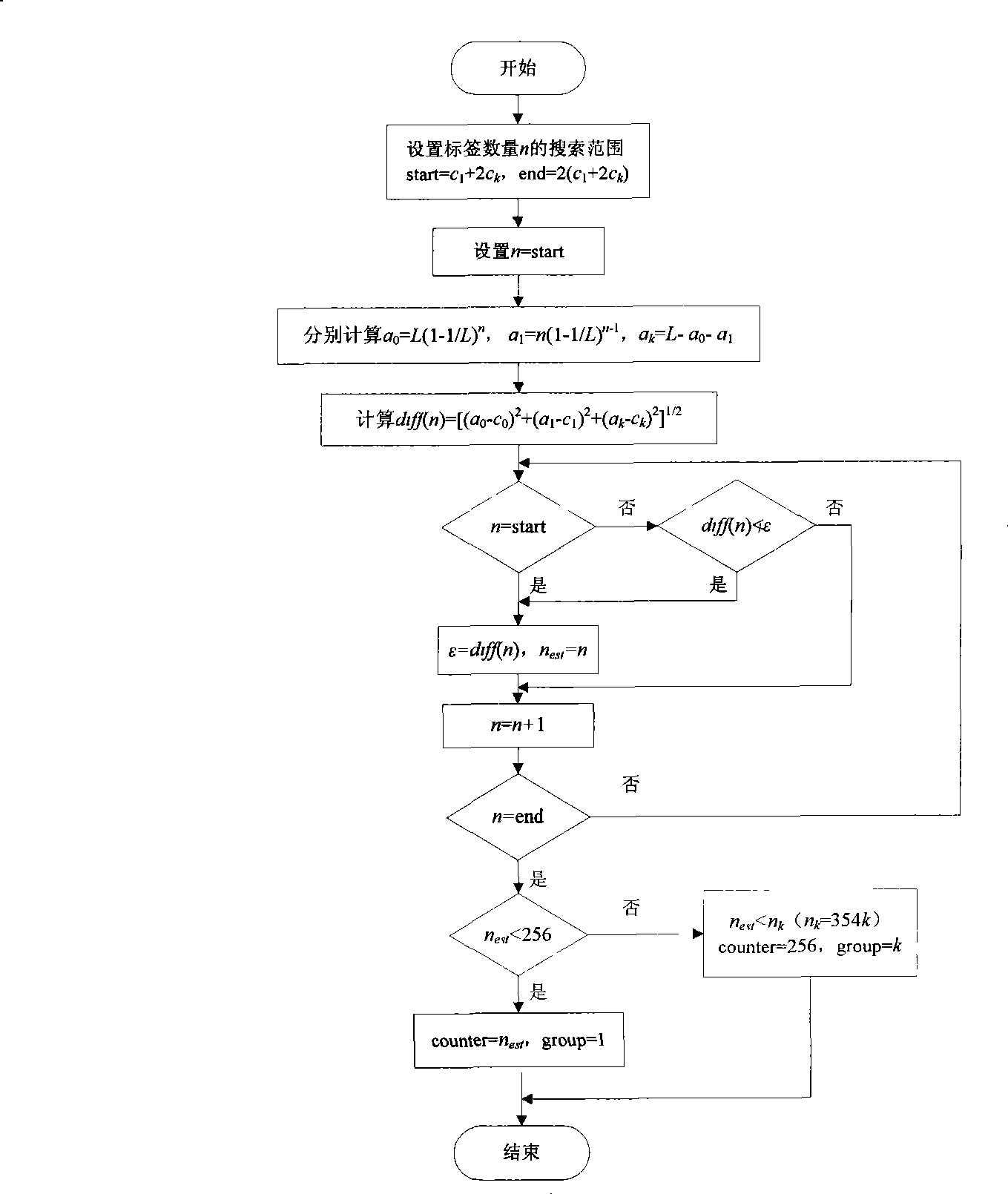
[0033] Such as figure 2 As shown, first, set the initial value of the number of packets and the initial value of the frame length according to the needs of specific applications. Here, the initial value of the number of packets is set to 1, and the initial value of the frame length is 64. According to the above settings, the reader sets the frame length count value counter=64, the current group number register group=1, and clears the free time slot register, single tag time slot register and collision time slot register. Then the reader sends a modification command, which includes the above-set number of packets, frame length and a random number generated by the reader, and sends an I command to start the current frame cycle, and then waits for the tag to reply.
[0034] I...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com