A method for fault location in electric power lines
A fault location, power line technology, applied in fault location, information technology support system, etc., can solve problems such as expensive, slow, dangerous, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0237] Example of an embodiment of the invention for a three-terminal power line
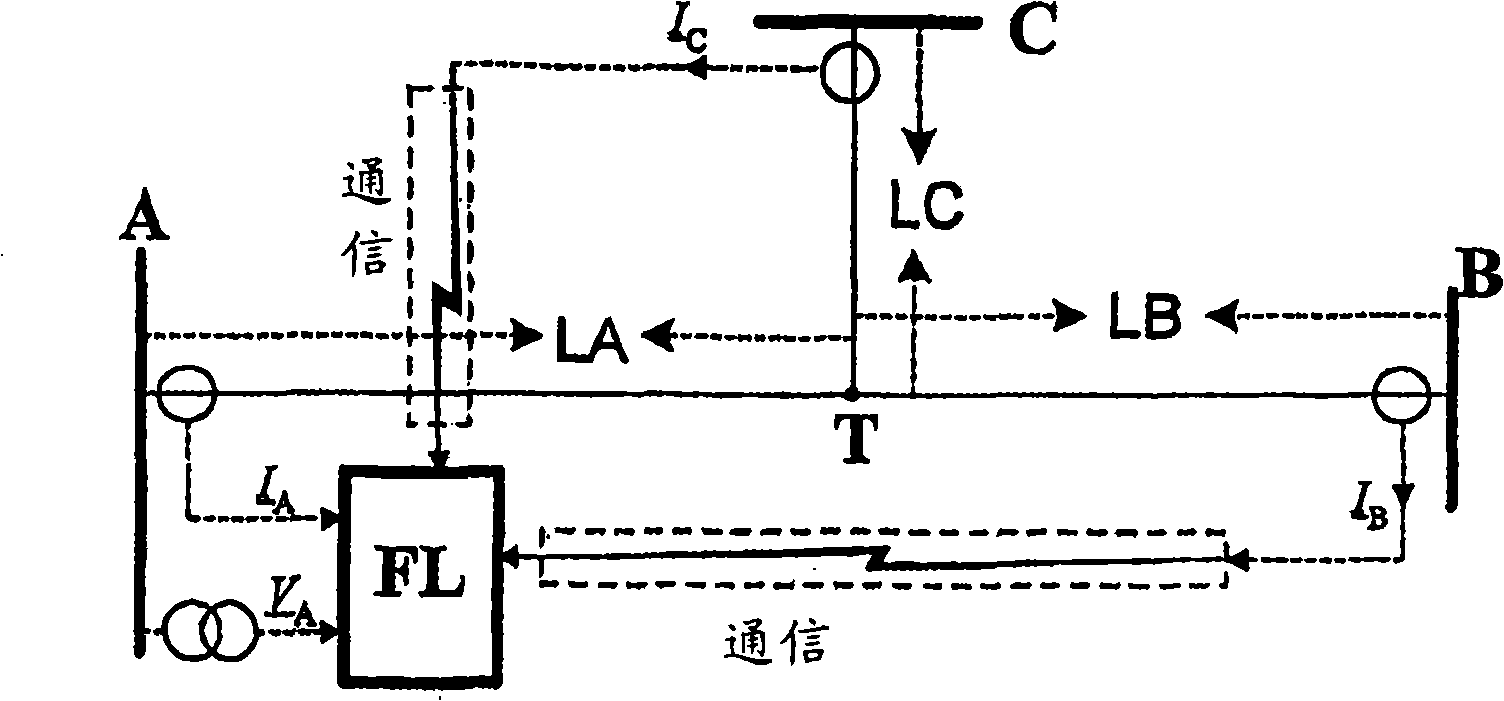
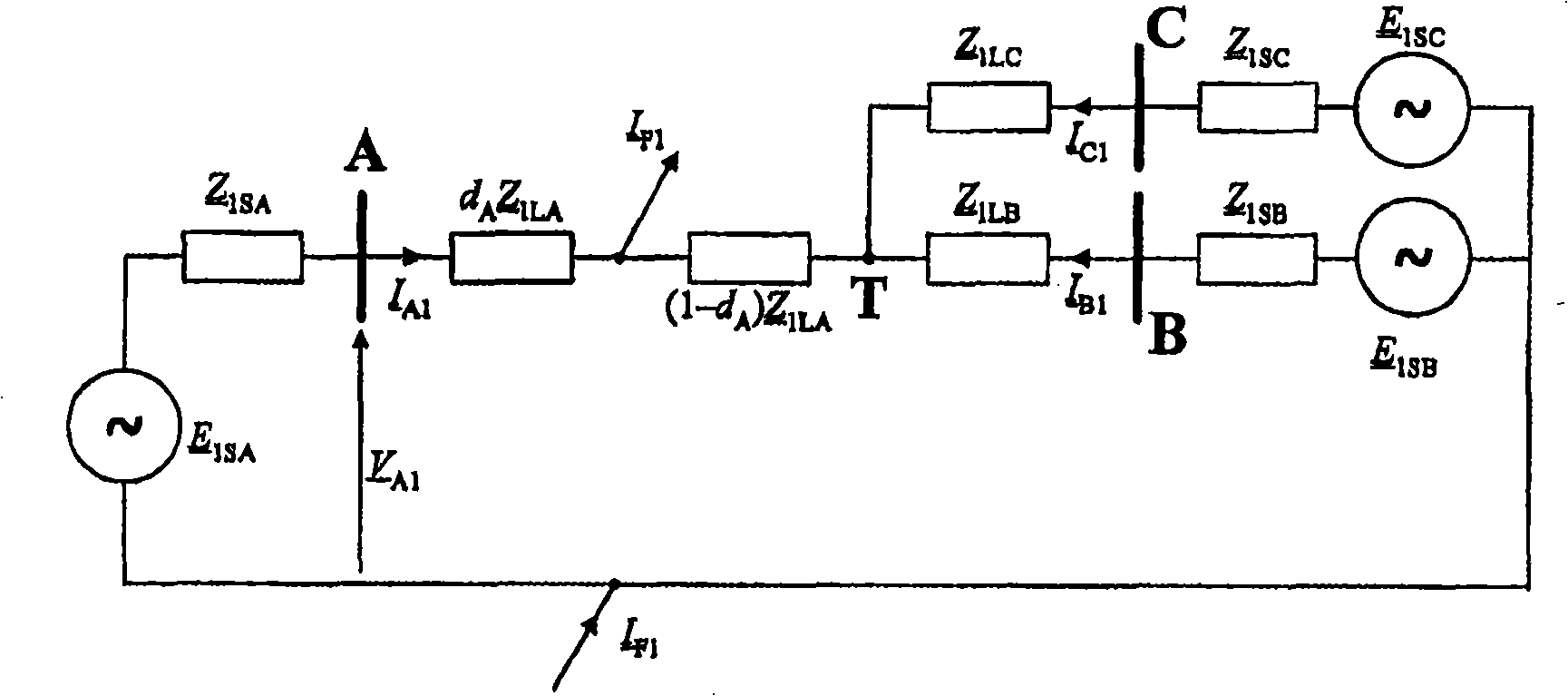
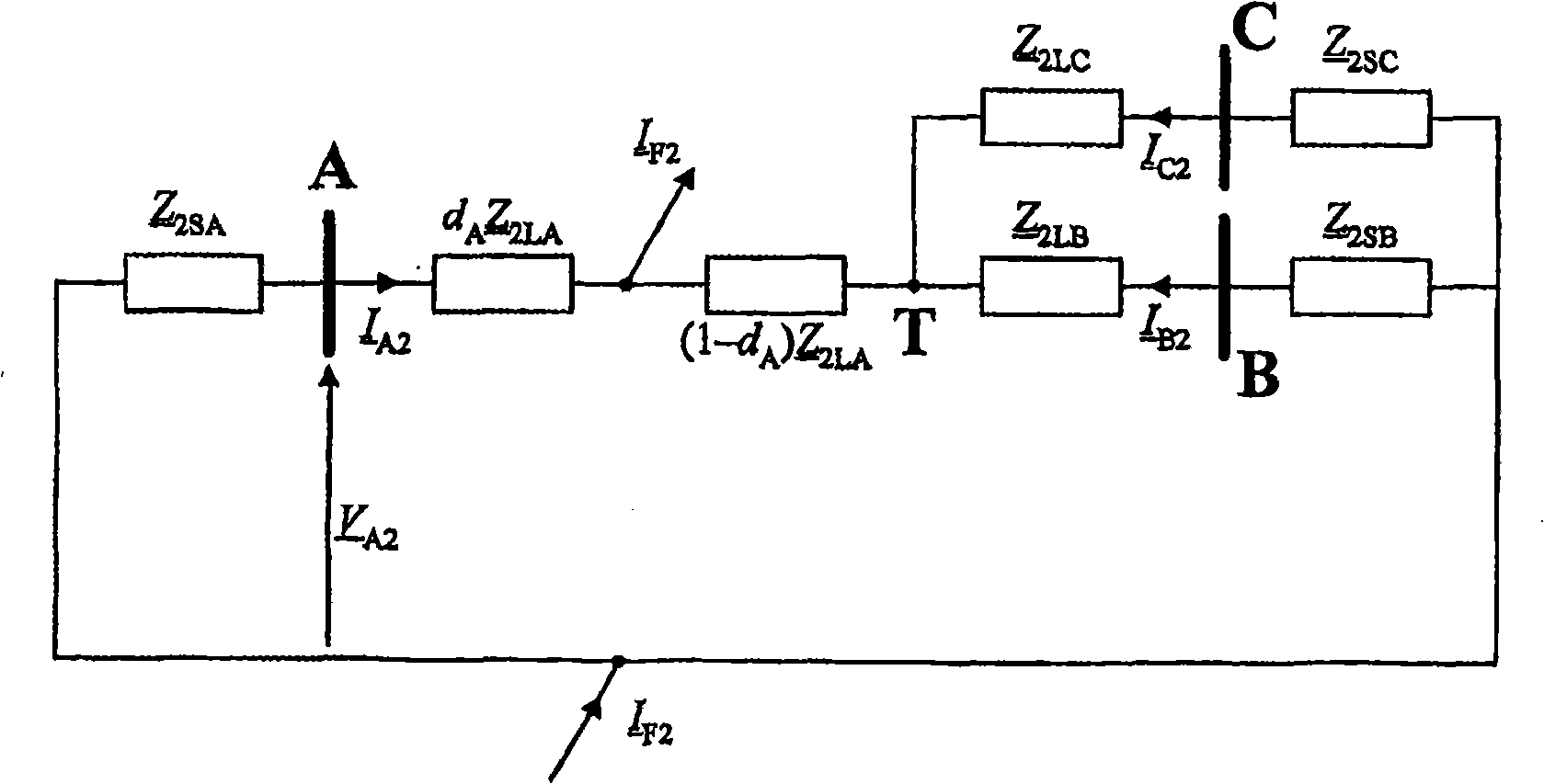
[0238] figure 1 The transmission system shown in includes three generating stations A, B and C. Station A is at the beginning of the line, station B is at the end of the line, and station C is in tap T after the line branching off from the line between stations AB. Tap point T divides the transmission system into three sections LA, LB and LC. In station A there is a fault locator FL. Using fault models and fault circuits for symmetrical components as well as for different types of faults, is defined by applying a F1 , a F2 , a F0 Appropriate share coefficients and weight coefficients for a 1 , a 2 with a 0 For fault location, the share factor determines the relationship between the symmetrical components of the total fault current when estimating the voltage drop across the fault resistance, and the weight factor defines the share of each component in the total model of the fault cir...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com