Chemically assisted milling of silicas
A technology of silica and chemical reagents, applied in the direction of silica, silica, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of unstable and complex porous particle dispersion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] Preparation of Submicron Surface Modified Silica Gels
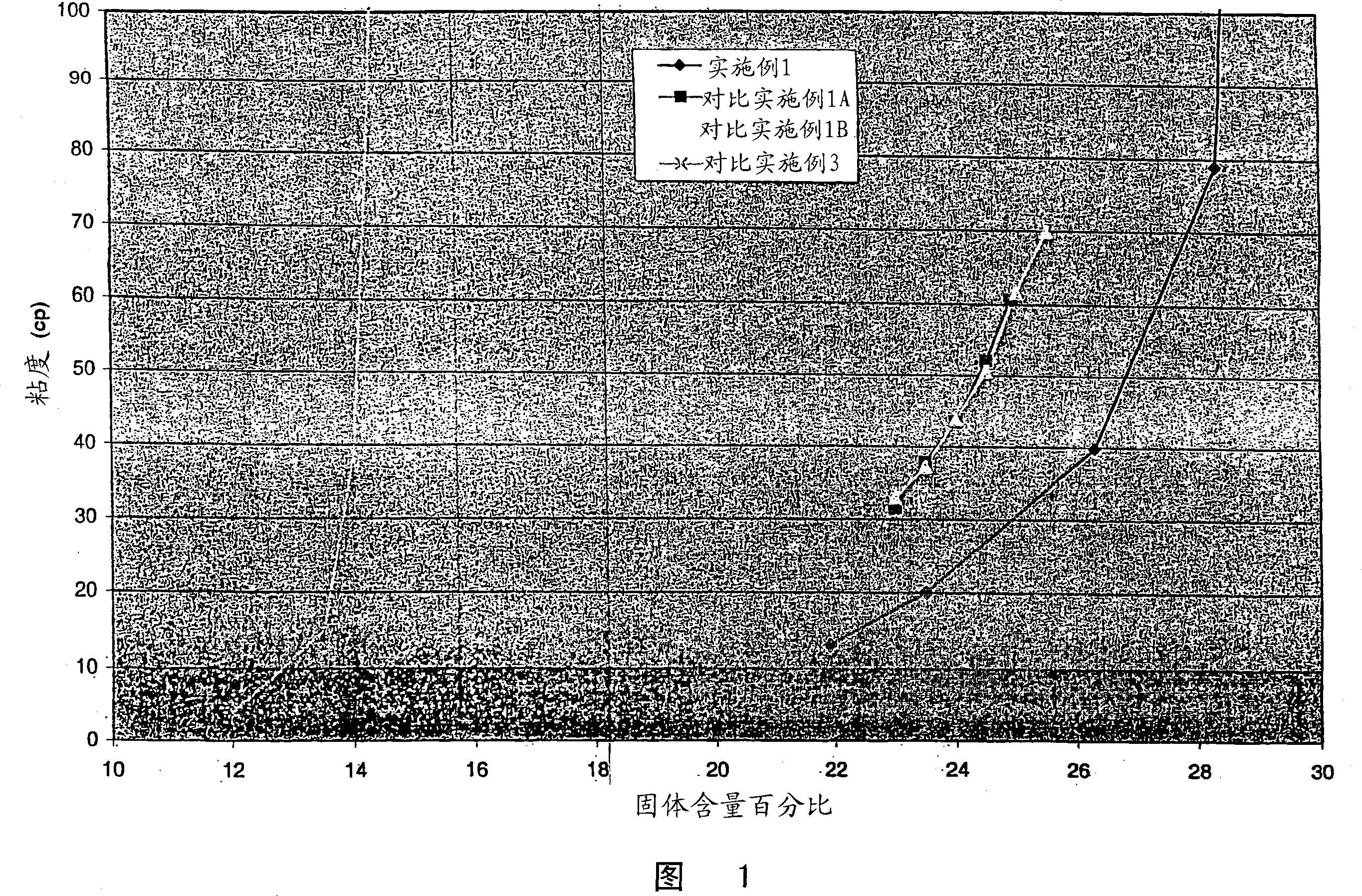
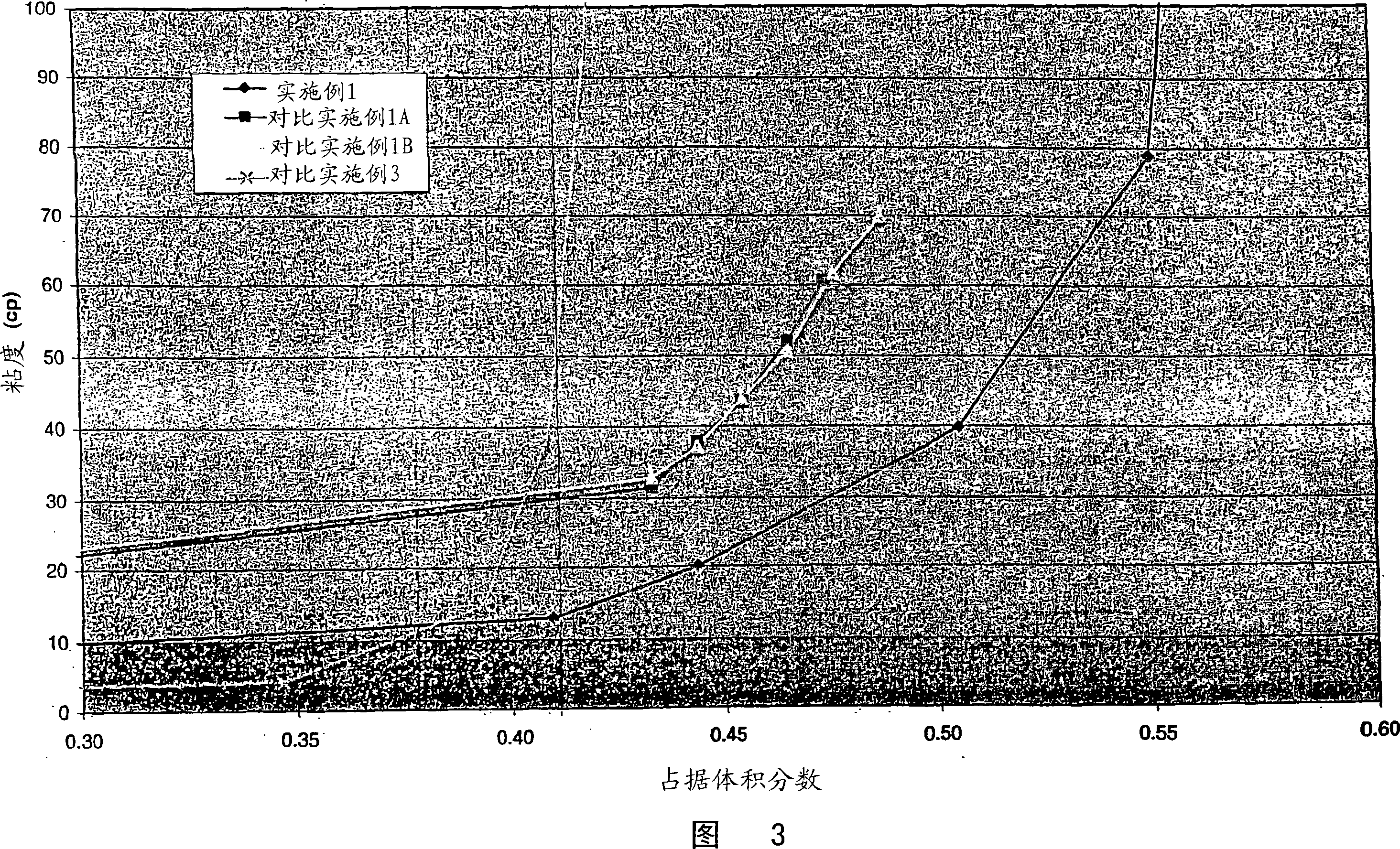
[0088] This example illustrates the preparation of a high solids content, low viscosity dispersion by wet milling a silica gel material in the presence of a surface modifier. First, by adding an appropriate amount of NaAlO to deionized water 2 Preparation of NaAlO 23% w / w solution of surface modifier (from EM Scientific). The parent silica slurry was then prepared in the following proportions: 410 g of 3 wt % NaAlO 2 The solution was added to 1230 g of deionized water. To this solution was added 2731 g (aqueous basis: 45% solids) of Syloid TM W500. For these ratios, the surface modifier (Al 2 o 3 ) at a concentration of 1% (w / w SiO 2 ). Syloid measured by nitrogen porosimetry after vacuum activation (removal of pore water) TM