Duplex steelmaking technique of revolving furnace
A duplex steelmaking and converter smelting technology, applied in the manufacture of converters, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to achieve predetermined results, uneconomical smelting process, and increased smelting costs, so as to improve dephosphorization equilibrium constants, eliminate thermodynamic contradictions, The effect of reducing smelting cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
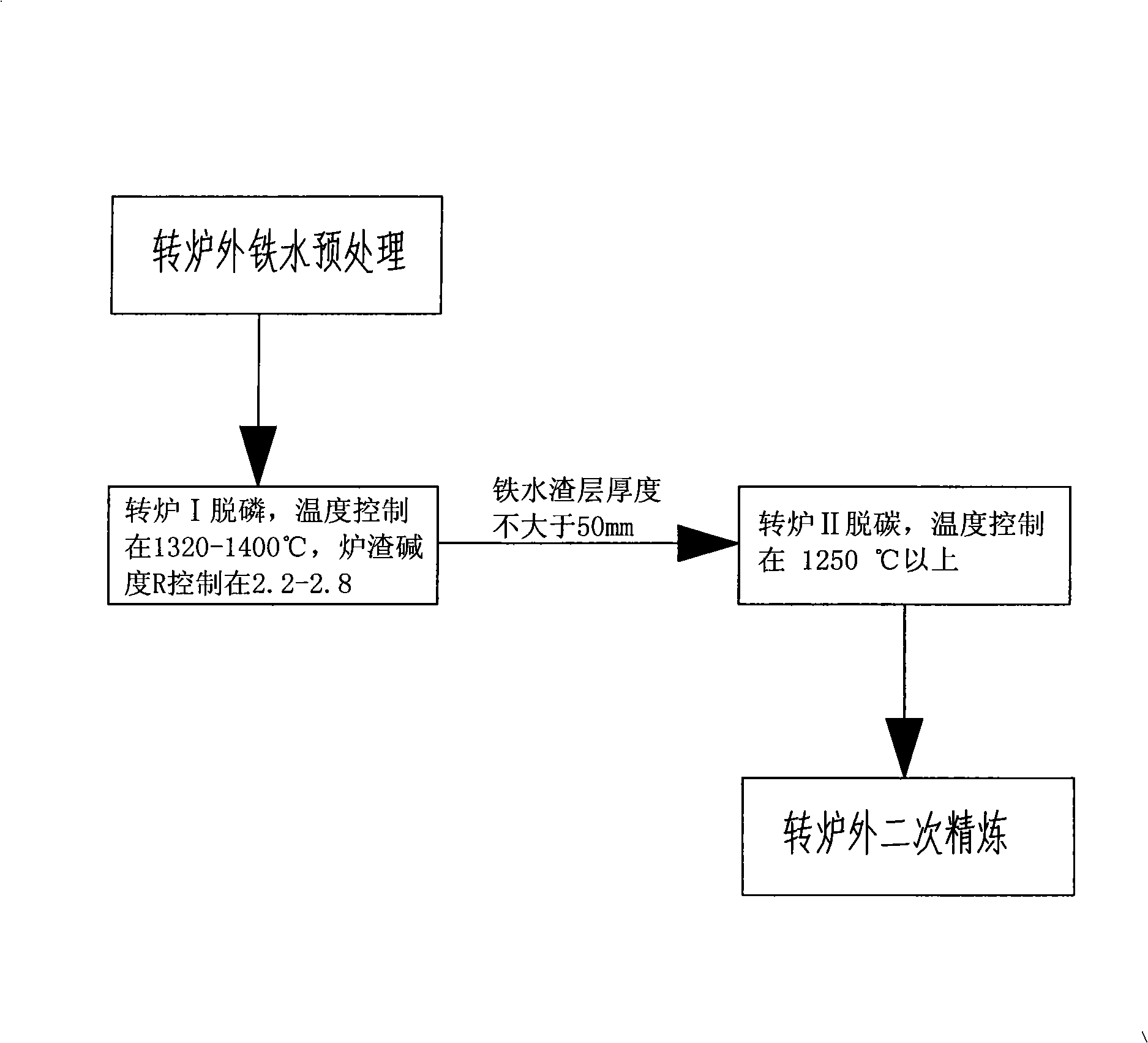
[0022] Converter duplex steelmaking process of the present invention specifically comprises the following steps:
[0023] a. The molten iron is pre-desulfurized outside the converter;
[0024] b. The molten iron is put into the converter I for dephosphorization. The temperature of the molten iron in the converter I is controlled at 1320-1350°C. The temperature control of the molten iron in the converter I is completed by adding scrap steel to the molten iron before the converter I works. Among the scrap steel, light scrap steel with a thickness of less than 25mm accounts for the scrap steel 90% of the total amount, to ensure the melting of steel scrap, the slag basicity R is controlled at 2.3-2.5;
[0025] c. The dephosphorization furnace is used to stop the slag and tap the iron. The thickness of the slag layer after tapping is not more than 50mm, and the carbon content of the molten iron is controlled above 3.2%;
[0026] d. The molten iron after dephosphorization and slag ...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Converter duplex steelmaking process of the present invention specifically comprises the following steps:
[0031] a. The molten iron is pre-desulfurized outside the converter;
[0032] b. The molten iron is put into the converter I for dephosphorization. The temperature of the molten iron in the converter I is controlled at 1350-1380°C. The temperature control of the molten iron in the converter I is completed by adding scrap steel to the molten iron before the converter I works. Among the scrap steel, the light scrap steel with a thickness less than 25mm accounts for the scrap steel 95% of the total amount, to ensure the melting of steel scrap, the slag basicity R is controlled at 2.0-2.3;
[0033] c. The dephosphorization furnace is used to stop the slag and tap the iron. The thickness of the slag layer after tapping is not more than 50mm, and the carbon content of the molten iron is controlled above 3.2%;
[0034] d. The molten iron after dephosphorization and slag...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Converter duplex steelmaking process of the present invention specifically comprises the following steps:
[0039] a. The molten iron is pre-desulfurized outside the converter;
[0040] b. The molten iron is put into the converter I for dephosphorization. The temperature of the molten iron in the converter I is controlled at 1380-1400°C. The temperature control of the molten iron in the converter I is completed by adding scrap steel to the molten iron before the converter I works. The scrap steel is light scrap steel with a thickness less than 25mm. To ensure the melting of steel scrap, the slag basicity R is controlled at 2.5-2.8;
[0041] c. The dephosphorization furnace is used to stop the slag and tap the iron. The thickness of the slag layer after tapping is not more than 50mm, and the carbon content of the molten iron is controlled above 3.2%;
[0042] d. The molten iron after dephosphorization and slag removal enters the converter II for decarburization, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com