A port convergence method and device
A port aggregation and port technology, which is applied in the network field and can solve problems such as long service interruption time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
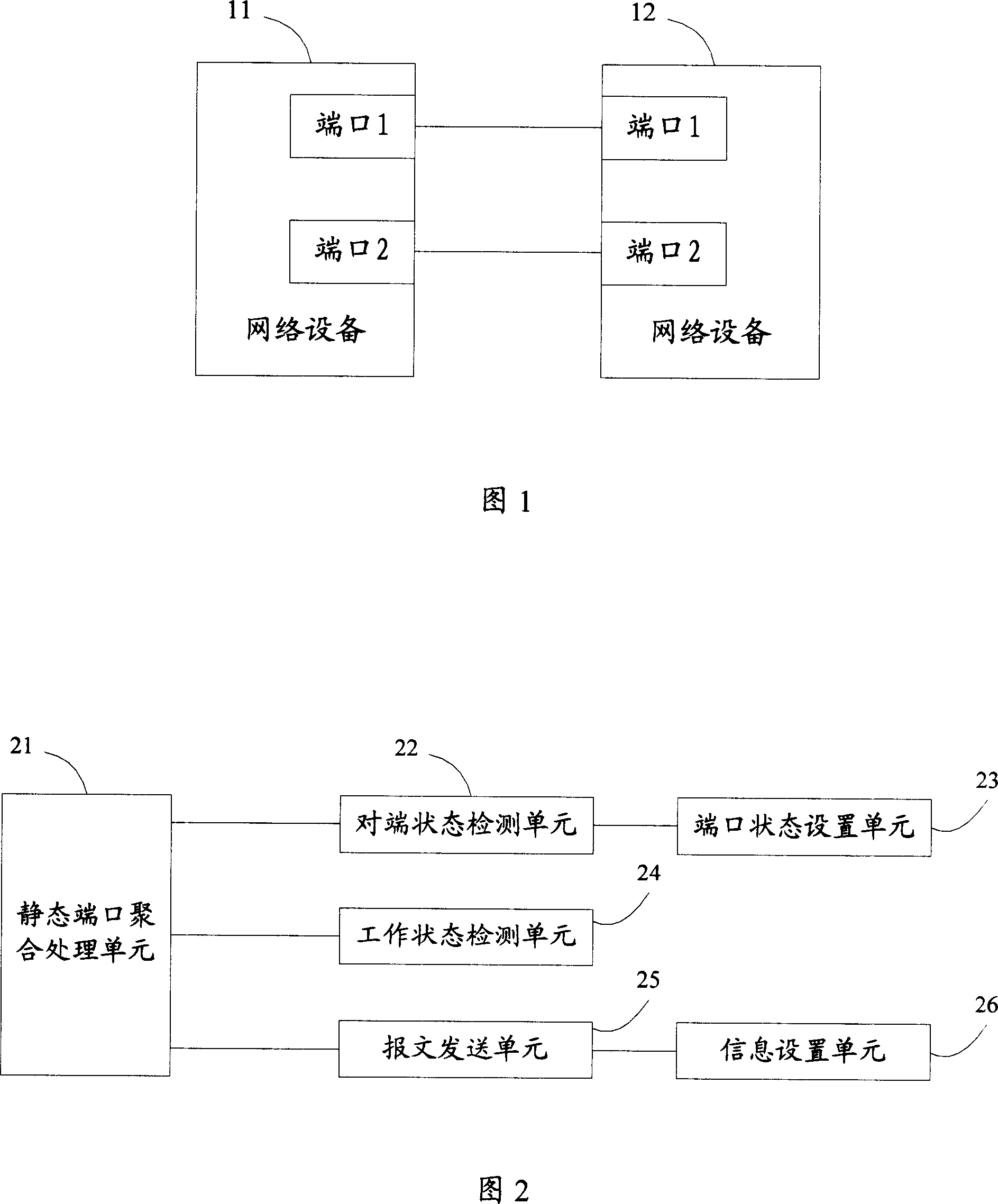
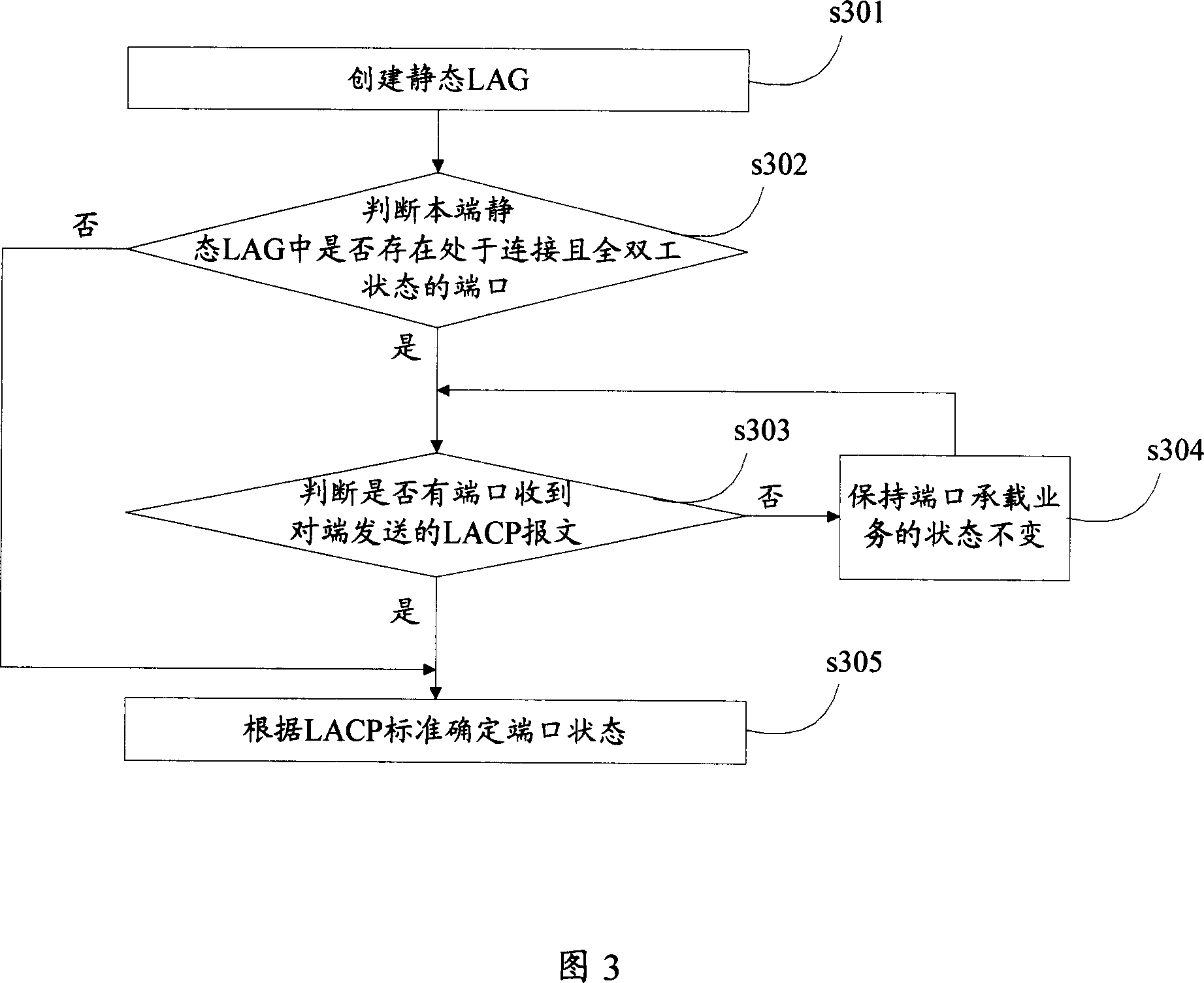
[0028] Embodiment 1, when the network device connection structure shown in FIG. 1 and the port aggregation device shown in FIG. 2 are adopted, the process of creating a static LAG in this embodiment is shown in FIG. 3 . In this embodiment, it is assumed that neither the network device 11 nor the network device 12 has created a static LAG. With reference to FIG. 3 , this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0029] In step s301 , the static port aggregation processing unit 21 of the network device 11 creates a static LAG1 including port 1 and port 2 of the network device 11 .
[0030]In step s302, the peer state detection unit 22 of the network device 11 judges whether there is a port in the static LAG1 that is connected and full-duplex. If yes, go to step s303, otherwise go to step s305. In this embodiment, both port 1 and port 2 of the network device 11 are connected and in a full-duplex state, so go to step s303.
[0031] In step s303, the peer state detection unit 22 ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2, when the network device connection structure shown in FIG. 1 and the port aggregation device shown in FIG. 2 are adopted, the process of deleting a static LAG in this embodiment is shown in FIG. 4 . In this embodiment, it is assumed that the network device 11 creates a static LAG1 including port 1 and port 2 of the network device 11 ; the