Horizontal inclined rotary fluidized bed desulfurizing reactor
A technology of inclined rotation and reactor, which is applied in the direction of chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical processes, and separation of dispersed particles, which can solve the problems of low desulfurization reaction efficiency and local accumulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
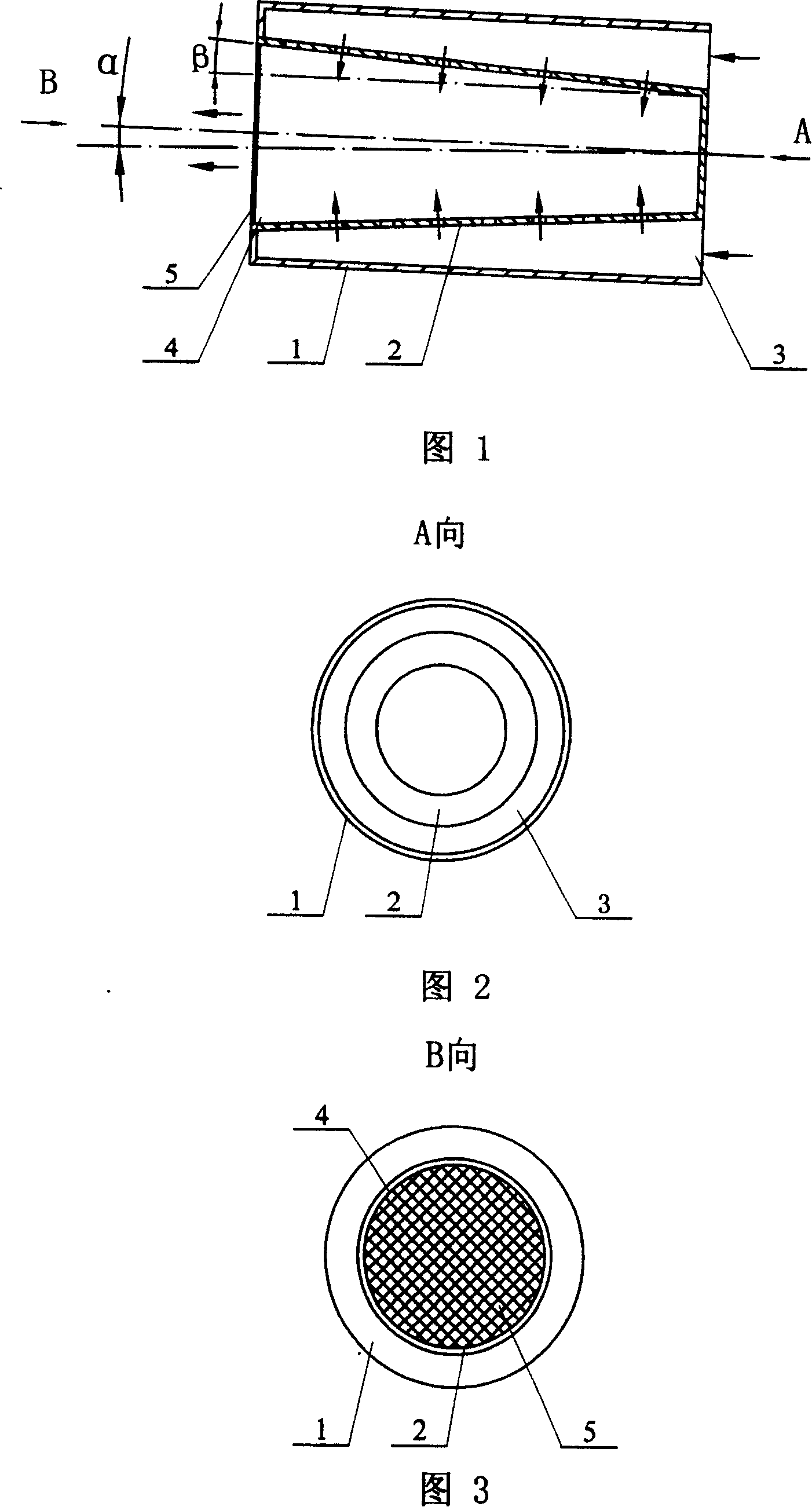
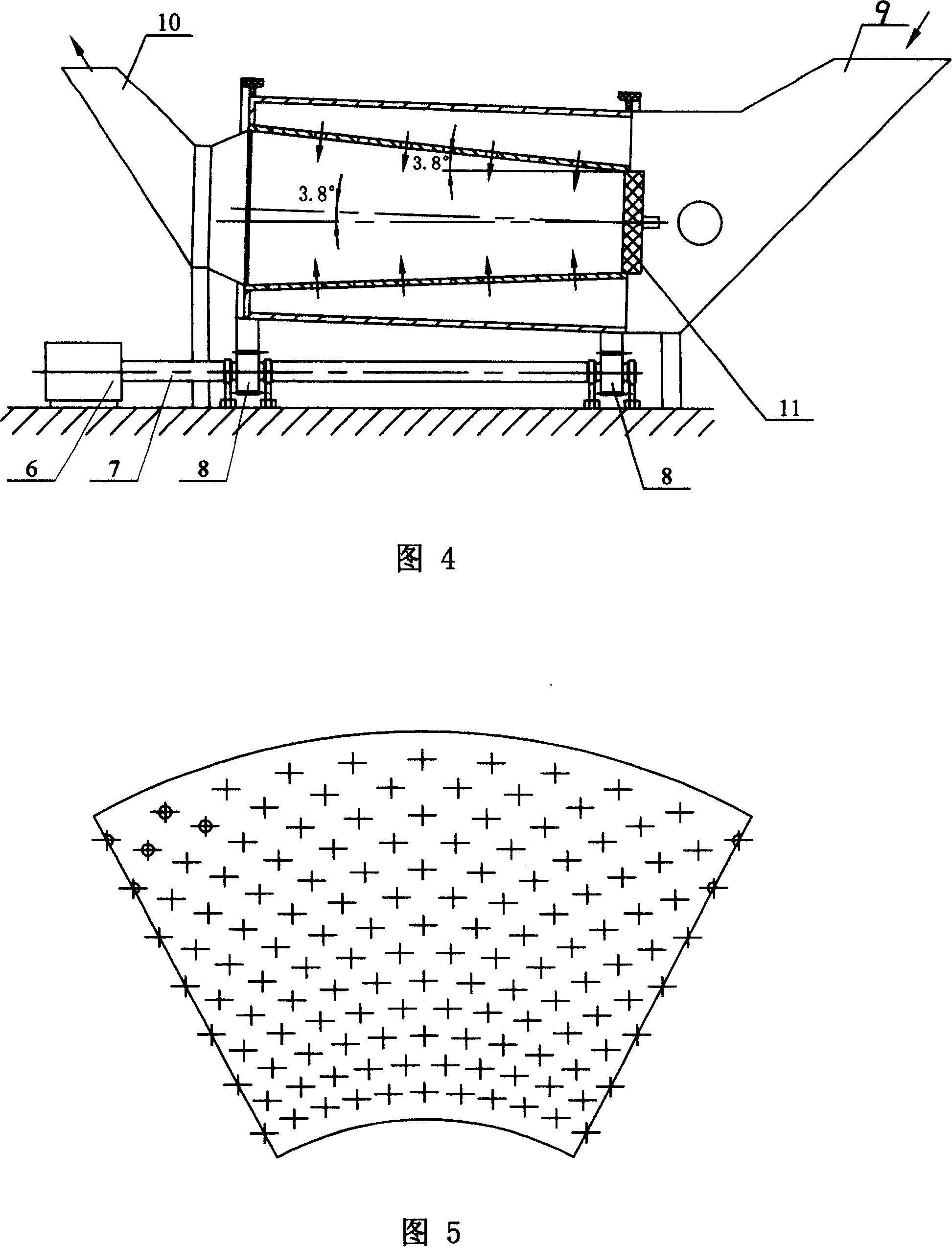
[0005] Embodiment 1: (see Fig. 1-Fig. 3) the horizontal inclined rotating fluidized bed desulfurization reactor described in this embodiment has an inner and outer double-tube structure, which includes an outer tube 1 and an inner tube 2, and the inner tube 2 is placed in the inner tube 2. In the outer cylinder 1, a gas inlet channel is formed between the inner cylinder 2 and the outer cylinder 1. The outer cylinder 1 is a cylindrical straight cylinder, the inner cylinder 2 is a truncated cone, and the circumferential wall of the inner cylinder 2 is an air distribution plate structure. The cone angle β is 0.5-12 degrees, the small-diameter end of the inner cylinder 2 is closed, the annular channel inlet 3 is formed between the small-diameter end of the inner cylinder 2 and the outer cylinder 1, the large-diameter end of the inner cylinder 2 is the gas outlet 4, and the inner cylinder The outer wall of the large-diameter end of 2 and the outer cylinder 1 are sealed and connected...