Cucumber downy mildew resistance main effect QTL linkage molecule labeling method and applying method
A technology for cucumber downy mildew and molecular markers, which is applied in the directions of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., and can solve the problem of long breeding cycle, difficulties in downy mildew-resistant materials, and difficulty in identifying resistant materials. Control and other issues to reduce workload, improve selection accuracy and breeding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
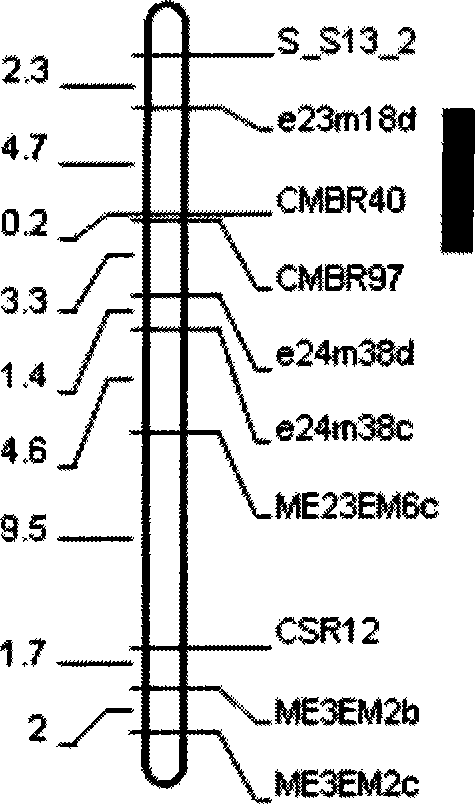
[0028] Molecular marker method of closely linked major QTL for cucumber downy mildew resistance
[0029] (1) Hybridization of S94 with cucumber downy mildew susceptible cultivar S06 to produce F 1 mongrel.
[0030] (2)F 1 F 2 , F 2 The 252 single plants of the 252 plants were randomly selected for planting a seed, and propagated to F 7 generation, resulting in 224 families.
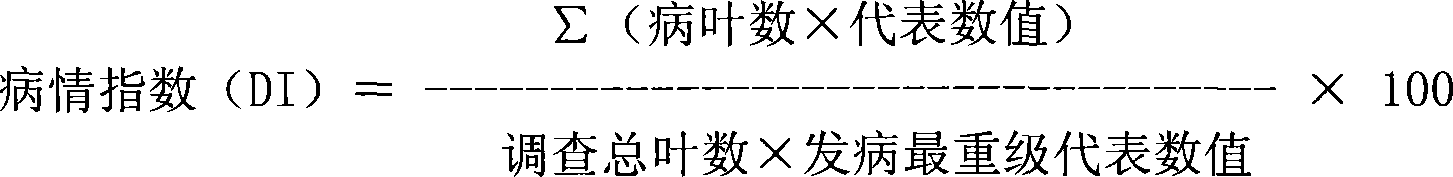
[0031] (3) Select SRAP, SSR, SCAR and STS primer combinations with amplified polymorphisms between the two parents, and use existing methods for 224 families (Wang Gang, Chinese Science C Life Science 2004, 34 (6): 510 ~516; Sakata Y, Theor Appl Genet (Applied Genetic Theory), 2006, 112: 243~250) for analysis, isolate the DNA of cucumber leaves of each recombinant inbred line, and use related sequence amplified polymorphism (SRAP), Microsatellite (SSR), sequence-specific amplification region (SCAR) and sequence tag site (STS) molecular marker primers carry out PCR amplification, and the amplified pr...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Verification of molecular markers linked to the main QTL for downy mildew resistance of S94 in high-generation genetic populations:
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com