W500 has a pore volume of 1.20cm 3 / g. This suspension was then wet milled using a Netzsch LabStar media mill and 0.4-0.7 mm SEPR media at a flow rate of approximately 0.7 L / min ...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Preparation of submicron surface-modified silica from fumed silica
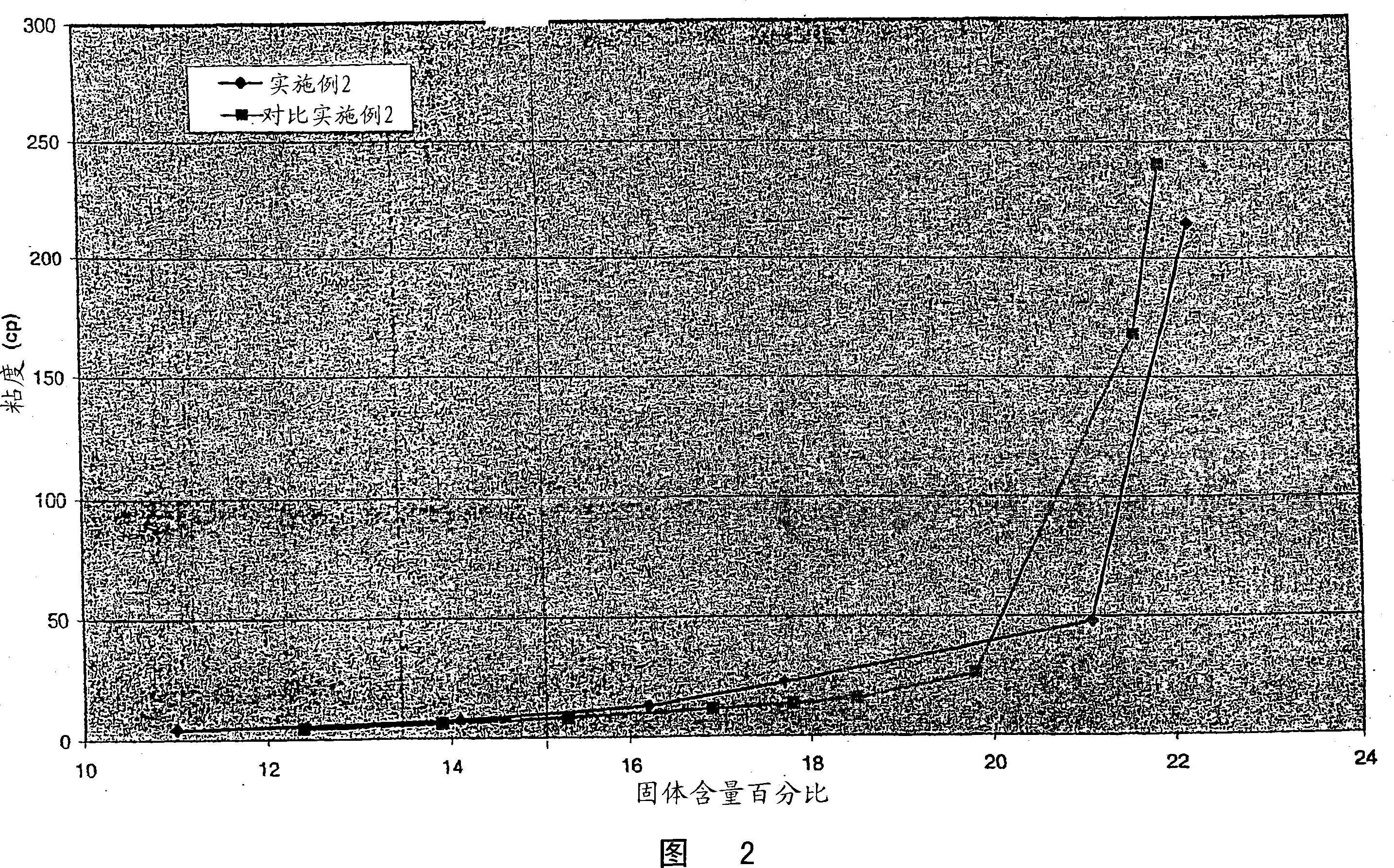
[0098] This example illustrates the preparation of high solids, low viscosity dispersions by wet milling fumed silica materials in the presence of surface modifiers. Add 21.4g NaAlO to 3269g deionized water 2 Surface modifier (from EM Scientific). A precursor silica slurry was then prepared by adding 1116.4 g of Degussa Aerosil A200. For these ratios, the surface modifier (Al 2 o 3 ) at a concentration of 2% (w / w SiO 2 ). This suspension was then wet milled using a Netzsch LabStar media mill and 0.4-0.7 mm SEPR media at a flow rate of about 0.7 L / min for a total time of 200 min. After milling, the pH of the dispersion was 7.8, the median particle size (D50) was 0.16 microns, and the dispersion solids content was 24.6%. A portion of the dispersion was dried and the pore volume of the dried dispersion measured by nitrogen porosimetry was 0.90 cm 3 / g. A plot of viscosity versus solids content fo...
Embodiment 3a
[0114] Preparation of Coating Formulations Including Surface-Modified Silicas of the Invention
[0115] Coating formulations consisting of silica and binder were prepared by mixing the materials in the following proportions. 250 g of a surface-modified silica gel prepared according to Example 1 with a solids content of 30.0 wt % was mixed with 161 g of a 15.5 wt % solution of polyvinyl alcohol (CelVol 523 from Celanese) and 175 g of deionized water. This mixture had a total solids content of 17.1% by weight and a silica:PVOH ratio of 3:1 on a solids basis. The mixture was coated on a plastic PET film (Mellinex 534 from ICI) and dried at 130C for 1 min. The final coating weight is 20.1g / m 2 . The test charts were printed onto the coated sheets using a commercially available narrow format inkjet printer (EPSONC80; EPSON880; Hewlett-Packard-970; EPSON870). The uniformity of the unprinted coating was recorded and a rating of 1-4 was given for the appearance of the printed test...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com