Encarsia Sophia artificial propagation production method
A technology for artificial reproduction of the pale yellow nephew aphid, applied in hunting equipment, applications, animal husbandry and other directions, can solve problems such as difficulty in mass reproduction, and achieve the effects of improving egg hatching rate, mass reproduction, and good natural control.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Embodiment 1, the mass production and reproduction of the light yellow aphid wasp
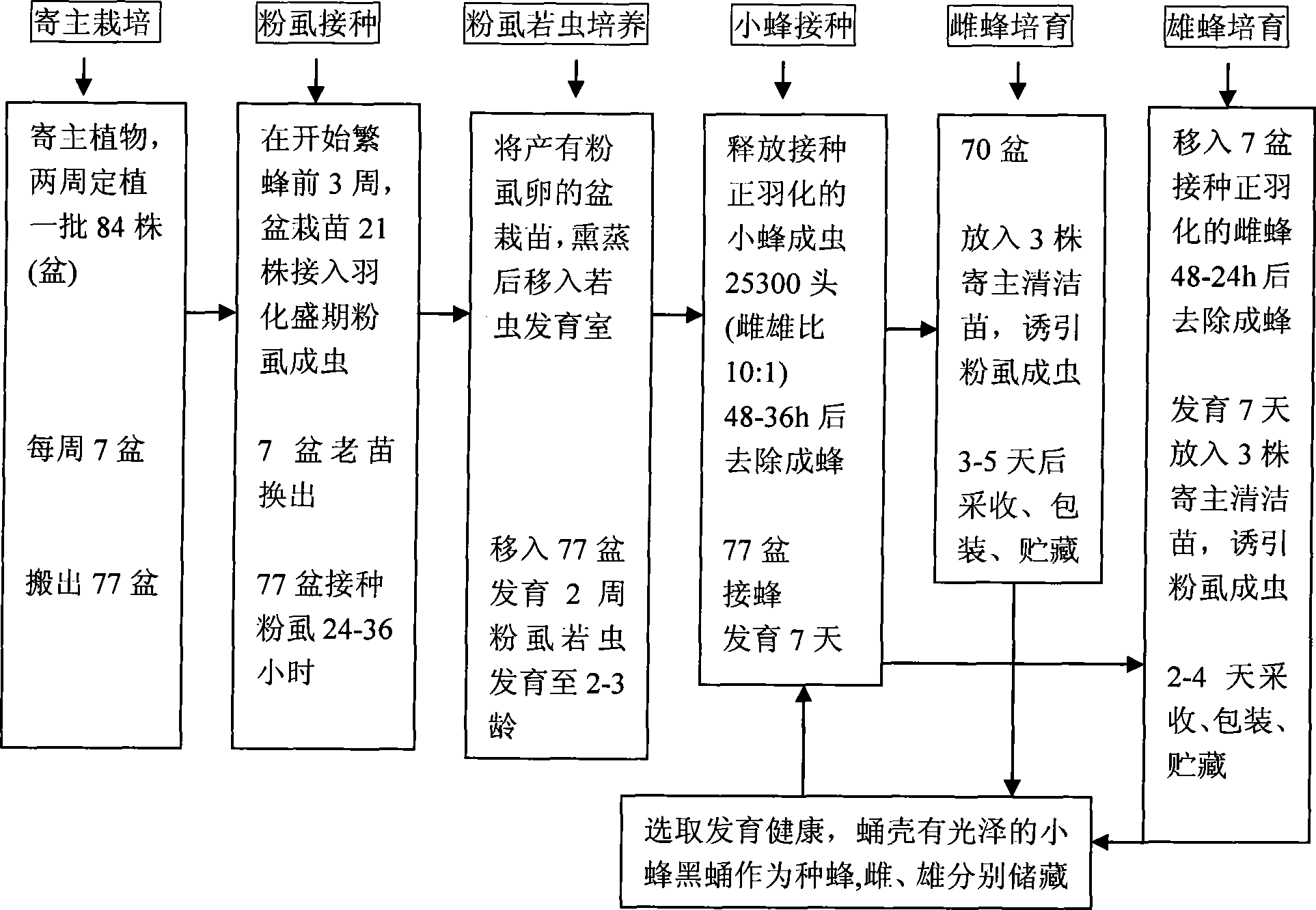
[0051] The main process of mass production and reproduction of A. figure 1 shown, specifically as follows:
[0052] 1. Collect and reproduce the species
[0053] (1) Collect bee species: collect the whitefly nymphs parasitized by Aphidia japonica, i.e. black pupae, on the leaves of field plants where whitefly occurs strictly;
[0054] (2) Purification and optimization of bee species: put the collected parasitic black pupae of Aphid japonica at 25-27°C and RH.60-70% for development, and transfer to the nymph of Bemisia tabaci after emerging from the queen bee , and then select excellent bee species through testing of parasitism rate, emergence rate, fecundity, sex ratio, storage characteristics and ability to search for eggs of target pests;
[0055] (3) Propagation of bee species: multiply the female and male bee species of E. flavonata respectively, and accumulate enough bee species ...
