Combined method for repairing lead pollution soil
A lead-contaminated soil and joint remediation technology is applied in the field of enhanced measures for phytoremediation of contaminated soil, which can solve the problems of secondary pollution, non-degradation, heavy metal infiltration, etc., and achieves the effects of high remediation efficiency, easy survival and fast growth.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] The potting experiment site is located in the open-air net room of Shenyang Institute of Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The site is in the center of Shenyang, with an altitude of about 50m. There are no pollution sources around the experimental site. It is an area not polluted by heavy metals. 9°C, the annual active accumulated temperature greater than 10°C is 3100-3400°C, and the annual total radiation is 520-544KJ / cm 2 , the frost-free period is 127-164 days, and the annual precipitation is 650-700mm. The soil used in the experiment was collected from the Shenyang Ecological Station of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (the geographical location is 123°41 east longitude 1 , latitude 41°31 1 ) topsoil (0-20cm) of the fallow land (a non-polluted area), and the soil type is meadow brown soil.
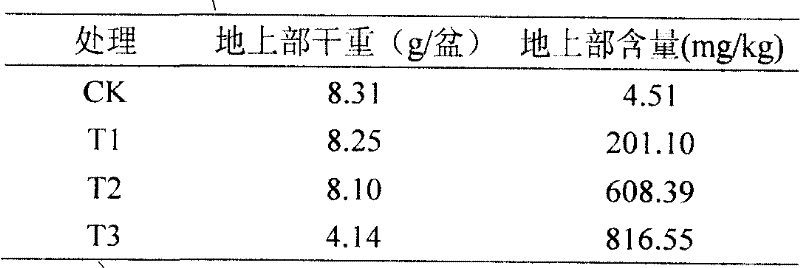
[0017] A total of 4 concentrations were set in the experiment, which were the control (CK, without adding Pb) and 3 different Pb concentration experiments. Pb concentration...
Embodiment 2
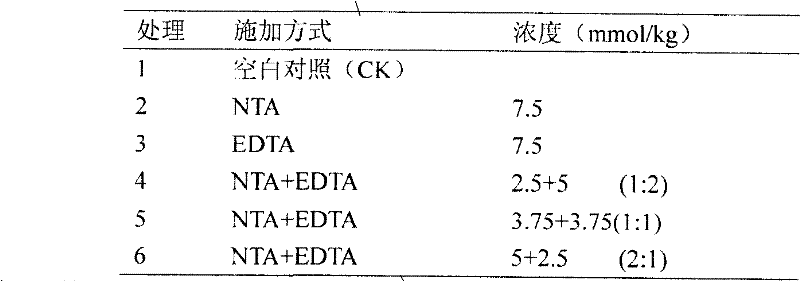
[0025] The lead content added to the soil is 3000mg / kg, and the form of heavy metal added is Pb(NO 3 ) 2 , add it to the soil in solid form, mix well, and use it half a year after balancing. Petunia seedlings with consistent growth were selected for transplantation. Two weeks after the seedlings were transplanted, NTA and EDTA in different proportions were applied near the root zone of the soil surface, and the artificial chelating agent was added at one time. Each treatment was repeated 3 times. Harvest after 2 weeks, see Table 2 for specific application methods.
[0026] Table 2 Application mode and concentration of mixed chelating agent
[0027]
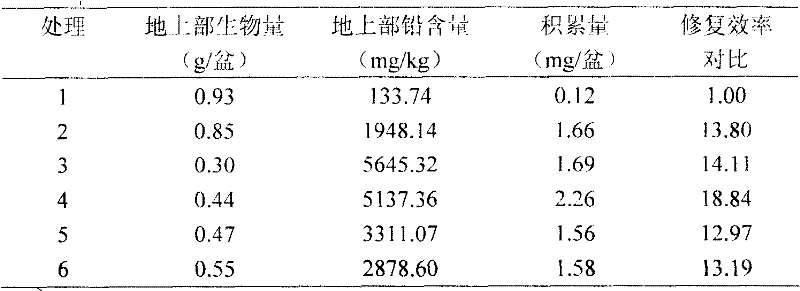
[0028] The experimental results show (Table 3) that one-time application of chelating agent 2 weeks before harvest will improve the repair efficiency. Although the aboveground biomass has decreased, the lead content in the aboveground part of the plant has increased significantly, making the total amount of lead accumulated i...
Embodiment 3
[0032] The basic implementation conditions are the same as in Example 2, but the artificial chelating agent is added in twice, and the second addition is carried out one week after the first addition, and each treatment is repeated 3 times, and the plants are harvested in 2 weeks after the first treatment. See Table 4 for specific application methods.
[0033] The application sequence and concentration of the mixed chelating agent in table 4
[0034]
[0035] The experimental results show (Table 5): the application of mixed chelating agents significantly increased the absorption and accumulation of lead in petunia (Table 5), wherein EDTA was added first, and the effect was the best when NTA: EDTA = 1: 2, so that petunia The lead accumulation of cattle reached 20.87 times that of the control. This treatment was better than EDTA alone, and better than the one-time application of the mixed chelating agent in Example 2. The divided application further improves the remediation...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com