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0006] Embodiment 2: (see Figures 1 to 3) The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the cone angle β of the inner cylinder 2 is 2 degrees, and the angle formed between the axis of the reactor and the horizontal plane is α is 3.0 degrees. Other components and connection relationships are the same as in the first embodiment. The temperature is 165℃, with 3000ppm SO 2 , the flow is 620000m 3 The gas per hour enters the small diameter end of the inner cylinder 2 and the outer cylinder 1 to form an annular channel inlet 3 and the inner cylinder 2. The treated gas, after desulfurization reaction, contains SO 2 The concentration dropped to 100ppm, and the desulfurization efficiency was 96.6%.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0007] Embodiment 3: (see Figures 1 to 3) The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the cone angle β of the inner cylinder 2 is 3.9 degrees, and the angle formed between the axis of the reactor and the horizontal plane is α is 3.9 degrees. Other components and connection relationships are the same as in the first embodiment. The temperature is 160℃, with 2400ppm SO 2 , the flow is 600000m 3 The gas per hour enters the small diameter end of the inner cylinder 2 and the outer cylinder 1 to form an annular channel inlet 3 and the inner cylinder 2. The treated gas, after desulfurization reaction, contains SO 2 The concentration dropped to 200ppm, and the desulfurization efficiency was 91.6%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com