Hard alloy material powder dispersing agent
A technology of cemented carbide and raw material powder, which is applied in the field of dispersant and can solve the problems of uneven microstructure of ultrafine cemented carbide.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
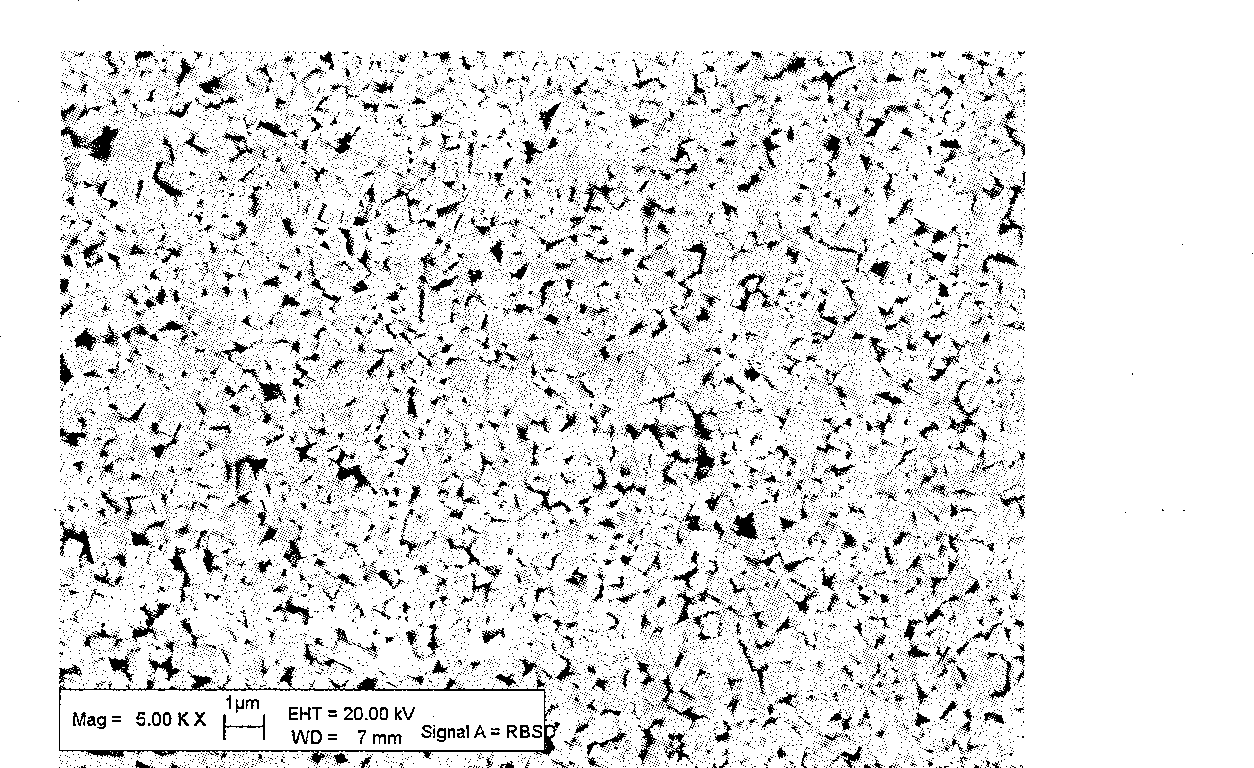
[0010] Example 1: WC powder with a BET particle size of less than 0.4 and Co powder with a Fsss particle size of less than 2.0 are used in a mass ratio of 9:1 to prepare 1 kg of a mixture. Adopting alcohol as wet grinding medium, 2% molding agent PEG4000 (the following examples are all the same), in the mixed slurry, add 0.4g Tween 60, 0.2g stearic acid, 0.1g lauryl by every kilogram of mixed material Trimethylammonium bromide, respectively 0.04%, 0.02% and 0.01% of the powder mass. The above materials are wet-milled for more than 48 hours, and then dried, sieved, pressed and sintered at 1410°C under low pressure to make ultra-fine cemented carbide. figure 1 The SEM picture of the alloy made by adding the compound dispersant according to the above conditions; Figure 4 SEM pictures of the alloy made without dispersant. Table 1 lists the physical properties of alloys made without adding dispersant and alloys made by adding compound dispersant according to the above conditions...
