Lcd device and drive method thereof
A liquid crystal display device and transistor technology, applied in static indicators, nonlinear optics, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as difficult detection of flicker, incorrect alignment of liquid crystals, and easy generation of afterimages on the panel, so as to facilitate adjustment and improve Expressiveness, the effect of eliminating the afterimage problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
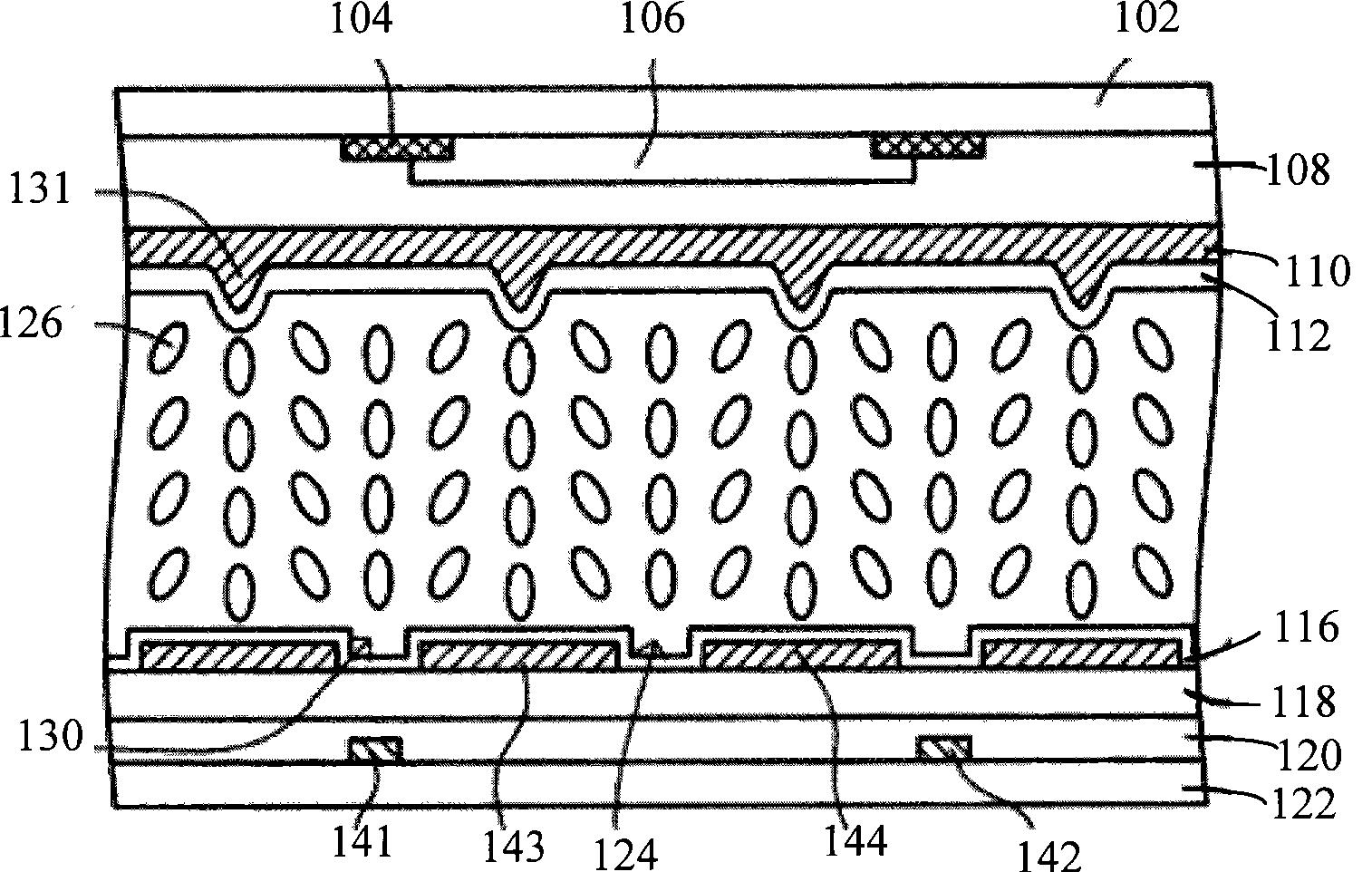
[0050] Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of the liquid crystal display device in the first embodiment of the present invention, such as Figure 5 As shown, the liquid crystal display device in this embodiment includes scanning lines 510 (Gn, Gn+1, Gn+2, Gn+3 shown in the figure); data lines 520 arranged crosswise with the scanning lines 510 ( Dn, Dn+1, Dn+2, Dn+3, Dn+4, Dn+5 as shown in the figure); set in the pixel area 500 formed by the intersecting of the scanning lines 510 and the data lines 520 pixel electrodes and transistors, and the pixel electrodes in each pixel area 500 include a first sub-pixel electrode 501 and a second sub-pixel electrode 502, and the transistors in each pixel area include a sub-pixel electrode connected to the first sub-pixel electrode 501 The first transistor 503 and the second transistor 504 connected to the second sub-pixel electrode 502 .