Embodiment 2
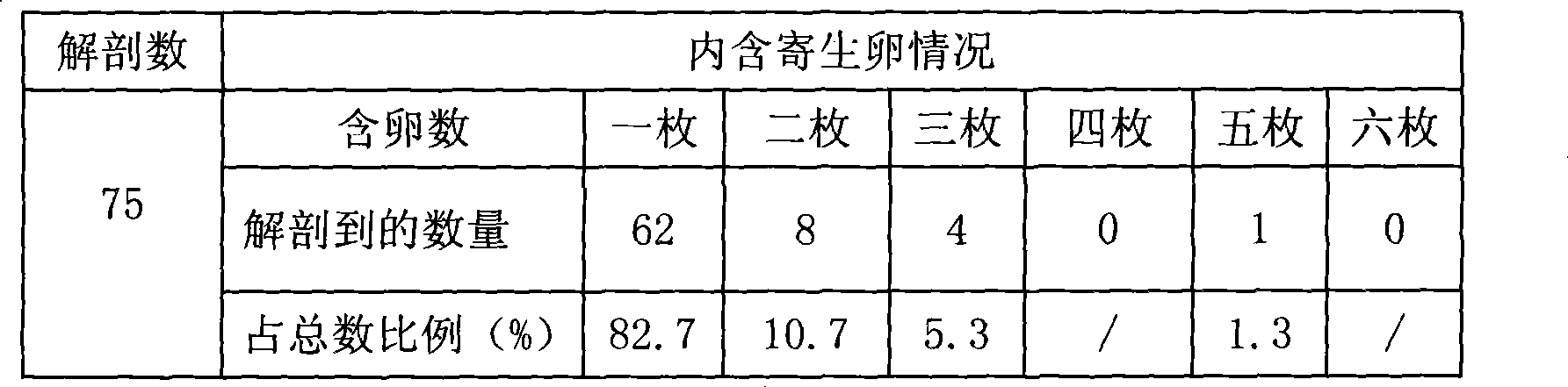
[0080] Embodiment two: comparative experiment
[0081] Comparative experiment 1: Screening of host plants
[0082] (1) Materials and methods
[0083] i) Insects to be tested
[0084] Bemisia tabaci were collected from tomato plants in the greenhouse of Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences.
[0085] The light yellow bee (black pupa) came from the Agricultural Experiment Station of Texas A&M University in the United States.
[0086] ii) Host plant
[0087] Kidney bean, cucumber, cotton, poinsettia, cabbage, sweet potato and tomato were used as test hosts.
[0088] Bean, cucumber, cabbage, and tomato seeds were purchased from the Special Vegetable Center of Vegetable Institute, Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences. Cotton and sweet potatoes were provided by the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and poinsettias were purchased from Beijing Supermarket.
[0089] iii) Experimental conditions and equipment
[0090] Carried out in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com