network device 12 creates a static LAG2 including port 1 and port 2 of the network device 12 . Referring to Fig. 4, the process of deleting static LAG1 in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0035] In step s401, the working state detection unit 24 of the network device 11 judges whether the port 1 and the port 2 of the network device 11 are in the working state. If yes, go to step s402, otherwise go to step s404. In this embodiment, the port 1 of the network device 11 is in the working state, and the port 2 is in the non-working state. Taking the processing of port 1 as an example, because port 1 is in worki...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3, when the network device connection structure shown in FIG. 1 and the port aggregation device shown in FIG. 2 are adopted, the flow of deleting member ports in this embodiment is shown in FIG. 5 . In this embodiment, it is assumed that the network device 11 creates a static LAG1 including port 1 and port 2 of the network device 11 ; the network device 12 creates a static LAG2 including port 1 and port 2 of the network device 12 . Referring to Fig. 4, the process of deleting the port 1 of the network device 11 in the present embodiment includes the following steps:
[0041] In step s501, the working state detection unit 24 of the network device 11 judges whether the port 1 of the network device 11 is in the working state. If yes, go to step s502, otherwise go to step s504. In this embodiment, the port 1 of the network device 11 is in the working state, so go to step s502.
[0042] In step s502, the information setting unit 26 of the network device 11 sets ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com