[0051] In this embodiment, each row of pixel regions is driven by two data lines, and the gates of ...
no. 2 example
[0069] Image 6 It is a schematic diagram of the liquid crystal display device in the second embodiment of the present invention, such as Image 6 As shown, the liquid crystal display device in this embodiment includes scanning lines 610 (including Gn, Gn+1, Gn+2, and Gn+3 shown in the figure); data lines 620 arranged crosswise with the scanning lines 610 ( Including Dn, Dn+1, Dn+2, Dn+3, Dn+4, Dn+5 shown in the figure); arranged in the pixel area 600 formed by the crossing of the scanning lines 610 and the data lines 620 pixel electrodes and transistors, and the pixel electrodes in each pixel area 600 include a first sub-pixel electrode 601 and a second sub-pixel electrode 602, and the transistors in each pixel area include a sub-pixel electrode connected to the first sub-pixel electrode 601 The first transistor 603 and the second transistor 604 connected to the second sub-pixel electrode 602 .
[0070] In this embodiment, each row of pixel regions is driven by two data lin...
no. 3 example
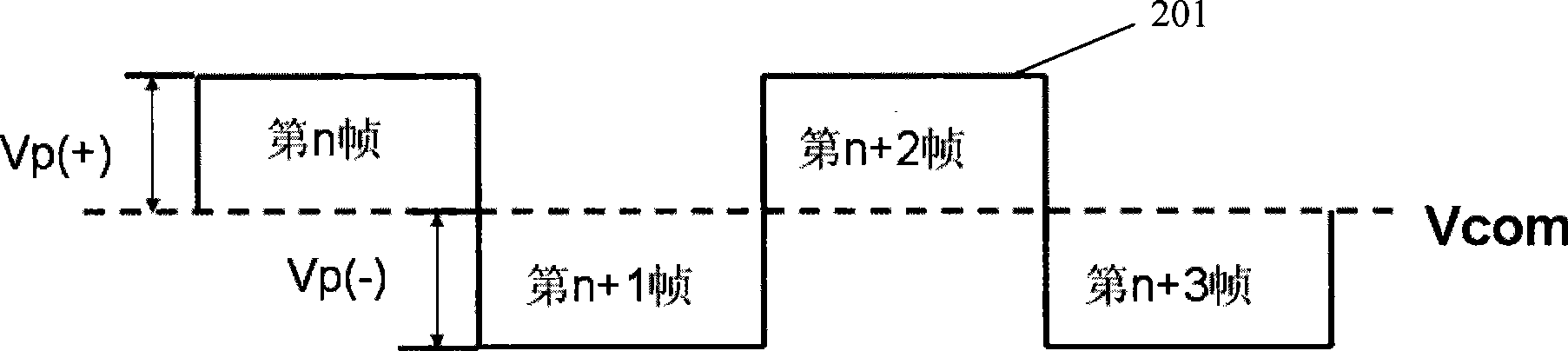
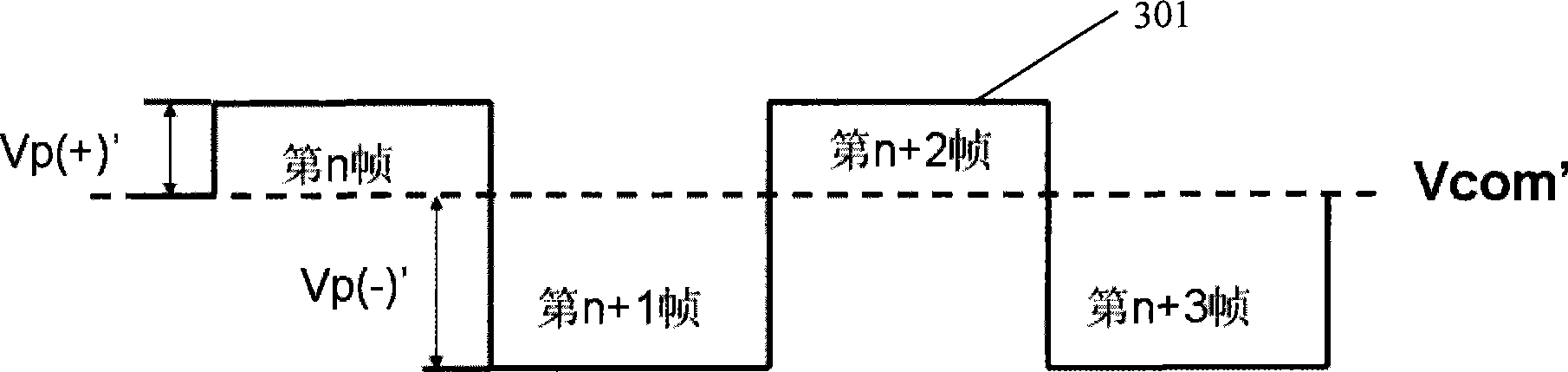
[0088] This embodiment provides a method for driving a liquid crystal display device, Figure 7 It is a flow chart of the driving method of the liquid crystal display device according to the third embodiment of the present invention, combined below Figure 7 A third embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail.
[0089] The driving method of the liquid crystal display device in the present embodiment comprises steps:
[0090] Step 701: forming an array of pixel regions by intersecting scan lines and data lines;
[0091] Step 702: setting a first sub-pixel electrode and a second sub-pixel electrode in each of the pixel regions;
[0092] Step 703: setting a first transistor and a second transistor in each pixel area to control the first sub-pixel electrode and the second sub-pixel electrode respectively;
[0093] Step 704: Use two adjacent scanning lines to send scanning signals to control the first transistor and the second crystal in the pixel area of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com