Embodiment 2
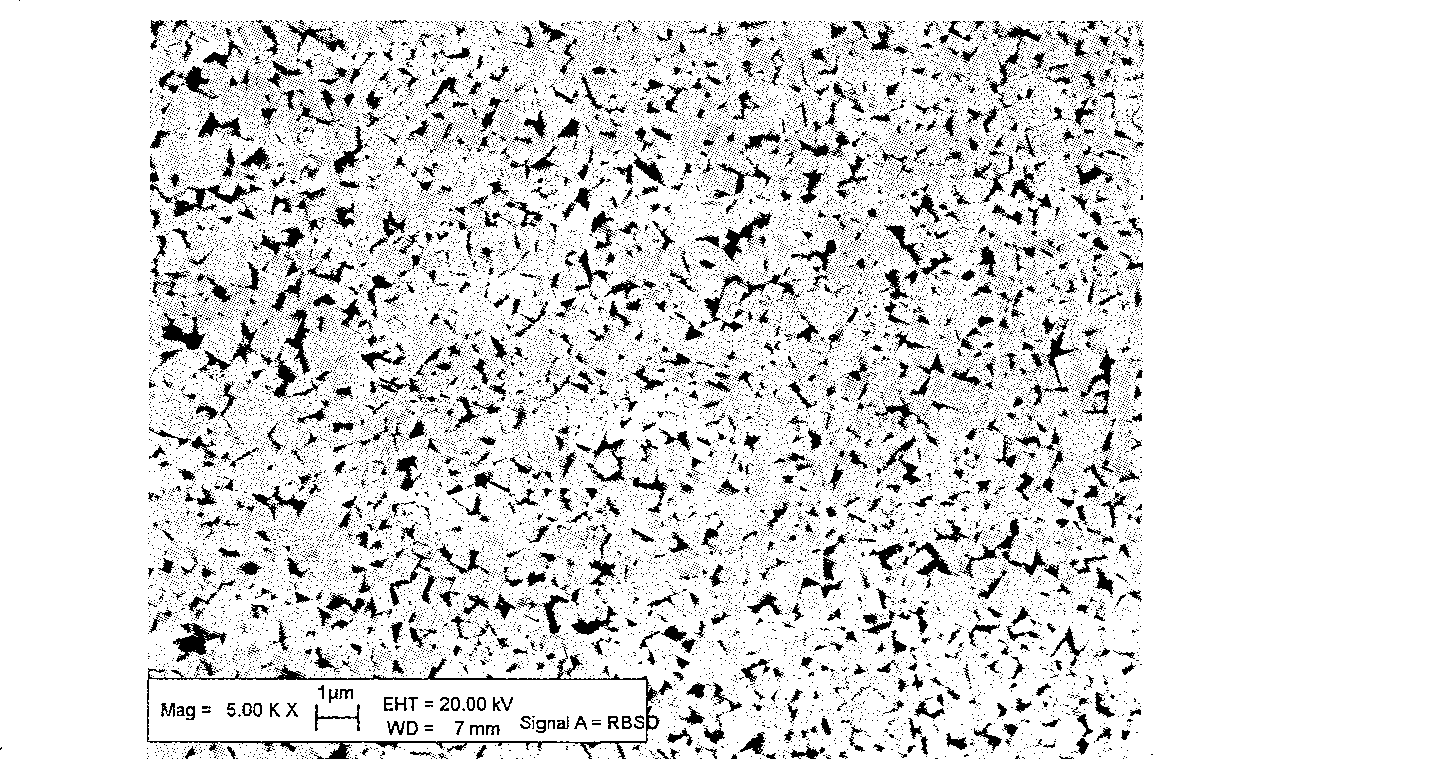
[0011] Embodiment 2: Add 0.8g Tween 60, 0.3g stearic acid, 0.1g dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide by every kilogram of mixture in the mixed slurry, which are respectively 0.08% and 0.03% of the powder mass and 0.01%. The above materials are subjected to the same wet grinding, drying, sieving, pressing, and low-pressure sintering to make superfine hard alloy. figure 2 The SEM picture of the alloy made by adding the compound dispersant according to the above conditions. Table 1 lists the physical properties of the alloy prepared by adding the compound dispersant according to the above conditions.
Embodiment 3
[0012] Embodiment 3: Add 2.0g Tween 60, 1.0g stearic acid, 0.3g dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide by every kilogram of mixture in the mixed slurry, which are respectively 0.2% and 0.1% of the powder mass and 0.03%. The above materials are subjected to the same wet grinding, drying, sieving, pressing, and low-pressure sintering to make superfine hard alloy. image 3 The SEM picture of the alloy made by adding the compound dispersant according to the above conditions. Table 1 lists the physical properties of the alloy prepared by adding the compound dispersant according to the above conditions.
[0013] Table 1
[0014] make up
[0015] from Figure 1 ~ Figure 4 It can be seen from Table 1 that the alloy with compound dispersant added during the ball milling of the mixture has a more uniform structure and about 10% higher flexural strength.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com